Low Latency Trading Infrastructure: Servers, Networks & Execution Explained
In high-frequency trading (HFT), every microsecond counts. The right infrastructure can mean the difference between capturing a profit or missing an opportunity. Low latency trading systems rely on three key components:
- High-performance servers: Focus on CPUs with high clock speeds, large L3 caches, and optimized memory configurations. Colocated servers near exchange data centers reduce physical delays.
- Optimized networks: Use proximity hosting, direct connections, and technologies like kernel bypass to minimize data transmission delays. Microwave networks and fiber optics ensure faster communication.
- Ultra-fast execution systems: Implement FPGA-based NICs, binary protocols, and event-driven architectures for rapid order processing.
For traders, reducing latency improves order execution speed, profitability, and competitiveness. QuantVPS offers tailored solutions for low-latency trading, with servers located near major financial hubs and configurations designed for demanding trading workloads. Whether you're running a single strategy or multiple platforms, choosing the right infrastructure is critical for success in today's fast-paced markets.
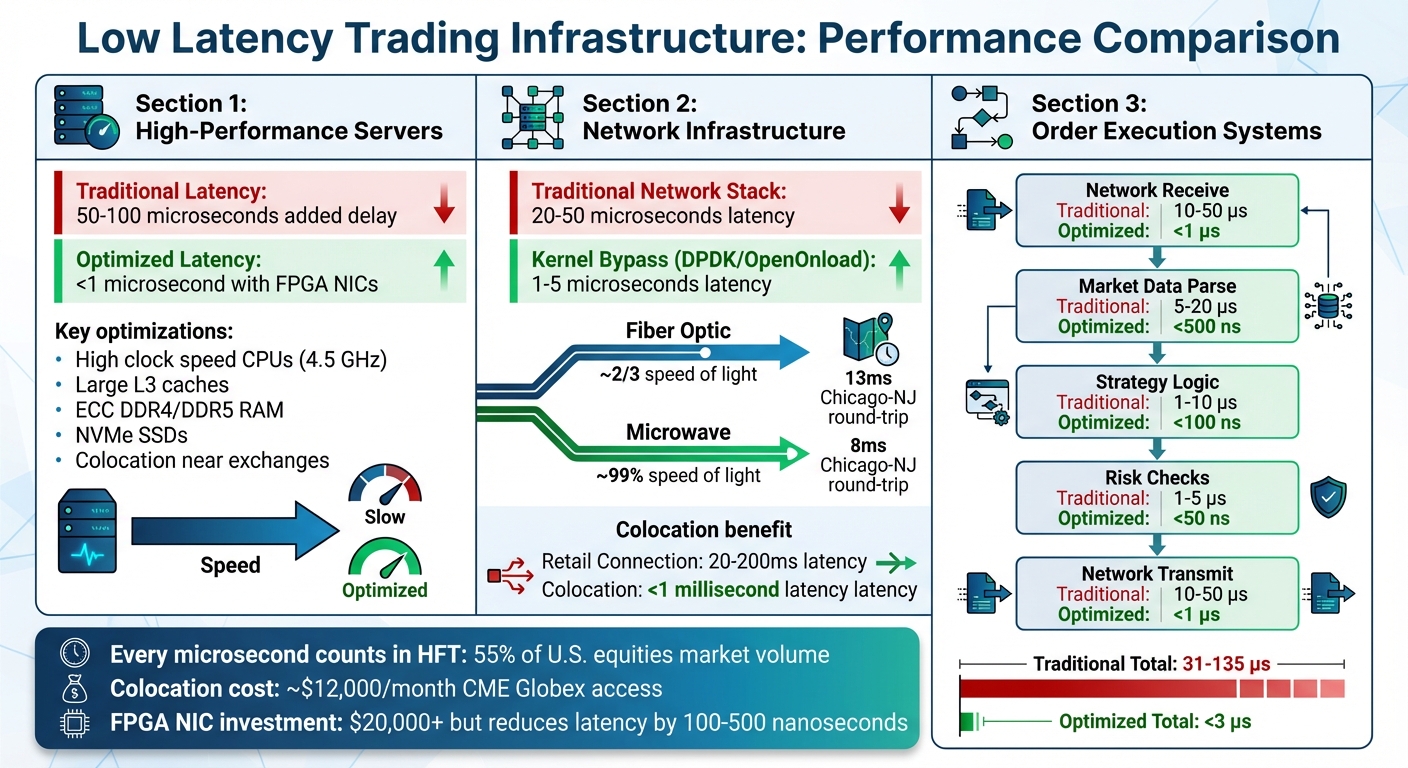
Low Latency Trading Infrastructure: Traditional vs Optimized System Performance
Low Latency Trading Infrastructure: Traditional vs Optimized System Performance
High-Performance Servers for Trading
When it comes to trading, your server is the backbone of your operations. It handles market data parsing, processes strategies, and generates orders. A poorly configured server could add 50–100 microseconds of delay, potentially wiping out any advantages from fast networks or proximity to exchanges. Simply put, your hardware choices set the stage for how fast and efficient your trading system can be.
CPU selection is critical. Trading servers thrive on high single-thread performance and large L3 caches, not necessarily a high core count. For many trading workloads, a processor with fewer cores but a higher clock speed (like one running at 4.5 GHz) will outperform a chip with more cores but lower speeds. Disabling hyper-threading is another key step to avoid scheduling inconsistencies and latency spikes. These optimizations at the CPU level ensure that your trading system operates with minimal delays.
Memory configuration also plays a key role. To maximize bandwidth, populate all memory channels with ECC DDR4 or DDR5 RAM. Using huge pages (2 MB or 1 GB instead of the standard 4 KB pages) in your operating system can significantly reduce TLB misses, cutting down on latency jitter. For systems with multiple processors, NUMA-aware memory allocation ensures trading threads access local memory instead of crossing inter-processor buses, further reducing delays.
Storage needs to be fast and separate from trading threads. PCIe-based NVMe drives like Intel Optane or Samsung PM1733 deliver the high-speed read/write capabilities required for logging and state persistence. Make sure to isolate storage I/O from trading threads to prevent interference.
Colocated Servers and Hardware Optimization
Being physically close to exchange data centers is essential. Colocating your servers inside or near exchange facilities drastically reduces network propagation delays. For instance, light traveling through fiber optic cables takes about 124 miles per millisecond. If your server is 62 miles away from an exchange, that alone adds at least 1 millisecond of round-trip latency.
Optimizing colocated hardware means fine-tuning every component in the data path. Even cable length matters - each meter of fiber optic cable adds about 4 nanoseconds of latency. Some firms go as far as using custom-length cables or hollow-core fiber within racks. Others employ "port warming", where a steady stream of messages keeps network paths and CPU caches ready for action.
"If you cannot explain every hop between your process and the exchange gateway, you do not own your latency." – Digital One Agency
"If you cannot explain every hop between your process and the exchange gateway, you do not own your latency." – Digital One Agency
Interestingly, a stable 15-microsecond path often outperforms a faster 9-microsecond path that suffers from load-induced jitter. To achieve stability, traders disable power-saving features (like C-states), pin critical threads to specific cores, and route hardware interrupts to non-trading cores. This sacrifices some energy efficiency but ensures consistent, predictable performance.
FPGA-Based NICs and PCIe SSDs
For ultra-low latency, your server's network solutions must be just as advanced as its hardware. Standard network cards can become a bottleneck. Traditional NICs introduce 20–50 microseconds of latency due to kernel processing and interrupt handling. The operating system has to copy packets through multiple buffers and process them before they reach your application - too slow for high-frequency trading.
FPGA-based NICs eliminate this problem. Field-Programmable Gate Arrays process data using dedicated hardware logic rather than software, achieving sub-microsecond latencies. A fully hardware-implemented tick-to-trade path can deliver latencies between 100–500 nanoseconds - reducing delays by hundreds of nanoseconds compared to software-based execution.
These cards use kernel bypass technologies like Solarflare's OpenOnload or Intel's DPDK, which map NIC memory directly into the application’s address space. This allows the trading application to poll the NIC directly, cutting network processing time from 20–50 microseconds to just 1–5 microseconds.
"The NIC choice often determines the latency floor for the entire system regardless of software optimization." – Nadcab Labs
"The NIC choice often determines the latency floor for the entire system regardless of software optimization." – Nadcab Labs
FPGAs aren't just for networking - they handle market data parsing, order book construction, and even pre-stage orders in transmit buffers. When a signal is received, the system can update price and quantity fields in a pre-built order template and send it out within a few hundred nanoseconds. High-end FPGA cards come with hefty price tags, often exceeding $20,000.
| Component | Traditional Latency | Optimized (FPGA/Bypass) | Optimization Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Receive | 10–50 μs | <1 μs | Kernel bypass, FPGA NIC |
| Market Data Parse | 5–20 μs | <500 ns | FPGA parsing, zero-copy |
| Strategy Logic | 1–10 μs | <100 ns | FPGA logic, cache tuning |
| Risk Checks | 1–5 μs | <50 ns | Inline checks, FPGA gates |
| Network Transmit | 10–50 μs | <1 μs | Kernel bypass, pre-staging |
QuantVPS Server Plans Comparison
QuantVPS offers two server plans designed for different trading needs. The Standard Plan is ideal for retail algorithmic traders using platforms like NinjaTrader or MetaTrader. It provides enough resources for most automated strategies. The Performance Plan, on the other hand, is tailored for more demanding applications, such as running multiple strategies, conducting complex backtesting, or executing high-frequency trades.
Both plans include NVMe SSD storage for fast data access, 1 Gbps network connectivity, and full Windows Server compatibility. The Performance Plan doubles the CPU cores and RAM, offering more storage capacity as well. This extra power ensures smooth performance even during peak market activity.
| Feature | Standard Plan | Performance Plan |
|---|---|---|
| CPU Cores | 4 cores | 8 cores |
| RAM | 8 GB | 16 GB |
| Storage | 100 GB NVMe SSD | 250 GB NVMe SSD |
| Network | 1 Gbps | 1 Gbps |
| Monthly Price | $79.99 | $149.99 |
If you're managing a single automated strategy with moderate data needs, the Standard Plan should work well. But for traders juggling multiple strategies or planning to scale up, the Performance Plan offers the added capacity to handle more complex workloads without slowing down.
With server hardware fine-tuned for low latency, the next step is to explore advanced network configurations that complete the infrastructure for high-speed trading.
Optimized Network Configurations
Once your server hardware is fine-tuned, the next big piece of the puzzle is the network. The route your data travels is just as important as the hardware processing it. A poorly set-up network can introduce delays that completely cancel out the benefits of high-performance servers. The objective? Shorten the distance your data travels, avoid unnecessary processing, and ensure every packet takes the quickest path possible. Let’s dive into how proximity hosting, advanced transmission methods, and routing strategies can help achieve ultra-low latency.
Proximity Hosting and Colocation
NEVER MISS A TRADE
Your algos run 24/7
even while you sleep.
99.999% uptime • Chicago, New York & London data centers • From $59.99/mo
When it comes to low-latency trading, physical distance is your enemy. Even the length of a cable can add delays, and for high-frequency traders, those nanoseconds add up fast. Colocation addresses this by placing your server in the same data center as the exchange’s matching engine, cutting the travel distance for data to just a few meters.
The real edge with colocation isn’t just being close - it’s about having a direct connection. Colocated setups use "cross-connects", which are physical fiber cables linking your server directly to the exchange's switch. This setup avoids the public internet entirely, eliminating unpredictable delays and jitter caused by multiple network providers. While retail traders on home Wi-Fi may experience 20–200 milliseconds of latency, colocation reduces that to less than 1 millisecond.
"At the highest level, it's not about having 'good internet' - it's about controlling the physical path your packets travel." – RPC Fast
"At the highest level, it's not about having 'good internet' - it's about controlling the physical path your packets travel." – RPC Fast
To ensure fairness, some exchanges implement measures like "fiber equalization." For instance, Cboe Global Markets standardizes cable lengths across its Equinix NY4, NY5, and NY6 data centers, so no trader has an unfair advantage based on physical proximity to the exchange hardware.
For those unable to afford full colocation, renting a VPS in the same metro area as the exchange - like Chicago for CME - can still provide a much cleaner network path with fewer hops. While it’s not as fast as true colocation, proximity hosting still offers a noticeable improvement compared to standard retail connections.
Fiber Optic and Microwave Networks
Fiber optic cables are the gold standard for reliable, high-capacity data transmission. They can handle enormous bandwidth and are largely unaffected by weather. However, fiber has one drawback: light travels about 31% slower through glass than through air. Over long distances, this difference becomes significant. For example, the round-trip latency between Chicago and New Jersey is around 13 milliseconds via fiber, but only 8 milliseconds via microwave.
Microwave networks are the fastest option for long-distance data transmission because signals travel through air at nearly the speed of light. High-frequency trading firms have invested heavily in microwave towers between major financial hubs to gain an edge over competitors relying solely on fiber. Between 2010 and 2012, the introduction of latency-optimized fiber and microwave networks shaved 3 milliseconds off the one-way communication time between Chicago and New York.
| Feature | Fiber Optic Networks | Microwave Networks |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Medium | Glass/Plastic Fiber | Air (Radio Waves) |
| Speed | ~2/3 the speed of light | ~99% the speed of light |
| Reliability | High; unaffected by weather | Lower; weather-dependent |
| Bandwidth | Extremely high | Limited |
| Path | Cable routes (indirect) | Direct line-of-sight |
The trade-off with microwave networks is reliability. Signals can weaken during heavy rain or due to atmospheric interference. To balance speed and stability, many firms use a hybrid approach: microwave for the fastest execution signals and fiber for high-bandwidth data feeds or as a backup. This redundancy ensures trading operations remain uninterrupted, even if weather impacts microwave performance.
Kernel Bypass and Low-Latency Routing
Standard network stacks are too slow for high-frequency trading. When a packet reaches your server, the operating system processes it through multiple layers - interrupts, context switches, and data copying - all of which add 20–50 microseconds of latency. For traders operating in microsecond timeframes, this is unacceptable.
Kernel bypass technologies solve this problem. Tools like DPDK (Data Plane Development Kit) and Solarflare OpenOnload allow your trading application to interact directly with the network card, skipping the operating system entirely. This reduces processing latency from 20–50 microseconds to just 1–5 microseconds. By cutting out the middleman, data flows directly from the network card to your application without any extra steps.
"Kernel bypass technologies like DPDK and Solarflare OpenOnload eliminate OS overhead, reducing network latency from milliseconds to microseconds." – Arpit
"Kernel bypass technologies like DPDK and Solarflare OpenOnload eliminate OS overhead, reducing network latency from milliseconds to microseconds." – Arpit
Routing optimization is another critical factor. Performance-based routing, which monitors packet loss and jitter, can reduce latency by 25–32% compared to traditional BGP routing. Modern 10 Gigabit Ethernet cut-through switches minimize buffering delays, and Layer 1 switches enable sub-microsecond data distribution. Since each network hop adds roughly 100 nanoseconds of latency, minimizing the number of hops is crucial.
Other optimizations include CPU pinning, which isolates trading threads to specific CPU cores using isolcpus and nohz_full to avoid interference from the OS scheduler. Disabling power management features like C-states also prevents wakeup delays that cause jitter. These tweaks sacrifice some energy efficiency but ensure the consistent, predictable performance needed for high-frequency trading. While servers provide the backbone, these network adjustments ensure every microsecond is maximized. With network delays minimized, the next step is converting these fast signals into rapid order executions.
Ultra-Fast Order Execution Systems
Once your hardware is fine-tuned and network delays are under control, the next step is ensuring your trading system processes and transmits orders as efficiently as possible. Even with sub-millisecond network latency, a poorly optimized execution system can waste precious microseconds on processing, locking, or database interactions. The ultimate goal? A direct, predictable pathway from market data events to order submission - free from unexpected delays or bottlenecks. This is where all the layers of optimization come together, transforming quick signals into lightning-fast orders.
FIX Protocols and Direct Market Access
The Financial Information eXchange (FIX) protocol is the backbone of communication between trading systems and exchanges. It’s a universal, vendor-neutral language that brokers, order management systems, and exchanges use to communicate seamlessly. FIX messages rely on a tag-value structure - like tag 35=D for a New Order - and are typically transmitted over TCP for reliable delivery.
FIX engines act as gateways for Direct Market Access (DMA), routing orders directly to exchange order books without manual intervention. However, the text-based nature of FIX introduces latency. Parsing and validating these messages can slow down systems targeting tick-to-order latencies of 10–12 microseconds.
"While the FIX Protocol is widely adopted... it introduces inherent latency due to its text-based messaging format. FIX messages require parsing and validation, which adds computational overhead." – FIXSOL
"While the FIX Protocol is widely adopted... it introduces inherent latency due to its text-based messaging format. FIX messages require parsing and validation, which adds computational overhead." – FIXSOL
To combat this, many firms use a hybrid strategy: employing binary protocols like Simple Binary Encoding (SBE) for speed during execution while keeping FIX for post-trade tasks and compliance. Binary SBE messages are often less than 25% the size of their text-based FIX counterparts, and they serialize and deserialize much faster. This is a critical advantage in high-frequency trading (HFT), which accounts for about 55% of U.S. equities market volume.
| Feature | Standard FIX Protocol | Binary SBE (Simple Binary Encoding) |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Text-based (Tag-Value) | Binary-based |
| Readability | Human-readable; good for debugging | Machine-readable; optimized for speed |
| Parsing Speed | Slower due to text parsing/validation | Faster serialization/deserialization |
| Network Protocol | Primarily TCP | Often used with UDP Multicast |
| Primary Use | Order entry, post-trade, compliance | HFT, market data feeds, co-located execution |
Direct exchange connectivity doesn’t come cheap. For instance, the CME Group charges around $12,000 per month (plus a $2,000 setup fee) for client-managed access to its CME Globex platform. But for traders operating in microsecond environments, the speed advantage justifies the expense.
Event-Driven Architectures and Thread Pinning
Event-driven architectures are designed to react instantly to market data events, bypassing slower polling mechanisms. By using event queues (like Pub/Sub), these systems trigger actions as soon as new data arrives. This approach separates execution from upstream processing, ensuring the trading core remains highly responsive.
Thread pinning adds another layer of optimization by dedicating specific CPU cores to critical trading tasks. Using kernel settings like isolcpus and nohz_full, you can isolate cores from the operating system's scheduler, preventing background processes from interfering. This eliminates costly thread migrations, which can cause cache misses and add latency. By keeping "hot" data in the CPU’s L1/L2 cache, thread pinning ensures consistent, predictable performance.
Standard thread scheduling can introduce delays ranging from 5 to over 100 microseconds due to sleep/wake cycles. Thread pinning removes these delays entirely. Pair this with lock-free data structures - such as Single-Producer Single-Consumer (SPSC) queues that rely on atomic operations instead of mutexes - and you avoid issues like lock contention and priority inversion that can slow order processing.
"A narrow, stable execution window beats erratic bursts of speed every time." – Code Your Edge
"A narrow, stable execution window beats erratic bursts of speed every time." – Code Your Edge
STOP LOSING TO LATENCY
Execute faster than
your competition.
Sub-millisecond execution • Direct exchange connectivity • From $59.99/mo
High-frequency trading systems typically process an order book update in 10–50 microseconds. To achieve this, firms often disable hyper-threading, which can cause resource competition, and pre-allocate memory at startup to eliminate allocation delays during trading. This meticulous attention to detail ensures consistent performance, even during volatile market conditions.
Asynchronous Data Pipelines for Execution
Asynchronous pipelines are another critical component in maintaining ultra-low latency. By decoupling non-critical tasks from the core execution process, these pipelines allow the trading engine to focus solely on high-speed operations. Tasks like logging, accounting, and database writes are offloaded to separate threads, preventing them from slowing down execution.
These pipelines use messaging queues or event streaming to broadcast trade details instantly. For instance, when an order is filled, the execution engine sends the details to an asynchronous queue and immediately moves on to the next task. Background threads handle slower processes like database updates and logging, ensuring the execution path remains unblocked.
"Asynchronous messaging queues let the trading core broadcast data instantly, without waiting for a slow database to acknowledge it." – B2BROKER
"Asynchronous messaging queues let the trading core broadcast data instantly, without waiting for a slow database to acknowledge it." – B2BROKER
Lock-free structures further enhance this setup by offloading complex tasks without disrupting execution speed. For example, Smart Order Routing (SOR) parameters can be updated asynchronously to refresh routing tables without interfering with live order flow. These techniques ensure consistent throughput, even during high-volume trading bursts, keeping the system steady under load.
| Pipeline Component | Function | Latency Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Messaging Queues | Decouples core from database/ledger | Prevents execution stalls due to slow acknowledgments |
| Lock-Free SPSC Queues | Facilitates inter-thread communication | Eliminates lock contention and priority inversion |
| Ring Buffers | Captures telemetry and logging data | Offloads logging to background threads without impacting the hot path |
| Event Streaming | Propagates trade details independently | Maintains execution speed during high-volume bursts |
Through these designs, trading systems achieve the seamless flow needed for lightning-fast execution, even in the most demanding market conditions.
Using QuantVPS for Low Latency Trading
QuantVPS provides an all-in-one solution tailored for low-latency trading, seamlessly integrating optimized hardware, networks, and execution systems. It’s designed for traders who demand fast and reliable performance without the hassle of managing on-site hardware. With servers strategically located in key financial hubs - Chicago, New York, London, and Amsterdam - QuantVPS places your trading systems close to exchange matching engines. This proximity ensures sub-millisecond execution speeds, offering a streamlined trading experience.
Compatibility with NinjaTrader, MetaTrader, and TradeStation
QuantVPS supports major trading platforms like NinjaTrader, MetaTrader (MT4/MT5), and TradeStation, ensuring smooth operation on its Windows Server 2022 environment. To maximize performance, it’s crucial to identify your broker's server location - whether it’s in Chicago for CME futures, London LD4 for European markets, or New York NY4 for equities. Use ping tests to confirm the server’s physical location, then select a VPS in the same data center or nearby city to minimize delays caused by data transmission.
For scalpers aiming for sub-5ms latency, a minimum of 4GB RAM per trading terminal is necessary. Traders running multiple platforms or complex strategies should consider configurations with 8GB RAM or more. All QuantVPS plans include NVMe storage, ensuring quick platform initialization and efficient data handling.
DDoS Protection, Uptime, and Monitoring Features
QuantVPS prioritizes uninterrupted connectivity and robust security. The platform guarantees 99.999% uptime, ensuring your automated trading systems operate around the clock. Integrated DDoS protection shields your operations from external threats, which is critical in a trading environment where even milliseconds can affect profitability. Real-time monitoring ensures that core network infrastructure remains stable, with status updates available for key hubs like Chicago.
Additionally, built-in backups and advanced cybersecurity measures safeguard sensitive trading data and configurations. The platform’s redundant infrastructure is designed to meet the demands of high-frequency trading. Pricing starts at $59.99/month for the VPS Lite plan (4 cores, 8GB RAM, 70GB NVMe) and goes up to $299.99/month for Dedicated Servers (16+ cores, 128GB RAM, 2TB+ NVMe). For traders requiring peak performance, Performance+ plans offer enhanced specifications, ideal for multi-monitor setups and heavy processing needs.
Steps to Deploy QuantVPS Infrastructure
Getting started with QuantVPS begins with verifying your broker's server location. Use ping tests to pinpoint the exact location, then choose a plan that matches your trading requirements. For instance, the VPS Pro plan ($99.99/month) is suitable for traders running 3–5 charts, while the VPS Ultra plan ($189.99/month) is designed for more demanding setups, supporting 5–7 charts with 24 cores and 64GB RAM.
Once you’ve selected a plan, install your trading platform on the Windows-based VPS environment. Configure the network to prioritize your broker's IP addresses for optimal performance. Conduct a 24–48 hour ping test during peak trading hours (e.g., the London-New York market overlap) to identify any latency spikes. Start with paper trading to compare actual order execution times with theoretical ping results. For added stability, apply thread pinning to ensure consistent performance during volatile market conditions. These steps complete your low-latency trading setup, equipping you to handle even the most fast-paced trading scenarios effectively.
Conclusion
Building a low-latency trading infrastructure demands precise coordination across three main layers: high-performance servers, optimized network setups, and ultra-fast execution systems. Each layer serves a specific purpose - servers deliver the processing power needed for consistent performance, networks reduce physical delays using colocation and advanced technologies like kernel bypass, and execution systems ensure market data is turned into orders within microseconds. In high-frequency trading, even the smallest latency difference can significantly impact profitability, especially for strategies like scalping or arbitrage.
As discussed earlier, proximity to exchange matching engines is critical for reducing latency. Hosting your infrastructure in the same data center as your broker’s matching engine cuts propagation delays to just nanoseconds, offering a significant competitive advantage.
QuantVPS addresses this need by offering servers in major financial hubs such as Chicago, New York, London, and Amsterdam. Their configurations ensure ultra-low latency (0–1ms), NVMe storage for fast data access, and compatibility with all major trading platforms. Pricing starts at $59.99/month for the VPS Lite option, scaling up to $299.99/month for Dedicated Servers designed for intensive trading workloads.
Before deploying your setup, it’s important to verify your broker’s server location using ping tests and select a VPS that matches. Conduct a 24–48 hour latency test during peak trading hours to pinpoint any bottlenecks. Additionally, fine-tune your server settings to eliminate scheduling jitter, ensuring your trading threads get dedicated processing power. These steps turn theoretical speed gains into real-world performance improvements, giving you the edge in today’s ultra-competitive, microsecond-sensitive trading environment.
FAQs
How do I find my broker’s server location?
To find your broker's server, start by identifying the main colocation site where their matching engine or gateway operates. This location typically offers the fastest connection to exchanges, ensuring minimal latency. Since brokers don’t always make server locations public, you can review their infrastructure documentation or reach out to their support team for accurate information. Knowing this can help you fine-tune your trading setup for better performance.
What latency should I aim for in my strategy?
For high-frequency trading, it's crucial to aim for latency measured in microseconds or even nanoseconds. Many systems strive for under 100 microseconds, with some pushing into the nanosecond range. Achieving these ultra-low latency levels can dramatically improve trading efficiency and keep you competitive in the fast-paced trading environment.
Do I need an FPGA NIC to trade faster?
Using an FPGA NIC (Field-Programmable Gate Array Network Interface Card) can slash latency in high-frequency trading by handling order generation and transmission directly in hardware. This approach operates at nanosecond-level speeds, giving traders a crucial edge in ultra-fast markets.
To find your broker's server, start by identifying the main colocation site where their matching engine or gateway operates. This location typically offers the fastest connection to exchanges, ensuring minimal latency. Since brokers don’t always make server locations public, you can review their infrastructure documentation or reach out to their support team for accurate information. Knowing this can help you fine-tune your trading setup for better performance.
For high-frequency trading, it's crucial to aim for latency measured in microseconds or even nanoseconds. Many systems strive for under 100 microseconds, with some pushing into the nanosecond range. Achieving these ultra-low latency levels can dramatically improve trading efficiency and keep you competitive in the fast-paced trading environment.
Using an FPGA NIC (Field-Programmable Gate Array Network Interface Card) can slash latency in high-frequency trading by handling order generation and transmission directly in hardware. This approach operates at nanosecond-level speeds, giving traders a crucial edge in ultra-fast markets.
"}}]}




