Arbitrage trading is a strategy where traders exploit price differences for the same asset across markets to earn profits. By buying low in one market and selling high in another, they capitalize on temporary price gaps caused by supply-demand imbalances or delays in price updates. This method minimizes risk if trades are executed quickly and efficiently.
Key types of arbitrage include:
- Statistical Arbitrage: Uses quantitative models to find pricing mismatches in correlated assets, focusing on mean reversion (e.g., pairs trading).
- Triangular Arbitrage: Profits from exchange rate differences among three currency pairs in forex markets.
- Cross-Exchange Arbitrage: Involves buying an asset on one exchange and selling it on another at a higher price (e.g., cryptocurrency or stocks).
Success in arbitrage depends on speed, precise execution, and tools like low-latency servers, real-time data feeds, and automated platforms. While profits can be slim, managing risks like slippage, transaction costs, and market volatility is critical. Advanced infrastructure, such as trading-specific VPS plans, ensures traders stay competitive in fast-moving markets.
Quant Strategy: Arbitrage Trading Algorithm (Cross-Exchange)
Main Types of Arbitrage Strategies
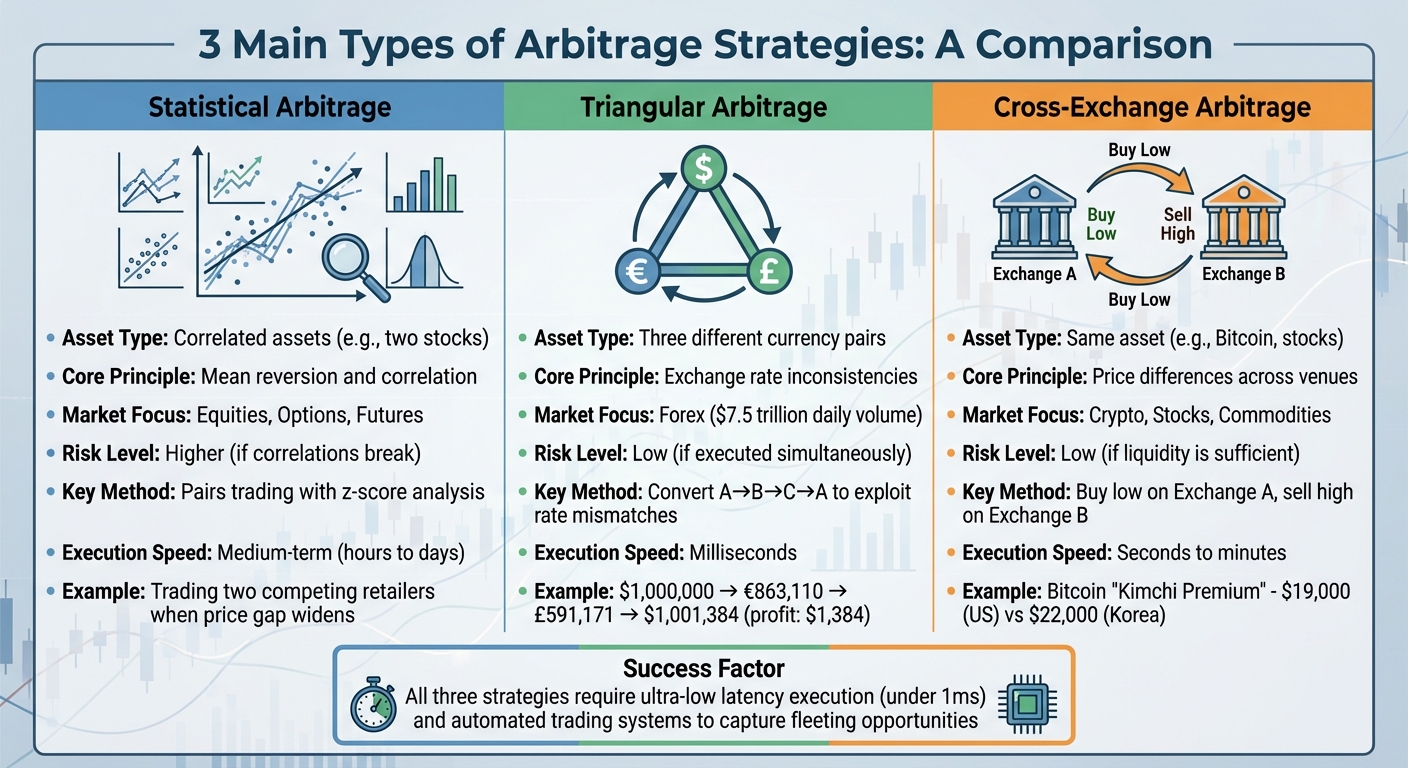
Comparison of Three Main Arbitrage Trading Strategies
Comparison of Three Main Arbitrage Trading Strategies
Traders employ various arbitrage strategies, including statistical, triangular, and cross-exchange arbitrage. Here’s a closer look at how each works, along with their execution methods and associated risks.
Statistical Arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage, often called "stat arb", relies on quantitative models to identify pricing discrepancies in related assets. Instead of taking advantage of immediate price gaps, this approach focuses on mean reversion, where prices tend to return to their historical averages over time.
One popular method within this strategy is pairs trading. For instance, a trader might analyze two stocks in the same industry – like competing retailers or oil companies – that typically move in tandem. If the price gap between the two widens beyond a specific threshold (measured by a z-score), the trader takes a long position on the underperforming stock and shorts the outperforming one. As the price gap narrows back to its usual range, both positions are closed, locking in a profit.
"Statistical arbitrage is a market-neutral strategy, meaning that delta of the strategy will be close to 0." – Bookmap
"Statistical arbitrage is a market-neutral strategy, meaning that delta of the strategy will be close to 0." – Bookmap
An example of this strategy in action is Long-Term Capital Management (LTCM), which used statistical arbitrage in the 1990s. However, the firm suffered massive losses when market conditions unexpectedly deviated from historical norms.
Next, let’s look at triangular arbitrage, which focuses on currency markets.
Triangular Arbitrage
Triangular arbitrage takes advantage of exchange rate mismatches across three currency pairs in the forex market, which handles around $7.5 trillion in daily trading volume. The process involves converting Currency A to B, B to C, and then C back to A, creating a profit from inconsistencies in the exchange rates.
Here’s an example: A trader starts with $1,000,000 and notices the following exchange rates – USD/EUR at 1.1586, EUR/GBP at 1.4600, and USD/GBP at 1.6939. They first convert $1,000,000 into €863,110. Then, they exchange the euros for £591,171. Finally, they convert the pounds back into $1,001,384, netting a risk-free profit of $1,384 (assuming no transaction costs).
However, these opportunities are fleeting, disappearing within milliseconds as automated trading systems eliminate the discrepancies. To succeed, traders must execute all conversions simultaneously to avoid "leg risk", where one part of the trade completes, but the others don’t, potentially turning a no-risk trade into a speculative one.
Now, let’s explore cross-exchange arbitrage, a straightforward yet effective approach.
Cross-Exchange Arbitrage
Cross-exchange arbitrage involves buying an asset on one exchange where it’s undervalued and selling it on another where it’s priced higher. This strategy is commonly used in forex, stocks, and cryptocurrency markets, where decentralized exchanges often exhibit price differences due to lagging updates or varying liquidity levels.
"Arbitrageurs act quickly on these opportunities by buying from the lower-priced exchange and selling on the higher-priced one to capitalize on the disparity." – StoneX
"Arbitrageurs act quickly on these opportunities by buying from the lower-priced exchange and selling on the higher-priced one to capitalize on the disparity." – StoneX
A well-known example occurred in December 2017 during the Bitcoin "Kimchi Premium." Bitcoin prices on U.S. exchanges hovered around $19,000, while South Korean exchanges like Bithumb listed it at $22,000. Traders capitalized by purchasing Bitcoin in the U.S. and selling it in South Korea. Similarly, in the Indian stock market, shares of Reliance Industries Limited (RIL) might trade at INR 2,000 on the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and INR 2,050 on the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), offering a profit margin of INR 50 per share.
The main challenge here is liquidity. Sufficient trading volume on both exchanges is essential to execute large orders without causing slippage. While even small price differences can be profitable, transaction fees and transfer times can quickly eat into those margins if not managed carefully.
| Feature | Statistical Arbitrage | Triangular Arbitrage | Cross-Exchange Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asset Type | Correlated assets (e.g., two stocks) | Three different currency pairs | The same asset (e.g., Bitcoin, a stock) |
| Core Principle | Mean reversion and correlation | Exchange rate inconsistencies | Price differences across venues |
| Market Focus | Equities, Options, Futures | Forex | Crypto, Stocks, Commodities |
| Risk Level | Higher (if correlations break) | Low (if executed simultaneously) | Low (if liquidity is sufficient) |
Tools and Infrastructure for Arbitrage Trading
To take advantage of short-lived price differences, traders need cutting-edge technology. In the fast-paced world of arbitrage, even a millisecond can mean the difference between profit and a missed opportunity.
Low-Latency VPS Solutions
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) can significantly reduce the delays associated with typical home internet connections. While a home setup might process orders in 50–100 milliseconds, a well-optimized VPS can bring this down to under 1 millisecond. That tiny reduction in latency can potentially boost high-frequency trading profits by up to 15% annually.
"In high-frequency trading, a single millisecond can determine whether you capture a profitable arbitrage opportunity or watch it vanish to faster competitors." – Ace Zhuo, Fintech Entrepreneur
"In high-frequency trading, a single millisecond can determine whether you capture a profitable arbitrage opportunity or watch it vanish to faster competitors." – Ace Zhuo, Fintech Entrepreneur
The location of your VPS matters – a lot. Hosting your server in the same data center as your broker’s matching engine (like Equinix NY4 in New York) minimizes the time it takes for signals to travel. Always check with your broker to confirm their data center location before choosing a VPS provider.
When selecting a VPS, prioritize the following specs for optimal performance:
- High CPU clock speeds (3.0+ GHz for single-threaded processing)
- DDR5 RAM (50% faster than DDR4)
- NVMe SSD storage (up to 10x faster than SATA drives)
- Network speeds of 1–10Gbps to handle market volatility without bottlenecks.
NEVER MISS A TRADE
Your algos run 24/7
even while you sleep.
99.999% uptime • Chicago, New York, London & Amsterdam data centers • From $59.99/mo
QuantVPS offers plans tailored for traders who demand ultra-low latency. For example:
- VPS Pro: $99.99/month ($69.99/month annually) with 6 cores, 16GB RAM, 150GB NVMe storage, and 1Gbps+ network speeds – ideal for monitoring 3–5 charts.
- VPS Ultra: $189.99/month ($132.99/month annually) with 24 cores, 64GB RAM, 500GB NVMe storage, and support for up to 4 monitors.
For the most demanding strategies, such as high-frequency triangular arbitrage, a Dedicated Server ($299.99/month or $209.99/month annually) provides 16+ dedicated cores, 128GB RAM, 2TB+ NVMe storage, and 10Gbps+ network speeds, ensuring consistent performance during periods of market volatility.
Once your low-latency setup is in place, the next step is securing real-time market data and reliable trading platforms to execute your strategy seamlessly.
Market Data Feeds and Trading Platforms
Real-time data is the lifeblood of arbitrage trading. Access to Market by Price (MBP/L2) or Market by Order (MBO/L3) data allows traders to spot and act on price discrepancies across markets. Providers like Databento deliver ultra-fast data feeds, offering latency as low as 42 microseconds via cross-connect or around 590 microseconds over the internet.
Popular trading platforms like NinjaTrader, MetaTrader, and CQG integrate with real-time data feeds to help traders identify and execute arbitrage opportunities. These platforms often include automated systems that monitor markets around the clock.
"Arbitrage requires precise timing, quick data analysis, and robust tools to capitalize on price discrepancies across markets." – TrendSpider
"Arbitrage requires precise timing, quick data analysis, and robust tools to capitalize on price discrepancies across markets." – TrendSpider
Automation is essential since many arbitrage opportunities exist for only a few seconds. Cloud-based alerts and trading bots can handle continuous monitoring and execution without requiring constant human oversight. Tools like CQG Spreader even manage the different "legs" of an arbitrage trade on the server side, ensuring near-instant execution.
When hosting these platforms, using a VPS located in a major colocation facility like Equinix NY4 ensures sub-millisecond execution speeds. Some traders have reported execution speed improvements of 40% to 60% after switching from generic hosting providers to specialized trading VPS services.
QuantVPS Plan Comparison
Choosing the right VPS plan is crucial for efficient arbitrage trading. Here’s a breakdown of QuantVPS plans:
| Plan | Cores | RAM | Storage | Network | Charts | Monthly | Annual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VPS Lite | 4 | 8GB | 70GB NVMe | 1Gbps+ | 1–2 | $59.99 | $41.99 |
| VPS Lite+ | 4 | 8GB | 70GB NVMe | 1Gbps+ | 1–2 | $79.99 | $55.99 |
| VPS Pro | 6 | 16GB | 150GB NVMe | 1Gbps+ | 3–5 | $99.99 | $69.99 |
| VPS Pro+ | 6 | 16GB | 150GB NVMe | 1Gbps+ | 3–5 | $129.99 | $90.99 |
| VPS Ultra | 24 | 64GB | 500GB NVMe | 1Gbps+ | 5–7 | $189.99 | $132.99 |
| VPS Ultra+ | 24 | 64GB | 500GB NVMe | 1Gbps+ | 5–7 | $199.99 | $139.99 |
Plans marked with "+" are hosted in data centers with direct cross-connects to major exchanges, reducing latency to as little as 0.3ms. Lower-tier plans like VPS Lite and Pro are suitable for less frequent strategies, while VPS Ultra and Dedicated Servers are better for high-intensity trading across multiple exchanges.
Suggestions for traders:
- Start with VPS Pro if you’re monitoring a few currency pairs or using moderate-frequency strategies.
- Upgrade to VPS Ultra or a Dedicated Server for high-frequency trading or strategies involving thousands of trades daily.
- Regularly evaluate your execution speeds and consider adding redundant data feeds to minimize the risk of lag disrupting your trades.
How to Implement Arbitrage Strategies
Executing an arbitrage strategy demands precision, speed, and constant attention. Markets move at lightning speed, and opportunities can disappear in the blink of an eye.
Finding Price Discrepancies
The core of any arbitrage strategy lies in identifying price differences across markets before they vanish. Advanced algorithms and high-frequency trading systems monitor multiple markets simultaneously, scanning for price variations in real-time using MBP/L2 or MBO/L3 data.
In the forex market, which sees an astounding $7.5 trillion in daily trading volume, these price discrepancies can present numerous opportunities for arbitrage.
"Arbitrage is the financial equivalent of bargain hunting on a grand scale, with traders and investors constantly searching – using the latest algorithms and fastest internet speeds to act in microseconds – for opportunities to buy low in one market and sell higher in another." – Investopedia
"Arbitrage is the financial equivalent of bargain hunting on a grand scale, with traders and investors constantly searching – using the latest algorithms and fastest internet speeds to act in microseconds – for opportunities to buy low in one market and sell higher in another." – Investopedia
Quantitative traders take it a step further by using statistical models and big data analytics. These tools help identify historical patterns and correlations between related assets, triggering trades when those relationships deviate from their usual behavior.
Event-driven arbitrage, such as merger arbitrage, also plays a significant role. Take the example of Microsoft’s 2016 announcement to acquire LinkedIn for $196 per share in a $26.2 billion deal. LinkedIn’s stock jumped from $131 but still traded at a discount due to uncertainty surrounding the deal. Arbitrageurs capitalized on this by buying the discounted shares and holding them until the deal was finalized.
In rare cases, unexpected events create gaps that traders must detect and act on quickly. The key is to calculate potential net gains and execute trades before the opportunity fades.
Evaluating Risks and Executing Trades
Once you’ve identified an opportunity, assessing and managing risks is critical. Start by ensuring the profit margin covers all transaction costs, including broker commissions, exchange fees, and taxes. For instance, in forex arbitrage, opening a £20,000 GBP/USD position might require a margin of just 3.33% (£666), but your risk is based on the full trade value.
Liquidity is another key factor. The market must have enough volume to handle your trade without causing slippage – where the execution price differs from your expected price.
"Arbitrage transactions must occur simultaneously to minimize the risk of the price changing before both transactions are complete." – StoneX
"Arbitrage transactions must occur simultaneously to minimize the risk of the price changing before both transactions are complete." – StoneX
Timing is everything. Your buy and sell orders must execute simultaneously to avoid execution risk. Opportunities often last only seconds, or even less. Considering that high-frequency trading now accounts for about 50% of all U.S. trading volume, you’re up against institutional players with microsecond-level advantages.
Automation is essential. Algorithmic tools allow you to execute both sides of the trade instantly. Manual execution simply can’t compete; by the time you’ve clicked, the opportunity could already be gone.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Strategy
Arbitrage is not a "set it and forget it" approach. Markets change constantly, and strategies that worked yesterday may fail today. Real-time performance monitoring is crucial – keep an eye out for execution delays, system glitches, or any technical issues that could impact your profits.
Your algorithms need regular updates to stay effective. Successful traders continuously refine their models to reflect evolving market structures and liquidity patterns. For example, if you’re using statistical arbitrage on correlated securities, you’ll need to recalibrate your models as market conditions shift.
Regular audits of your models are equally important. Watch for volatility spikes or anomalies that could disrupt your strategy. A reliable VPS setup can improve execution consistency, but ongoing adjustments ensure your profits remain protected.
STOP LOSING TO LATENCY
Execute faster than
your competition.
Sub-millisecond execution • Direct exchange connectivity • From $59.99/mo
Also, monitor your data feeds closely. Even a millisecond of lag can eat into your profits. Redundant data feeds can help mitigate the risk of delays, and a dependable VPS with consistent uptime is critical during active trading hours. Downtime or partial trade execution could expose you to unnecessary risks or missed opportunities.
Risks and Risk Management
Arbitrage strategies can be a double-edged sword – while they offer potential profits, they come with risks that could quickly turn gains into losses. To succeed, it’s essential to have safeguards in place to navigate these challenges effectively.
Execution Delays and Slippage
In arbitrage, speed isn’t just important – it’s everything. Even a split-second delay can change the game entirely. Execution risk happens when a trade is delayed, causing the price to shift before your transaction is completed. This can erase the gains you were counting on.
A stark example of execution risk occurred in August 2012, when Knight Capital Group suffered a massive technology failure. A software glitch lasting just 0.001 seconds triggered millions of unintended orders, leading to a staggering $460 million loss.
"The success of an arbitrage strategy relies on a trader’s ability to execute trades quickly… Any delays, system failure, or human error can reduce or eliminate potential profits." – StoneX
"The success of an arbitrage strategy relies on a trader’s ability to execute trades quickly… Any delays, system failure, or human error can reduce or eliminate potential profits." – StoneX
Adding to the challenge is slippage, the difference between the price you expect and the price at which the trade is actually executed. In fast-moving markets, this gap can completely wipe out the razor-thin margins typical of arbitrage. To counter this, traders use advanced order types to set slippage limits and rely on automated systems to execute trades simultaneously, reducing exposure to price changes.
Another critical tool is a low-latency VPS (Virtual Private Server), which minimizes delays. For example, during the March 2020 "Black Thursday" crypto crash, liquidity dried up within minutes. Traders without reliable systems lost big, as they couldn’t react in time to market changes.
Next, let’s look at how transaction costs and market volatility can chip away at your profits.
Transaction Costs and Market Volatility
Arbitrage profits are often paper-thin, so keeping costs in check is crucial. Before executing a trade, ensure your margins can comfortably cover transaction fees and other associated costs.
Then there’s market volatility, which adds another layer of unpredictability. Sudden price swings can widen or narrow spreads unexpectedly, turning what seemed like a sure win into a losing trade. To mitigate these risks, many traders follow the 3-5-7 Rule: risk no more than 3% of your capital per trade, limit your market exposure to 5%, and aim for at least a 7% profit on successful trades. This strategy acts as a safety net during turbulent market periods.
Automation is your best ally in volatile markets. High-frequency trading algorithms can spot and act on fleeting price discrepancies faster than any human could. Proper position sizing is also key. Using the formula Position size = Maximum risk ÷ Stop-loss distance ensures that no single trade exceeds your acceptable risk level.
Finally, diversifying your strategies and maintaining reliable infrastructure can help protect your portfolio from unexpected setbacks.
Diversification and Infrastructure Reliability
Diversification is a tried-and-true way to reduce risk. By spreading your investments across multiple uncorrelated assets or strategies, you can limit the damage from any single failed trade. For example, pair trading focuses on two correlated assets, while basket trading spreads risk across several positions. Both approaches help cushion the impact of poor performance in any one area.
Equally important is infrastructure reliability. In May 2021, a major outage at Binance left users unable to trade during a period of high market volatility. This highlights the importance of having systems that can handle peak activity without crashing. To ensure reliability, traders often use redundant data feeds, load balancing, and predictive maintenance to keep their systems running smoothly.
A dependable VPS solution is essential for consistent execution. For instance, QuantVPS offers ultra-low latency (0-1ms), a 100% uptime guarantee, and DDoS protection. These features are critical for staying competitive during high-pressure trading moments. Their plans range from VPS Lite at $59.99/month (or $41.99/month annually) for light workloads to Dedicated Servers at $299.99/month (or $209.99/month annually) for professional-grade operations. Regularly monitoring latency and system performance can help you catch issues before they disrupt your trades.
| Risk Type | Primary Cause | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Risk | System latency or delays | Use low-latency VPS and automated bots |
| Liquidity Risk | Low trading volume | Monitor market depth; avoid thin markets |
| Model Risk | Market unpredictability | Stress-test models; diversify strategies |
| Cost Risk | High fees and commissions | Calculate net profit before trading |
Conclusion
Arbitrage trading thrives on identifying and exploiting brief market inefficiencies. Success in this fast-paced strategy depends heavily on speed, accuracy, and technology that can seize opportunities before they vanish. Whether you’re diving into statistical arbitrage, triangular arbitrage, or cross-exchange trading, the stakes are high, and the margin for error is razor-thin.
Given the need for rapid execution, risk management becomes non-negotiable. Even the slightest delay or oversight can wipe out potential profits. At its core, arbitrage involves the simultaneous buying and selling of assets across different markets, requiring high-performance systems to execute trades with precision and speed.
Managing risks effectively means accounting for every cost – fees, slippage, and potential setbacks. A helpful guideline is the 3-5-7 Rule: risk no more than 3% per trade, limit overall exposure to 5%, and aim for a 7% return. Diversifying your strategies and incorporating redundant systems can also provide a safety net against unexpected disruptions.
For those ready to take their arbitrage game to the next level, QuantVPS offers the infrastructure needed to stay competitive. With ultra-low latency (0–1ms), guaranteed 100% uptime, and DDoS protection, their plans cater to traders of all levels. Options range from the VPS Lite plan at $59.99/month (or $41.99/month with an annual subscription) for lighter trading needs to Dedicated Servers at $299.99/month (or $209.99/month annually) for high-intensity operations.
While it’s true that 97% of day traders lose money due to overtrading and fees, disciplined arbitrageurs armed with the right tools can maintain an edge. Focus on automated execution, account for every cost, and invest in reliable infrastructure to turn fleeting opportunities into consistent gains.
FAQs
What are the key risks involved in arbitrage trading?
Arbitrage trading isn’t without its challenges, and traders need to stay sharp to navigate the risks involved. One of the biggest concerns is market divergence – when price differences between assets or markets don’t close as quickly as expected. This can leave traders exposed to unexpected losses.
Another common hurdle is the failure of trades to execute as intended. Factors like slippage or execution delays can throw off even the most well-planned strategies. On top of that, price fluctuations during the trading process can eat into profits, especially in markets prone to sudden volatility.
Arbitrage also demands a lot of capital. Since the profit margins are typically small, having limited funds can not only limit opportunities but also magnify potential losses. To succeed, traders need to fully grasp these risks and have a solid plan to manage them effectively.
How do traders use technology to profit from arbitrage opportunities?
Traders depend heavily on advanced technology to pinpoint and capitalize on arbitrage opportunities with incredible speed and accuracy. They rely on sophisticated algorithms to scan for price differences across markets, use high-frequency trading systems to execute trades in mere milliseconds, and stay informed with real-time data feeds that track market shifts as they happen.
These tools do more than just identify market inefficiencies – they also help traders reduce risks by enabling quicker reactions compared to manual approaches. By incorporating technology into their processes, traders can fine-tune their strategies and boost profitability in a fiercely competitive landscape.
Why is speed so important when executing arbitrage strategies?
Speed plays a crucial role in arbitrage because price gaps between markets don’t last long. Financial markets adapt rapidly, and even a small delay can mean missing out on a potential profit.
Successful traders depend on quick decision-making and advanced tools to execute trades in a flash. Without speed, the chance to take advantage of price differences disappears, rendering arbitrage unworkable.






