High Frequency Trading Algorithms: Strategies, Technology & Execution Explained
High-frequency trading (HFT) uses algorithms to execute trades in fractions of a second, capitalizing on small price differences across millions of transactions. This guide breaks down the key strategies, technology, and execution methods behind HFT.
Key Takeaways:
- Strategies: HFT relies on three main approaches - market making (profit from bid-ask spreads), statistical arbitrage (exploit price deviations in correlated assets), and latency arbitrage (leverage speed advantages across exchanges).
- Technology: Success hinges on tools like FPGA chips, co-location services, and kernel bypass technology to minimize latency and maximize speed.
- Execution: Direct Market Access (DMA), optimized order types, and low-latency infrastructure ensure fast and precise trade execution.
HFT is a high-stakes field where even a microsecond delay can mean lost opportunities. Firms invest heavily in cutting-edge infrastructure to stay competitive, from FPGA systems to low-latency VPS options for sub-millisecond trades. Read on to learn how it all works.
HFT Strategies Explained
High-frequency trading (HFT) firms use strategies designed to capitalize on tiny, fleeting inefficiencies in the market. The three main approaches - market making, statistical arbitrage, and latency arbitrage - each have unique methods for generating profits and interacting with the market. Understanding these strategies lays the groundwork for exploring the technology and execution methods that make HFT possible.
Market Making
Market makers play a key role in the market by posting both buy and sell orders for the same security, acting as intermediaries. Their profit comes from the bid-ask spread, which is the difference between the price they're willing to pay (bid) and the price at which they sell (ask). For example, purchasing at $50.00 and selling at $50.01 results in a $0.01 gain per share.
This strategy adds liquidity to the market, enabling quicker trade execution for other participants. To manage inventory risk - the possibility that prices shift unfavorably before they can adjust - market makers rely on mathematical models. Market making works best in stable, high-liquidity environments, but during volatile times, market makers face adverse selection risk, where informed traders exploit their quotes before adjustments can occur.
The technology needed for market making includes Level I and Level II order book data, which show both the best bid/ask prices and the depth of orders. Additionally, high-speed order cancellation systems and stochastic control techniques are essential for dynamically adjusting quotes based on inventory.
Statistical Arbitrage
Statistical arbitrage focuses on temporary price differences between securities that usually move together. Algorithms identify these deviations, allowing traders to buy the undervalued asset and sell the overvalued one, expecting their prices to realign.
For example, if two oil companies' stocks typically move in sync and one unexpectedly drops slightly while the other stays steady, the algorithm might see this as an opportunity. It would execute trades, anticipating that the price gap will close within seconds or minutes.
This strategy relies on stable relationships between assets. However, during periods of high volatility, these correlations can break down, leading to potential losses. To operate efficiently, statistical arbitrage systems use one-pass algorithms, which process data sequentially to minimize memory usage and keep critical calculations within the CPU's L1 cache for speed.
Latency Arbitrage
Latency arbitrage takes advantage of delays in how market information spreads across exchanges. For instance, when a large order changes the price on one exchange, there’s often a microsecond lag before this information reaches others. Traders with the fastest systems can act on the updated price on slower exchanges, buying before the price adjusts and selling once it catches up.
This strategy is all about speed. Success depends on having ultra-low latency infrastructure, such as co-location services (placing servers near exchange matching engines), microwave or shortwave radio transmission systems, and GPS clocks for nanosecond-level precision. Microwave transmissions, for example, are faster than fiber optics, which are slowed by over 30% compared to the speed of light in a vacuum. Latency arbitrage opportunities are most common during volatile periods in fragmented markets, where the fastest firms dominate profits.
Table: Summary of HFT Strategy Key Elements
| Strategy Type | Primary Profit Source | Market Role | Best Market Condition | Key Technology Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Market Making | Bid-Ask Spread | Liquidity Provider | High Liquidity / Low Volatility | Order book data, stochastic control |
| Statistical Arbitrage | Correlation Divergence | Price Efficiency | Stable Correlations | One-pass algorithms, L1 cache |
| Latency Arbitrage | Speed Discrepancies | Arbitrageur | High Volatility / Fragmented Markets | Microwave towers, co-location, GPS clocks |
As competition has grown and similar technologies have become widespread, profit margins per trade have shrunk. To stay ahead, firms must continually upgrade their infrastructure. Next, we’ll dive into the technological backbone that powers these strategies.
Technology Infrastructure for HFT
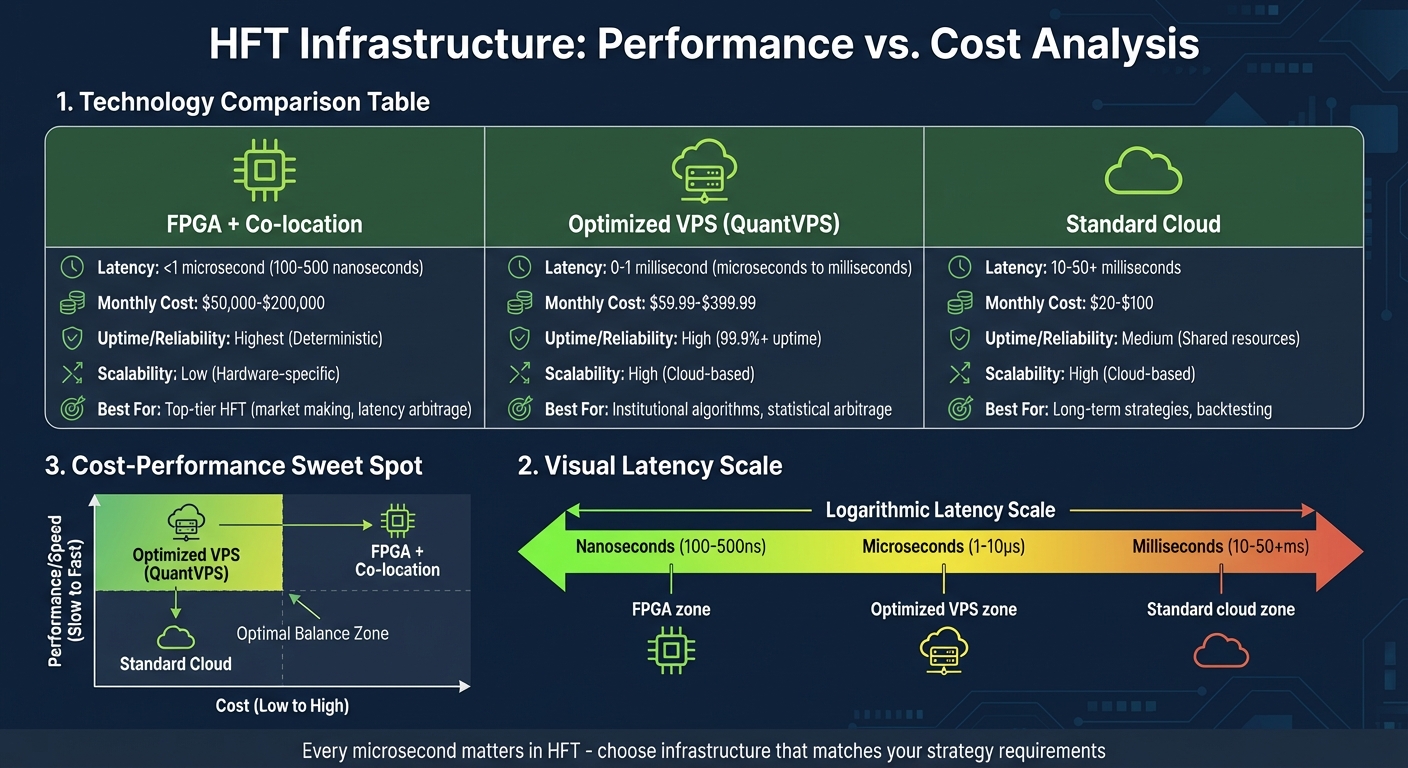
HFT Infrastructure Comparison: Latency, Cost and Performance
HFT Infrastructure Comparison: Latency, Cost and Performance
High-Frequency Trading (HFT) demands a technology setup that can process orders within nanoseconds. This requires a carefully designed combination of hardware and network systems to achieve ultra-low latency.
Core Components of HFT Infrastructure
FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Arrays) are the fastest tools in the HFT arsenal. These chips handle market data and orders directly on the hardware, bypassing the operating system entirely. This approach allows for tick-to-trade latencies of just 100–500 nanoseconds. By comparison, even highly optimized CPU-based software operates at a slower 3–8 microseconds. However, developing an FPGA-based system is no small feat - it can take over three years and cost upwards of $5 million.
NEVER MISS A TRADE
Your algos run 24/7
even while you sleep.
99.999% uptime • Chicago, New York, London & Amsterdam data centers • From $59.99/mo
"FPGA acceleration provides nanosecond-level latency for critical trading paths by implementing logic directly in hardware rather than software."
– Arpit, Technical Author
"FPGA acceleration provides nanosecond-level latency for critical trading paths by implementing logic directly in hardware rather than software."
– Arpit, Technical Author
Co-location services bring trading servers physically close to exchange data centers, cutting down network delays to under 100 nanoseconds. To put it into perspective, light in fiber travels roughly 200 kilometers per millisecond, so even small physical distances can significantly impact latency. Co-location facilities also boast 99.99% network uptime, making them a cornerstone for many HFT strategies.
Kernel bypass technology is another game-changer. By mapping NIC (Network Interface Card) memory directly into user space, this technology reduces latency from 20–50 microseconds to just 1–5 microseconds.
Specialized hardware plays a critical role in HFT setups. High-performance CPUs, large L3 caches, NVMe SSDs for logging, and low-latency NICs with hardware timestamping are all standard. ECC memory is also used to prevent data corruption during critical trading moments.
These components work together seamlessly. Market data arrives via multicast feeds at a co-located facility, where FPGA-based NICs process it using kernel bypass technology. The data updates an in-memory order book, triggers risk checks in hardware, and sends orders back to the exchange - all in a matter of nanoseconds.
Comparing FPGA, Co-location, and QuantVPS
Each piece of technology serves a specific purpose and caters to different trading needs. Here's a breakdown of their performance and costs:
| Technology | Latency | Uptime/Reliability | Scalability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPGA | 100–500 nanoseconds | Highest (Deterministic) | Low (Hardware-specific) | Very High (>$5M) |
| Co-location | Sub-100 nanoseconds | 99.99% Uptime | Medium (Physical space) | High (Monthly fees) |
| QuantVPS | Microseconds to Milliseconds | High (99.9%+ Reliability) | High (Cloud-based) | Moderate ($59.99–$399.99/month) |
For strategies like market making, futures algorithms, or latency arbitrage, where every nanosecond matters, FPGA combined with co-location is often the go-to solution. On the other hand, statistical arbitrage and institutional strategies that operate in the 10–100 microsecond range can achieve sufficient speed with optimized software on a high-performance VPS. QuantVPS, for instance, offers dedicated CPU cores, NVMe storage, and uptime guarantees, supporting platforms like NinjaTrader and MetaTrader with latencies as low as 0–1ms.
Reliability and Security Requirements
In HFT, uptime is critical. Even a brief disruption lasting milliseconds can lead to significant losses or missed opportunities during volatile market conditions. To manage risks effectively, systems often include replicated in-memory order books for seamless failover if a process stalls. Hardware kill switches, which operate independently of software, can instantly halt order flow during malfunctions.
Pre-trade risk checks embedded in FPGA hardware prevent invalid orders at wire speed, enforcing limits on size and price without adding latency.
Robust DDoS protection and data backup systems are also essential. Co-location services typically include strong DDoS defenses, while VPS providers like QuantVPS offer automatic backups and dedicated resources to ensure consistent performance. Additionally, real-time kernel patches and CPU isolation techniques eliminate scheduler interference, reducing latency spikes. Configuring large memory pages (1GB) minimizes Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB) misses, ensuring faster and more predictable memory access.
Finally, monitoring systems play a vital role in maintaining performance. By using lock-free ring buffers and hardware timestamps from network cards, these systems capture telemetry without adding overhead. This helps identify bottlenecks and ensures the low-jitter performance that HFT strategies demand.
Execution Methods and Latency Optimization
In high-frequency trading (HFT), precision and speed are everything. A delay of just one millisecond can flip a profitable trade into a loss. With HFT making up 50% to 60% of all U.S. equity trading volume, firms that can execute faster than their competitors often dominate. Even a slight edge in speed can help capture most of the profits from price discrepancies.
Direct Market Access (DMA)
Direct Market Access (DMA) is a game-changer for reducing latency. By bypassing brokers and connecting directly to exchange order books, traders eliminate unnecessary delays. Instead of orders being routed through a broker’s system, DMA ensures the fastest, most direct path to the exchange servers. Top HFT firms combine DMA with co-location - housing their servers near exchange data centers - to achieve round-trip execution times under 100 microseconds. When leveraging FPGA technology and co-location, network delays can drop below 100 nanoseconds.
Latency in trading is measured across the entire transaction cycle, starting from when market data is received to when an order is executed at the exchange. With FPGA-based systems, top-tier firms can achieve latencies of under 1 microsecond, while optimized software solutions with kernel bypass typically operate in the 1–10 microsecond range.
"If you're not measuring latency, you're guessing latency."
– Harsh Shukla, Software Developer
"If you're not measuring latency, you're guessing latency."
– Harsh Shukla, Software Developer
Order Types and Routing Strategies
The choice of order type and routing strategy can significantly impact both speed and execution quality. For example:
- Limit Orders: Offer price control but may not execute if the market moves away.
- Market Orders: Guarantee execution but can result in unfavorable pricing in volatile markets.
- Stop Orders: Trigger at a specific price, providing risk management but adding complexity.
In HFT, Smart Order Routing (SOR) plays a critical role. SOR systems analyze multiple trading venues in real time to determine the best execution path based on factors like latency, liquidity, and fees. This automated decision-making happens in microseconds, minimizing slippage and reducing transaction costs.
Another latency-reducing technique involves order staging and pre-computation. By keeping pre-built order templates in NIC (Network Interface Card) transmit buffers, traders can update only the price and quantity fields when a signal occurs. This process enables sub-microsecond order generation. Infrastructure choices, such as optimized VPS hosting, further contribute to reducing delays.
STOP LOSING TO LATENCY
Execute faster than
your competition.
Sub-millisecond execution • Direct exchange connectivity • From $59.99/mo
How VPS Hosting Reduces Execution Latency
While FPGA systems and co-location represent the pinnacle of HFT infrastructure, optimized VPS hosting provides a cost-effective alternative for institutional algorithmic strategies operating in the sub-millisecond range. QuantVPS, for instance, minimizes execution latency through:
- Dedicated CPU Resources: Prevents interference from other processes.
- NVMe Storage: Ensures rapid data access.
- Strategic Server Placement: Reduces physical distance to major exchanges.
Standard cloud services, on the other hand, often fall short for serious trading. Their shared environments and virtualization introduce unpredictable latency spikes. QuantVPS eliminates these issues by offering dedicated cores and memory, ensuring consistent performance. With network speeds exceeding 1Gbps (and 10Gbps+ on dedicated servers), high-frequency data feeds flow smoothly without interruptions.
For traders using platforms like NinjaTrader or MetaTrader, QuantVPS delivers 0–1 millisecond latency to major trading venues, compared to the 10–50+ millisecond delays typical of standard cloud services. This difference can be critical, as even slight delays can lead to missed opportunities or increased slippage, turning profitable trades into losses after fees.
| Infrastructure Type | Typical Latency | Monthly Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| FPGA + Co-location | <1 μs | $50,000–$200,000 | Top-tier HFT (market making, latency arbitrage) |
| Optimized VPS (QuantVPS) | 0–1 ms | $59.99–$399.99 | Institutional algorithms, statistical arbitrage |
| Standard Cloud | 10–50+ ms | $20–$100 | Long-term strategies, backtesting |
This table highlights how QuantVPS bridges the gap between the high costs of co-location and the poor performance of standard cloud hosting. For most algorithmic traders who don’t need nanosecond-level execution, QuantVPS offers a balance of speed, reliability, and affordability. It also includes features like dedicated resources, DDoS protection, and automatic backups, ensuring consistent performance without the unpredictability of shared environments.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
In high-frequency trading (HFT), success often comes down to microseconds. Strategies like market making, statistical arbitrage, and latency arbitrage thrive on exploiting opportunities that exist for mere fractions of a second. But spotting these opportunities is only part of the equation - having the right technology to act on them is what truly matters. Tools like FPGA systems, co-location services, and optimized VPS hosting create the backbone that transforms strategy into profit.
The importance of execution speed cannot be overstated. Consistency and precision are essential, with a focus on minimizing jitter and avoiding the inefficiencies of virtualization. Every component, from network interfaces to storage, must be fine-tuned for predictable and repeatable performance. In a market where HFT accounts for over 50% of U.S. equity trading volume, even a 100-microsecond advantage can separate the leaders from the rest.
The choice of infrastructure is equally critical. For traders operating in the low and ultra-low latency ranges, optimized VPS hosting often strikes the perfect balance between cost and performance. In such a competitive environment, even the smallest latency improvements can significantly impact profitability, making your infrastructure decisions a key factor in staying ahead.
Next Steps with QuantVPS
When speed and reliability are non-negotiable, your infrastructure becomes your edge. QuantVPS offers exactly what high-frequency and algorithmic traders need: dedicated CPU cores, NVMe storage, and servers placed near major exchanges. Unlike shared cloud setups that can introduce unpredictable latency, QuantVPS ensures consistent execution with network speeds exceeding 1Gbps - and up to 10Gbps on dedicated servers.
Whether your focus is on futures trading or statistical arbitrage, QuantVPS provides flexible plans starting at $59.99/month and scaling up to $399.99/month. These plans are designed for sub-millisecond trading strategies and include features like DDoS protection, automatic backups, and a 100% uptime guarantee. With QuantVPS, you gain access to institutional-grade infrastructure that grows with your trading success. Select a plan that aligns with your needs and take your HFT strategies to the next level.
FAQs
Is HFT legal in the U.S.?
Yes, high-frequency trading (HFT) is legal in the U.S., but it operates under strict regulations. Authorities like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) oversee these activities. Their role is to enforce guidelines and ensure that firms using algorithmic strategies maintain proper supervision and control over their practices.
How much capital do you need to start HFT?
Starting a high-frequency trading (HFT) firm demands a substantial investment - often running into several million dollars. This funding is essential to cover key expenses like state-of-the-art infrastructure, advanced technology, and meeting regulatory requirements. Without adequate capital, it’s nearly impossible to build a competitive and successful HFT operation in such a fast-paced industry.
Do you really need FPGA and co-location for HFT?
FPGA and co-location play a key role in the world of high-frequency trading. FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) technology allows for nanosecond-level latency in critical trading operations, making it invaluable in executing trades at lightning speed. On the other hand, co-location minimizes network delays by situating trading systems physically close to exchange servers.
In the ultra-competitive environment of high-frequency trading, where even microsecond delays can make or break profitability, these tools aren't just helpful - they're essential for staying ahead.
Yes, high-frequency trading (HFT) is legal in the U.S., but it operates under strict regulations. Authorities like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) oversee these activities. Their role is to enforce guidelines and ensure that firms using algorithmic strategies maintain proper supervision and control over their practices.
Starting a high-frequency trading (HFT) firm demands a substantial investment - often running into several million dollars. This funding is essential to cover key expenses like state-of-the-art infrastructure, advanced technology, and meeting regulatory requirements. Without adequate capital, it’s nearly impossible to build a competitive and successful HFT operation in such a fast-paced industry.
FPGA and co-location play a key role in the world of high-frequency trading. FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) technology allows for nanosecond-level latency in critical trading operations, making it invaluable in executing trades at lightning speed. On the other hand, co-location minimizes network delays by situating trading systems physically close to exchange servers.
In the ultra-competitive environment of high-frequency trading, where even microsecond delays can make or break profitability, these tools aren't just helpful - they're essential for staying ahead.
"}}]}




