15 Best Trend Indicators Every Trader Should Know (2026 Guide)
Trading in 2026 demands precision and speed. Whether you're navigating the E-mini S&P 500 (ES), Nasdaq-100 (NQ), Crude Oil (CL), or Gold (GC), understanding market trends is essential. Trend indicators help you identify direction, momentum, and potential reversals, giving you an edge in both day and swing trading.
Here’s a quick summary of the top 15 trend indicators every trader should know:
- Moving Averages (SMA & EMA): Simplifies price data, great for spotting trends and dynamic support/resistance.
- MACD: Tracks momentum and trend strength using moving averages and histograms.
- ADX: Measures trend strength, ideal for avoiding weak markets.
- Supertrend: Combines volatility and price action for clear trend signals and trailing stops.
- VWAP: Tracks average price weighted by volume, critical for intraday trading.
- Parabolic SAR: Provides clear entry, exit, and reversal signals.
- Ichimoku Cloud: Offers a complete view of trend direction, momentum, and support/resistance.
- Donchian Channels: Highlights breakout zones using price highs and lows.
- Keltner Channels: Uses EMA and ATR to confirm trends and identify pullbacks.
- Bollinger Bands: Measures volatility and potential breakouts.
- Hull Moving Average (HMA): Reduces lag for faster trend detection.
- Linear Regression Channel: Statistically identifies trend direction and deviations.
- Trendlines & Channels: Manually drawn for analyzing price structure and reversals.
- Heikin Ashi Candles: Smooths out noise, highlighting sustained trends.
- ATR-Based Indicators: Dynamically adjusts to volatility for better trend analysis.
Quick Comparison
| Indicator | Best for Day Trading | Best for Swing Trading | Key Markets | Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moving Averages | Yes | Yes | ES, NQ, CL, GC | Trend direction, support levels |
| MACD | Yes | Yes | ES, NQ | Momentum and trend strength |
| ADX | No | Yes | CL, GC | Trend strength |
| Supertrend | Yes | No | NQ, CL | Clear trend signals |
| VWAP | Yes | No | ES, NQ | Intraday volume analysis |
| Parabolic SAR | No | Yes | GC, CL | Entry/exit points |
| Ichimoku Cloud | No | Yes | ES, GC | Full trend overview |
| Donchian Channels | Yes | Yes | CL | Breakout signals |
| Keltner Channels | Yes | Yes | ES, NQ | Volatility-based pullbacks |
| Bollinger Bands | Yes | Yes | ES, GC | Volatility and breakout zones |
| Hull Moving Average | Yes | No | NQ, ES | Quick trend detection |
| Linear Regression | No | Yes | GC, ES | Statistical trend deviations |
| Trendlines & Channels | Yes | Yes | GC, CL | Price structure analysis |
| Heikin Ashi Candles | Yes | Yes | NQ, CL | Noise reduction, trend clarity |
| ATR-Based Indicators | Yes | Yes | ES, NQ, CL, GC | Volatility-adjusted signals |
These indicators are most effective when combined for confirmation and context. For example, pairing Moving Averages with MACD or using ATR-based tools alongside VWAP can refine entries and exits. The key is to align your tools with your trading style and timeframe while managing risk effectively. Implementing a robust futures trading risk management strategy is vital when using these indicators. Let’s dive deeper into how each indicator can enhance your trading strategy.
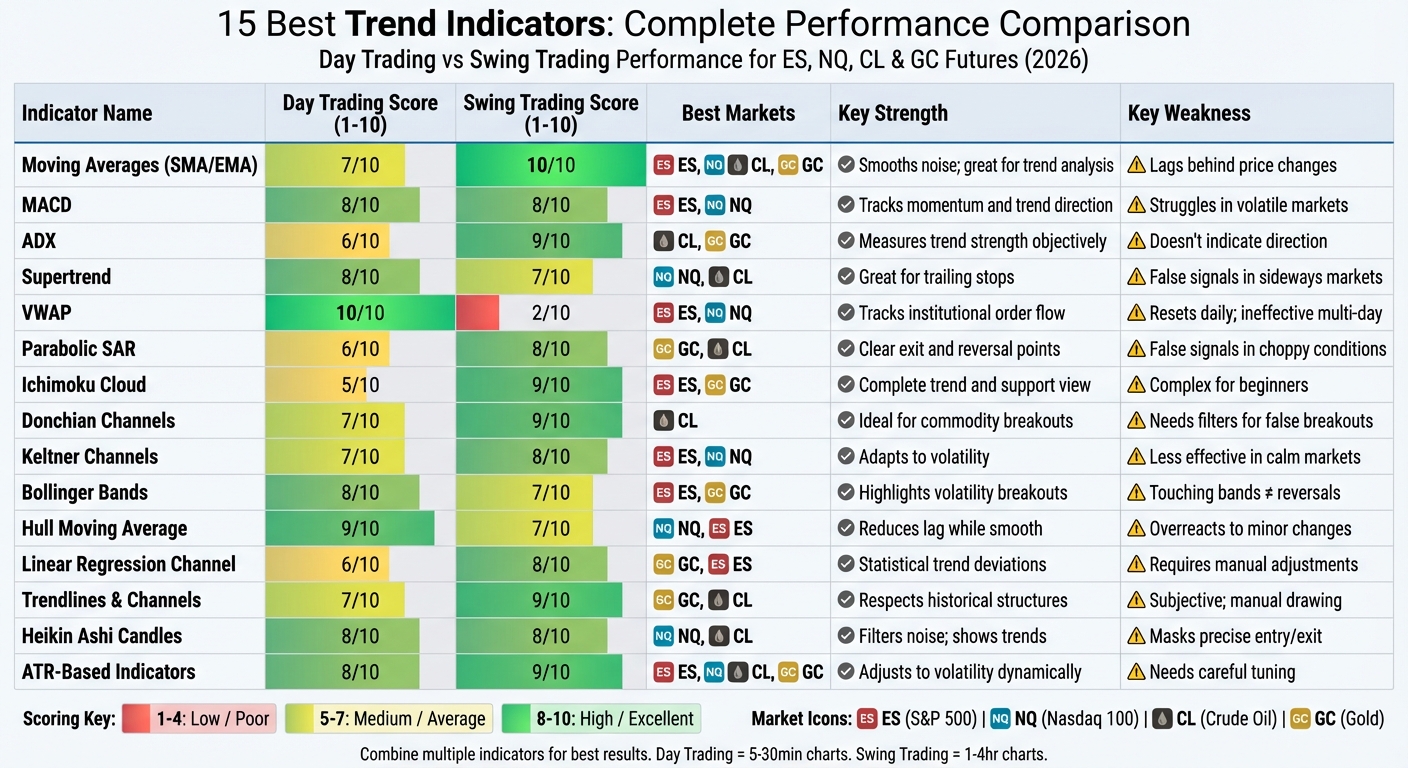
15 Best Trend Indicators Comparison: Day Trading vs Swing Trading Performance
15 Best Trend Indicators Comparison: Day Trading vs Swing Trading Performance
We Tested 100+ TradingView Indicators - These Are The TOP 30 in 2025
1. Moving Averages (SMA & EMA)
Moving averages help simplify price data, making it easier to spot the market's general direction. The Simple Moving Average (SMA) calculates the average price over a specific number of periods, treating all data points equally. On the other hand, the Exponential Moving Average (EMA) gives more weight to recent prices, allowing it to react more quickly to price changes.
When the price stays above a rising moving average, it typically signals an uptrend, while a price below a falling moving average suggests a downtrend. Combining moving averages with support and resistance levels allows traders to identify dynamic zones, where prices often bounce during pullbacks. This makes them an essential tool for creating strategies tailored to both day trading and swing trading.
Day Trading Performance (Speed, Momentum)
For day traders, the EMA is often preferred due to its faster response to price changes - ideal for quick-moving markets like ES (E-mini S&P 500) and NQ (Nasdaq-100). Traders commonly use shorter EMAs, such as a 9-period or 20-period EMA, on timeframes of 30 minutes or less. These shorter periods help reduce lag, allowing for earlier entries when prices break above or cross the moving average. In strong trends, prices rarely pull back sharply to the 20 EMA, making breakout entries a more effective approach than waiting for retracements.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength, Structure)
Swing traders prioritize trend strength and market structure. A 50-period moving average is a popular choice for identifying solid trends, as prices often respect this level during moderate pullbacks. On 1-hour to 4-hour charts, the 50-period moving average frequently serves as support in uptrends and resistance in downtrends. For a broader market perspective, a 200-period moving average helps swing traders decide whether to focus on long positions (when the price is above) or short positions (when the price is below). Swing traders often lean toward the SMA for its stability, as it’s less affected by temporary price spikes that could create misleading signals.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
Moving averages can be adapted to various futures markets, fine-tuned to match the asset's volatility. In markets like ES and NQ, day traders often rely on the 20-period EMA on lower timeframes, such as 5-minute charts, to capture intraday momentum. For more volatile assets like CL (Crude Oil) and GC (Gold), swing traders typically use the 50-period SMA on 4-hour charts to filter out noise and pinpoint meaningful trend reversals. Many traders also use key moving averages - such as the 25-day or 50-day - as reference points for placing stop-loss orders, protecting their capital if a trend reversal occurs.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader, TradingView)
Both TradingView and NinjaTrader make it easy to integrate moving averages into your trading strategy. In TradingView, you can add the "Moving Average" indicator and customize parameters like length (e.g., 9, 20, 50, or 200), price source (e.g., closing price), and type (SMA or EMA). On NinjaTrader, select the moving average type and period that align with your approach. For example, day traders focusing on ES and NQ might start with a 20 EMA on a 5-minute chart, while swing traders targeting CL or GC may find a 50 SMA on a 4-hour chart more suitable for identifying trends.
2. MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
The MACD is a tool that measures market momentum by comparing two EMAs (Exponential Moving Averages), helping traders gauge whether trends are strengthening or losing steam. It uses a 12-period EMA and a 26-period EMA to form the MACD line, while a 9-period EMA of this line, called the signal line, generates buy or sell signals. A histogram visually represents the difference between the MACD and signal lines, offering insight into whether momentum is growing or fading.
When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it signals bullish momentum, whereas a cross below suggests bearish momentum. The zero line acts as a key threshold: values above zero indicate an upward trend, while values below zero suggest a downward trend. Traders also keep an eye on divergences, such as when prices hit new highs but the MACD fails to do the same, which could hint at a weakening trend and a potential reversal.
Day Trading Performance (Speed, Momentum)
Day traders often rely on the MACD histogram to spot early signs of momentum shifts.
"The histogram is arguably the most useful part of MACD... when the histogram shrinks, it is a sign the market is moving slower."
"The histogram is arguably the most useful part of MACD... when the histogram shrinks, it is a sign the market is moving slower."
The histogram’s characteristic "hump" shape can signal slowing momentum even before a crossover happens, giving traders a chance to act sooner. On short timeframes like 5-minute to 30-minute charts for futures such as ES and NQ, traders monitor the histogram for peaks and contractions to detect early momentum changes.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength, Structure)
Swing traders tend to focus on the zero cross strategy for identifying major trend shifts. When the MACD line crosses above zero - indicating that the 12-period EMA has surpassed the 26-period EMA - it confirms an uptrend. This approach often produces fewer false signals compared to relying solely on signal line crossovers. On 4-hour charts of futures like CL and GC, swing traders may combine MACD zero crosses with additional criteria, such as ensuring the 50-period moving average is above the 200-period moving average, to align with broader trends. Watching for regular divergences, where prices make higher highs while the MACD makes lower highs, can also alert traders to a weakening trend before a potential reversal.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
The MACD’s focus on momentum, rather than static overbought or oversold levels, makes it adaptable across various futures markets. For day traders working with ES and NQ, the histogram provides quick momentum insights on shorter timeframes (like 5-minute charts), helping them identify intraday reversals. Swing traders in markets like CL often use 4-hour charts with standard MACD settings to confirm trend direction changes through zero line crosses. Meanwhile, in GC, the MACD's ability to highlight divergences is especially useful for spotting potential reversal points after long trends. These momentum signals work hand-in-hand with trading platforms to support both fast-paced day trades and methodical swing trades.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader, TradingView)
Customizing your MACD setup on platforms like TradingView or NinjaTrader can help you make the most of its insights. Both platforms offer full MACD customization, with the default settings (12, 26, 9) as a starting point. TradingView allows adjustments to parameters like the "Source" (usually set to the closing price), "Fast Length", "Slow Length", and "Signal Smoothing." It also features a "Wait for timeframe closes" option, which is particularly handy for day traders who want confirmation at the close of a bar before acting. On NinjaTrader, users can choose between EMA and SMA for the oscillator type - EMA responds more quickly to price changes (ideal for day trading ES and NQ), while SMA provides smoother signals with less noise (better suited for swing trading CL and GC).
For optimal performance, consider running these platforms on a high-performance futures trading VPS. Providers like QuantVPS offer solutions specifically tailored for futures trading, delivering ultra-low latency and reliable performance to ensure your MACD configurations operate smoothly and efficiently.
3. ADX (Average Directional Index)
The ADX, or Average Directional Index, is a tool designed to measure the strength of a trend, using a scale from 0 to 100. While it doesn’t indicate the direction of the trend, it gives a clear picture of how strong the current trend is. This makes it particularly helpful for avoiding weak or choppy markets where trend-following strategies tend to struggle. The ADX consists of three lines: the ADX line itself (which measures trend strength) and the Positive and Negative Directional Indicators (+DI and -DI), which provide clues about the market's direction. As the trend gains momentum, the ADX line moves upward.
Typically, an ADX reading below 20 points to a weak or non-trending market. When the ADX rises above 25, it signals a strong trend, while readings above 40 or 50 could suggest the trend is nearing exhaustion. Since the ADX is a lagging indicator based on historical data, it’s best used to confirm existing trends rather than predict new ones. Understanding these fundamentals is key to applying the ADX effectively across different trend-following trading strategies.
Day Trading Performance (Speed, Momentum)
For day traders dealing with fast-moving futures like ES and NQ, a 5-period ADX setting is often preferred. This shorter setting helps capture quick bursts of momentum on 5- to 15-minute charts. For instance, when the ADX climbs above 25 during a breakout, it indicates the move has strong momentum. However, if the ADX starts to drop - even if it stays above 25 - it could signal that the momentum is fading.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength, Structure)
Swing traders often stick to the standard 14-period or a slightly longer 20-period ADX, focusing on 4-hour or daily charts. The 20-period setting is particularly useful for filtering out market noise and avoiding false signals. In markets like CL or GC, swing traders wait for the ADX to rise above 25, paired with a directional signal from either the +DI or -DI lines. This combination ensures that the trend has enough structural strength to warrant a trade.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
In futures markets, the ADX proves especially valuable for identifying periods of volatility expansion - those moments when prices break out of tight ranges. For day traders in ES and NQ, a rising ADX above 25 on shorter timeframes can confirm that an intraday breakout is backed by solid momentum. Swing traders in markets like CL and GC, on the other hand, rely on ADX readings from 4-hour charts to determine whether a breakout is likely to hold, helping them steer clear of false signals.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader, TradingView)
Both TradingView and NinjaTrader offer the flexibility to adjust the ADX period settings. On TradingView, you’ll find the ADX under the "DMI" (Directional Movement Index) settings, with the default set to 14 periods. NinjaTrader also allows users to customize the look-back period, making it easy to switch to a 5-period setting for day trading or a 20-period setup for swing trading. For those trading fast-moving futures, running these platforms on a high-performance VPS like QuantVPS can ensure low latency futures trading and uninterrupted performance.
4. Supertrend Indicator
The Supertrend indicator is a trend-following tool that works based on volatility and overlays directly onto price charts, giving traders clear visual signals. It calculates upper and lower bands using the Average True Range (ATR). The default settings for this indicator are typically a 10-period ATR and a multiplier of 3. Here's how it works:
- Upper Band = (High + Low) / 2 + (Multiplier × ATR)
- Lower Band = (High + Low) / 2 - (Multiplier × ATR)
When the price closes above the lower band, the indicator signals a bullish trend (often displayed in green). Conversely, when the price closes below the upper band, it signals a bearish trend (usually shown in red). The Supertrend also serves as a dynamic trailing stop, helping traders manage risk while staying in trends.
Day Trading Performance (Speed and Momentum)
For day traders focusing on fast-moving futures like ES (E-mini S&P 500) and NQ (Nasdaq 100), shorter settings - such as a 7-period ATR with a multiplier of 2 - can help identify quick momentum shifts. Using these settings on 5- to 15-minute charts allows traders to catch breakouts early. However, these aggressive settings are more prone to false signals in choppy or sideways markets, so they work best when the market shows a clear directional trend. For traders with longer timeframes, the same principle applies, but with adjusted parameters to suit their trading style.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength and Structure)
Swing traders often stick to the standard 10-period ATR with a multiplier of 3, applying it to 4-hour or daily charts. This configuration filters out short-term noise, enabling traders to capture medium-term trends that unfold over days or weeks. In markets like Crude Oil (CL) and Gold (GC), the Supertrend can act as a dynamic support or resistance level. For instance, if the price bounces off the Supertrend line, it may indicate that the prevailing trend remains intact. The wider bands created by the higher multiplier also provide more room for normal pullbacks, reducing the chances of being stopped out prematurely.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
The Supertrend indicator is particularly effective in volatile futures markets because its ATR-based calculations automatically adapt to shifting conditions. For indices like ES and NQ, day traders can use the indicator on 5-minute charts to track intraday trends, while swing traders might prefer 4-hour charts for identifying multi-day moves. In commodity futures such as CL and GC, the Supertrend helps distinguish real breakouts from false ones by confirming that volatility is expanding in the trend's direction. Pairing the Supertrend with tools like the VWAP trading strategies can provide additional confirmation for significant price movements.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader and TradingView)
To apply these strategies, you’ll need to adjust the settings on your trading platform. Both TradingView and NinjaTrader allow for customizable Supertrend parameters, with default settings of 10 and 3. These can be fine-tuned based on your trading approach. Hosting these platforms on a high-performance VPS, such as QuantVPS, ensures ultra-low latency (0–1 ms) and uninterrupted execution - critical when reacting to signals in volatile markets generated by the Supertrend indicator.
5. VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price)
VWAP, or Volume Weighted Average Price, is a key tool for traders who want to refine their entry points by incorporating volume into their analysis. It calculates the average price of a security, weighted by trading volume throughout the day. Unlike standard moving averages, VWAP highlights where the majority of trading activity is happening. The formula is simple: multiply the price of each trade by its volume, then divide by the total volume. This makes it a go-to "fair value" benchmark for institutional traders aiming to minimize transaction costs and evaluate whether they're buying or selling above or below the market's average price.
Day Trading Performance (Speed and Momentum)
VWAP is especially useful for short-term charts, such as 1-minute to 1-hour timeframes, making it a favorite among day traders. If the price stays above VWAP, it signals bullish sentiment, while trading below it suggests a bearish outlook. Day traders often look for price pullbacks to the VWAP line during trending markets. If the price holds at this level, it can indicate a good entry point in the direction of the trend. However, it's best to avoid trading in the first few minutes of the market open, as the limited data can make VWAP less reliable. With a reliability rating of 8/10 for intraday trading, VWAP becomes even more effective when paired with oscillators like RSI to spot overbought or oversold conditions. Although day traders rely on VWAP the most, swing traders also use it to confirm market positioning.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength and Structure)
While VWAP resets daily and is primarily designed for intraday use, swing traders can still find value in it. During the trading day, VWAP helps identify ideal entry points, particularly during pullbacks in highly liquid markets dominated by institutional activity. For those holding positions over several days, VWAP acts more as a secondary confirmation tool rather than a primary indicator.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
VWAP shines in high-volume futures markets such as ES (E-mini S&P 500), NQ (Nasdaq 100), CL (Crude Oil), and GC (Gold). In these markets, VWAP often acts like a magnet, with prices moving away from it and then returning to test this critical level. For ES and NQ day traders, a 5-minute chart with VWAP can highlight opportunities when momentum drives prices away from institutional value, creating chances for mean reversion. In commodities like CL and GC, a breakout above VWAP in a downtrend might signal a reversal, especially if accompanied by increased volume.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader and TradingView)
Both NinjaTrader and TradingView include VWAP as a standard indicator, and setting it up is straightforward. By default, VWAP calculations start from the market open and reset at the beginning of each trading session. On TradingView, simply select "VWAP" from the indicators menu, while NinjaTrader users can find it in the indicator list after completing their NinjaTrader VPS setup. For day trading, VWAP works best on timeframes of 30 minutes or less. To ensure smooth performance during volatile sessions, consider running these platforms on a high-performance VPS like QuantVPS. With ultra-low latency (0–1ms), you'll get uninterrupted VWAP calculations and the precision needed for timely trades.
6. Parabolic SAR
The Parabolic SAR (Stop and Reverse) is a trend-following tool that stands out for its use of dots instead of continuous lines. Developed by J. Welles Wilder - the same mind behind the Relative Strength Index (RSI) - this indicator is designed to identify optimal entry and exit points. When the dots appear below the price, it signals a bullish trend, while dots above the price indicate a bearish trend. A "stop and reverse" signal is triggered when the dots flip positions.
Day Trading Performance (Speed and Momentum)
Day traders often turn to the Parabolic SAR for its ability to track quick momentum changes in fast-moving markets like the E-mini S&P 500 (ES) and Nasdaq 100 (NQ). Acting as a dynamic trailing stop, the dots adjust closer to the price as trends gain speed, helping lock in profits during rapid moves. To minimize false signals in sideways markets, pairing the Parabolic SAR with the ADX indicator (using a threshold of >25) can be effective. For instance, during the New York session open, this indicator excels at capturing sharp price movements on 5-minute charts.
NEVER MISS A TRADE
Your algos run 24/7
even while you sleep.
99.999% uptime • Chicago, New York & London data centers • From $59.99/mo
Swing Trading Performance (Strength and Structure)
Swing traders take a slightly different approach by using less sensitive settings to smooth out short-term price fluctuations. This is particularly useful in futures markets like Crude Oil (CL) and Gold (GC), where trends can be more extended. By reducing the sensitivity compared to day trading setups, traders can avoid getting caught in minor price swings. The dots serve as trailing stop-loss levels, protecting profits as trends develop, while waiting for a confirmed flip ensures a more calculated exit strategy.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
In the high-speed world of futures trading, the Parabolic SAR’s ability to track price movements based on time and acceleration makes it a valuable tool. It works well for identifying entry and exit points in trending markets, especially for assets like ES and NQ. For commodities like CL and GC, where trends often last longer, the indicator remains effective. However, traders should be cautious in range-bound conditions, as frequent reversals can lead to false signals. This ties into broader strategies for optimizing indicators across various futures markets.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader and TradingView)
Both NinjaTrader and TradingView include the Parabolic SAR as a standard feature, with adjustable settings for the Step (acceleration factor) and Maximum (acceleration limit). For day trading on shorter timeframes, default settings usually suffice. Swing traders, however, may benefit from lowering the Step value to prevent premature exits. For an edge in performance, consider hosting your trading platform on QuantVPS, which offers ultra-low latency (0–1ms) and reliable uptime.
7. Ichimoku Cloud

The Ichimoku Cloud, or Ichimoku Kinko Hyo, is a comprehensive trend-following tool that helps traders assess trend direction, momentum, and key support/resistance levels. It’s widely regarded as both effective and user-friendly for identifying trends. This system is built on five components: the Conversion Line (Tenkan-sen), the Base Line (Kijun-sen), the Lagging Span (Chikou Span), and two Leading Spans (Senkou Spans A and B), which together form the Cloud, or Kumo.
What sets the Ichimoku Cloud apart is its forward-looking nature. It projects data 26 periods ahead, offering insight into potential support and resistance zones before price action unfolds. When the price is above the Cloud, it signals bullish momentum; when below, bearish momentum. The thickness of the Cloud also reveals market dynamics - a thicker Cloud indicates stronger barriers, while a thinner one suggests weaker levels of support or resistance. Let’s dive deeper into how this tool performs in different trading scenarios.
Day Trading Performance (Speed and Momentum)
For day traders, the Ichimoku Cloud is invaluable in fast-paced markets. It helps traders stay aligned with the trend by focusing on the price’s position relative to the Cloud. In high-volatility futures markets like the E-mini S&P 500 (ES) and Nasdaq 100 (NQ), the Cloud adjusts dynamically to reflect shifting support and resistance. Crossovers between the Conversion Line and Base Line often signal momentum changes, making them useful for timing entries. For example, during the New York session’s open on a 5-minute chart, traders might wait for the price to break through the Cloud, using the Lagging Span as additional confirmation of momentum shifts.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength and Structure)
Swing traders use the Ichimoku Cloud on longer timeframes - such as 30-minute, hourly, or daily charts - to capture more substantial price movements in markets like Crude Oil (CL) and Gold (GC). In these scenarios, the Cloud acts as a structural guide, highlighting key levels to watch during retracements. As long as the price stays above the Cloud in an uptrend (or below it in a downtrend), the trend is considered intact. The tool’s reliability - rated 8/10 - makes it especially valuable for swing trading, where longer-term support and resistance zones are crucial.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
In volatile futures markets like NQ and CL, traders should approach thin Clouds cautiously, as they’re more prone to being breached during sudden price swings. Tight stop-losses near these thinner areas can result in unnecessary losses. To improve accuracy, many traders combine Ichimoku signals with momentum indicators like RSI or MACD, which can confirm potential reversals and minimize false signals. Regardless of the strategy, disciplined risk management is non-negotiable. Applying the 2% Rule - risking no more than 2% of account equity per trade - helps ensure sustainability. For instance, on a $50,000 account, this would mean limiting risk to $1,000 per trade.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader and TradingView)
Both TradingView and NinjaTrader offer the Ichimoku Cloud as a standard indicator, pre-configured with the classic 9, 26, 52 period settings. These settings automatically plot the Senkou Spans 26 periods ahead, forming the Cloud boundaries. Day traders often stick with these default settings on shorter timeframes, while swing traders might tweak them slightly to smooth out market noise on daily or weekly charts. For optimal performance, hosting your trading platform on QuantVPS ensures ultra-low latency (0–1ms) and uninterrupted uptime. This can be particularly helpful for traders relying on precise execution in volatile markets.
8. Donchian Channels
Donchian Channels are a powerful tool for analyzing trends, focusing on breakout signals to highlight potential market opportunities.
These channels consist of three key lines: an upper band that tracks the highest high over a 20-bar period, a lower band marking the lowest low, and a middle line calculated as the average of the two. Unlike Bollinger Bands, which rely on standard deviation, Donchian Channels use actual price highs and lows, making them particularly responsive to market volatility. When prices break above the upper band or dip below the lower band, it often signals a potential entry in the direction of the breakout.
In addition to identifying trends, Donchian Channels provide insights into trend structure. For example, during a bullish trend, prices generally stay between the middle and upper lines. Conversely, in a bearish trend, prices tend to hover between the middle and lower lines. If prices drop below the middle line during an uptrend, it could indicate weakening momentum, making the middle line a useful dynamic trailing stop to safeguard profits.
Day Trading Performance (Speed and Momentum)
For day traders working in fast-moving markets like the E-mini S&P 500 (ES) or Nasdaq 100 (NQ), Donchian Channels on 5-minute or 15-minute charts are excellent for spotting quick momentum shifts and breakouts. The default 20-period setting is effective, but during volatile sessions, shorter periods like 10 or 15 can improve sensitivity. To reduce false signals, pair Donchian breakouts with the Average Directional Index (ADX), and focus on trades where the ADX is above 25. For a broader look at tools, check out our guide on the best indicators for day trading.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength and Structure)
Swing traders often prefer using Donchian Channels on 1-hour, 4-hour, or daily charts to monitor significant trend changes in assets like Crude Oil (CL) or Gold (GC). When volatility spikes, the outer bands widen, highlighting areas of extreme price movements or potential breakout zones. Adding a 200-period Simple Moving Average (SMA) as a filter can refine entries - consider buying only when the price breaks above the upper band and remains above the 200 SMA. This approach helps avoid getting caught in false breakouts.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
In futures markets such as Nasdaq 100 (NQ) and Crude Oil (CL), Donchian Channels are often used to identify opening range breakouts during the first 30 to 60 minutes of the session. The lower band can serve as a trailing stop for long positions, locking in profits while allowing for natural price fluctuations. For added confirmation, consider using On-Balance Volume (OBV) alongside Donchian Channels. A breakout above the upper band accompanied by rising OBV could indicate institutional buying and a stronger, more sustainable trend. However, avoid trading breakouts when the bands are narrow and flat, as this signals low volatility and a higher chance of false signals.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader and TradingView)
Both TradingView and NinjaTrader offer Donchian Channels as standard indicators with a default 20-period setting. The primary input, often labeled "Length" or "Period", can be adjusted to match your trading style. For day traders focusing on fast-moving futures markets, shorter periods like 10–15 are ideal for capturing quicker price action. To ensure smooth execution, especially in volatile markets like ES and NQ, consider hosting your platform on QuantVPS. This setup provides ultra-low latency (0–1 ms) and uninterrupted uptime, which is essential for executing breakout trades during peak trading hours.
9. Keltner Channels
Keltner Channels are a type of volatility-based indicator that traders use to confirm trends and pinpoint low-risk pullback opportunities within ongoing trends. Unlike Bollinger Bands, which rely on standard deviation, Keltner Channels are built around an Exponential Moving Average (EMA) and use the Average True Range (ATR) to calculate their bands. This approach makes them less reactive to sudden price spikes and helps filter out market noise.
The indicator consists of three main lines: a middle line (commonly a 20-period EMA), an upper band (calculated as the middle line plus 2× ATR), and a lower band (the middle line minus 2× ATR). When prices hover between the middle and upper bands, it signals a strong uptrend. Conversely, prices staying between the middle and lower bands point to a downtrend. Pullbacks toward the middle line often create low-risk opportunities to enter trades in line with the prevailing trend. As with any tool, Keltner Channels work best when used alongside other indicators to confirm trends.
Day Trading Performance (Speed and Momentum)
For day traders focusing on instruments like the E-mini S&P 500 (ES) or Nasdaq 100 (NQ), Keltner Channels shine on shorter timeframes, such as 5-minute or 15-minute charts. Using the default 20-period EMA with a 2.0 ATR multiplier, traders can identify strong momentum when the price touches or tests the upper band during an uptrend. A pullback toward the middle line in these scenarios often signals a good entry point.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength and Structure)
Swing traders working with longer timeframes, such as 1-hour, 4-hour, or daily charts in markets like Gold (GC) or Crude Oil (CL), can use Keltner Channels to assess trend structure and strength. Widening bands indicate growing volatility and a strengthening trend, while narrowing bands suggest consolidation or weakening momentum. The middle line often acts as dynamic support in uptrends and resistance in downtrends. If prices break below the middle line during an uptrend, it could signal a potential reversal. For entries, traders might look to buy when the price touches the lower band during an uptrend and then rebounds above the middle line.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
In futures markets like Nasdaq 100 (NQ) and Crude Oil (CL), Keltner Channels are useful for spotting key price levels where market pressure might shift. The middle line can serve as a guide for setting trailing stops or identifying potential exit points. This makes the tool particularly practical for managing trades in volatile markets.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader and TradingView)
Both TradingView and NinjaTrader offer Keltner Channels with default settings. For day trading, consider adjusting the period to 10–15 for quicker signals. For swing trading, a longer period of around 50 can provide smoother, more reliable signals. If you're trading in fast-moving markets, hosting your platform on QuantVPS ensures ultra-low latency in algorithmic trading for better execution. To enhance your analysis, combine Keltner Channels with other trend-following tools for a more comprehensive market view.
10. Bollinger Bands (Trend Context Use)
Bollinger Bands are a go-to tool for traders thanks to their flexibility and insight. This indicator features a 20-period SMA (Simple Moving Average) with upper and lower bands positioned 2 standard deviations away. When trading trends, pay attention to how the price interacts with the bands. If the price consistently touches the outer bands without reverting to the middle SMA, it's often referred to as "walking the bands" - a sign of a strong trend.
The distance between the bands reveals a lot about market conditions. Wider bands suggest increased volatility and a potential continuation of the trend, while narrowing bands (known as a "squeeze") indicate reduced volatility and the possibility of a breakout. In an uptrend, prices tend to stay between the 20-period SMA and the upper band, while in a downtrend, they remain between the SMA and the lower band. If momentum slows and the price fails to reach the outer bands, it could signal that the trend is losing steam. Whether you're trading intraday or holding positions longer, Bollinger Bands provide actionable insights into market dynamics.
Day Trading Performance (Speed, Momentum)
For fast-paced day trading in futures like NQ (Nasdaq 100) and ES (E-mini S&P 500), Bollinger Bands shine on shorter timeframes - 30 minutes or less. The standard setup of a 20-period SMA with 2.0 standard deviations helps filter out noise and focus on momentum. Breakouts that close outside the bands during periods of expansion often signal the start of a strong move. When the price "walks" along the outer bands, it confirms a robust trend. However, if the price crosses back over the middle SMA, it might indicate that the trend is weakening or shifting to a range-bound phase, which could be a cue to exit.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength, Structure)
Swing traders, who operate on longer timeframes like 1-hour to 4-hour charts, can use Bollinger Bands to assess trend structure and sustainability. In markets like Gold (GC) or Crude Oil (CL), the 20-period SMA acts as a critical level. As long as prices stay above the SMA in an uptrend, the trend remains intact. A "band walk", where prices repeatedly touch the outer bands without returning to the middle, signals sustained momentum. A band squeeze, on the other hand, often precedes a significant breakout. If the price closes on the opposite side of the middle SMA, it can indicate that the trend has reversed, offering a clear exit signal.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
In high-volatility futures markets such as NQ and CL, Bollinger Bands adjust dynamically to reflect rapid shifts in volatility. During consolidation phases in markets like GC, failed breakouts at the outer bands can highlight strong support or resistance levels. For ES and NQ, expanding bands with prices sticking near the upper band often signal growing momentum. In trending markets, the middle band (20-period SMA) can also serve as a reliable reference point for trailing stops. Combining Bollinger Bands with other indicators, like RSI or MACD, can improve the reliability of your signals.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader and TradingView)
Both TradingView and NinjaTrader default to the standard Bollinger Bands setup: a 20-period SMA with 2.0 standard deviations. For day trading, it's essential to set the "Offset" to 0 to keep the bands aligned with current price movements. While these settings work well for most markets, traders in more volatile contracts like NQ may benefit from tweaking the bands - using 2.5 standard deviations, for instance, can help reduce false signals. Hosting your trading platform on QuantVPS can further enhance your trading experience by ensuring low-latency execution, especially during high-momentum moves when precision matters most.
11. Hull Moving Average (HMA)
The Hull Moving Average (HMA), introduced in 2005 by Australian mathematician and trader Alan Hull, was designed to overcome the lag often associated with traditional moving averages. Unlike the Simple Moving Average (SMA), which gives equal weight to all data points, or the Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which prioritizes recent prices, the HMA uses a unique calculation. It incorporates the square root of the selected period - for example, a 16-period HMA applies a 4-period weighted moving average in its final step. This approach minimizes lag while maintaining a smooth curve, making it highly effective for identifying trends early.
"The Hull moving average solves the age-old dilemma of making a moving average more responsive to current price activity whilst maintaining curve smoothness. In fact the HMA almost eliminates lag altogether and manages to improve smoothing at the same time." – Alan Hull
"The Hull moving average solves the age-old dilemma of making a moving average more responsive to current price activity whilst maintaining curve smoothness. In fact the HMA almost eliminates lag altogether and manages to improve smoothing at the same time." – Alan Hull
The HMA's slope is a reliable indicator of trend direction. An upward slope signals a bullish trend, while a downward slope points to bearish momentum. When prices cross above or below the HMA, it often reflects a shift in market sentiment. Additionally, in trending markets, the HMA can act as dynamic support or resistance, providing traders with valuable entry and exit points.
Day Trading Performance (Speed and Momentum)
For day traders working with 5- to 15-minute charts on assets like ES and NQ, the HMA’s reduced lag is a game-changer. A combination of a fast HMA (e.g., period 9–14) and a slower HMA (e.g., period 18–50) can help pinpoint rapid shifts and crossover signals. Its smooth curve also filters out much of the intraday noise, allowing traders to focus on genuine momentum changes instead of random price fluctuations.
During volatile periods, such as the opening hour of trading on NQ, the HMA’s quick response becomes especially valuable. For instance, if you’re holding a long position and the price dips below an upward-sloping HMA, it could signal fading momentum. Pairing the HMA with volume indicators like VWAP can further validate breakouts and help avoid false signals in choppy market conditions.
Swing Trading Performance (Trend Strength and Structure)
Swing traders using 1-hour to 4-hour charts on assets like GC (Gold) or CL (Crude Oil) often benefit from longer HMA periods, such as 50, 55, or 89. These settings strike a balance between responsiveness and trend clarity, helping traders spot medium-term moves while filtering out minor fluctuations. A price consistently staying above a rising HMA confirms a strong bullish trend, offering potential pullback entry points. Conversely, when the HMA flattens, it may signal market consolidation and the possibility of a breakout.
The HMA can also serve as a trailing stop. In an uptrend, as long as the price remains above a rising HMA, the trend is likely intact. A close below the HMA might indicate it’s time to exit or tighten stop-loss levels, helping protect profits while staying in winning trades. This versatility makes the HMA a practical tool for bridging the gap between short-term day trading and longer-term trend strategies.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
In high-leverage futures markets, the HMA refines trend analysis and adapts well to different trading environments. For assets like ES and NQ, where intraday volatility often spikes during economic announcements, shorter HMA periods (e.g., 12–16) can help capture rapid momentum changes. Meanwhile, for trending markets like CL and GC, which react to geopolitical events or commodity cycles, the HMA offers dynamic support and resistance levels, aiding in position management.
The key is to adjust the HMA period to suit the asset’s volatility and your timeframe. Shorter periods work well in fast-moving markets like NQ, while longer periods (50–89) are better suited for steadier markets like GC, filtering out noise and focusing on meaningful trends.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader and TradingView)
Both NinjaTrader and TradingView include the HMA as a built-in feature, making it easy to set up or integrate into Pine Script strategies. Alan Hull suggests a default period of 16 for general use, as it balances speed and smoothness across various market types. For day trading, opt for shorter periods (9–14), while swing trading typically benefits from longer settings (50–89). These platforms handle the weighted moving average calculations automatically.
To try a crossover strategy, add two HMA indicators to your chart - one fast (e.g., period 10) and one slow (e.g., period 50). Use contrasting colors to quickly identify crossovers. For highly volatile markets, shorter HMA periods enhance responsiveness, while longer periods in stable markets help reduce noise and false signals. Hosting your trading platform on QuantVPS ensures low-latency execution, which is crucial when trading fast-moving futures contracts. Combining a responsive indicator like the HMA with reliable infrastructure can give you an edge in spotting and acting on trend changes as they occur.
12. Linear Regression Channel
The Linear Regression Channel uses statistical analysis to draw a best-fit line through price data, with parallel lines plotted above and below based on standard deviations. This creates a channel that highlights the average trend direction while identifying areas where prices typically face support or resistance. Unlike manually drawn trendlines, this method relies on precise calculations, removing subjective judgment.
The middle line represents the mean price over a specific period, while the outer bands reflect how far the price deviates from that average. When prices approach the upper band, it often signals potential resistance or overbought conditions. On the other hand, prices nearing the lower band suggest support or oversold levels, which can act as critical entry or exit points. The channel's slope carries significance as well - steeper angles indicate stronger trends, while flatter slopes suggest consolidation or weakening momentum. This structured approach provides flexibility for various trading strategies.
Day Trading Performance (Speed and Momentum)
For day traders focusing on 5- to 15-minute charts for instruments like ES or NQ, the Linear Regression Channel is excellent for capturing intraday trends while filtering out market noise. A shorter period (50–100 bars) is typically used to monitor rapid momentum changes, especially during market opens or significant economic announcements. For instance, in an uptrend, a bounce off the lower band could signal a low-risk entry, with profit targets set at the middle or upper band.
The parallel structure of the channel also helps traders set realistic profit goals. During volatile sessions on NQ, observing how prices interact with the bands can reveal whether the trend is gaining strength or losing momentum. This insight can guide traders in adjusting position sizes or tightening stop-loss orders.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength and Structure)
STOP LOSING TO LATENCY
Execute faster than
your competition.
Sub-millisecond execution • Direct exchange connectivity • From $59.99/mo
For swing traders, extending the regression period helps identify longer-term trends. Using 1-hour to 4-hour charts for assets like GC or CL, longer periods (100–200 bars) smooth out short-term fluctuations, making it easier to identify the dominant trend direction. A rising channel with prices staying above the center line often confirms bullish momentum. Conversely, repeated touches of the upper band without breaking through may signal that the trend is losing steam.
The bands also serve as dynamic zones of support and resistance. In a strong uptrend on CL, pullbacks to the lower band often attract buyers, presenting high-probability entry points. However, if prices fall below the lower band and fail to recover, it could indicate a potential trend reversal or the start of a consolidation phase, signaling traders to reassess their positions.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
In futures markets, the Linear Regression Channel adapts well to different levels of volatility. Fast-moving contracts like NQ benefit from shorter periods, especially during tech-driven rallies or selloffs. Meanwhile, steadier markets like GC respond better to longer settings, which help filter out commodity-specific noise while maintaining clear trend boundaries. The parallel bands make it easier to spot areas where market pressure is likely to shift, aiding in precise trade timing.
Additionally, the channel's ability to project forward - extending the bands beyond the current price - can help traders anticipate future support or resistance zones. This is especially useful when planning trades around scheduled economic events or overnight price gaps.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader and TradingView)
Both NinjaTrader and TradingView offer the Linear Regression Channel as a built-in tool. On TradingView, the default settings typically include a 100-period length and a 2.0 standard deviation for the outer bands. Many traders enable the "Extend Right" feature to project future price levels beyond the current chart. For day trading, reducing the period to 50–75 bars increases responsiveness, while swing traders may prefer extending it to 150–200 bars for a clearer view of the trend.
In NinjaTrader, similar customization options are available, allowing traders to adjust period lengths and standard deviation multipliers. Shorter periods are ideal for intraday scalping on ES, while longer settings suit position traders managing GC or CL overnight. These adjustable features align with the need for tailored setups to fit different trading approaches. Hosting on QuantVPS ensures fast execution and reliable uptime, which are crucial during breakouts or sudden reversals.
13. Trendlines & Channels (Manual Indicator)
Manual trendlines provide a hands-on approach to understanding market structure, complementing automated indicators. When drawn properly, trendlines and channels can be effective tools for analyzing price action. A valid trendline connects at least two key swing points - such as higher lows in an uptrend or lower highs in a downtrend - and becomes more reliable with each additional touch. The steepness of a trendline often reflects the strength of momentum. Adding a parallel line to create a channel can help traders identify potential reversal zones by highlighting areas where opposing price forces might emerge.
"A mistake made by many traders is they become so involved in trying to catch the minor market swings that they miss the major price moves." – Jack Schwager, Author and Trader
"A mistake made by many traders is they become so involved in trying to catch the minor market swings that they miss the major price moves." – Jack Schwager, Author and Trader
This manual approach offers traders a deeper understanding of price action, making it adaptable to different timeframes and strategies. For example, one trend-following strategy based on these principles reportedly achieved an average annual return of 17.53% over a 24-year period, navigating through bull markets, bear markets, and even recessions.
Day Trading Performance (Speed and Momentum)
For day traders using 5- to 30-minute charts on futures like ES or NQ, trendlines can highlight critical support and resistance levels. In fast-paced trading sessions, a break of a trendline often signals a shift in momentum, while channels can help pinpoint areas for taking profits. Using line charts that focus on closing prices can reduce unnecessary visual clutter, making it easier to spot these shifts.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength and Structure)
Swing traders typically rely on 1- to 4-hour charts for instruments like GC or CL to capture the broader market structure. Zooming out to identify the dominant trend is crucial. A series of higher lows or lower highs confirms the trend, while the parallel channel line can serve as a target for exiting trades. In volatile markets like CL, these channels can help traders avoid staying in overbought conditions for too long.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
In futures markets such as ES and NQ, trendlines often coincide with areas where institutional orders tend to cluster, creating liquidity for new trade entries. For more stable markets like GC, trendlines drawn on daily charts can uncover long-term support levels. To confirm the validity of a trendline break, traders often use On-Balance Volume (OBV). If the price breaks a trendline but OBV does not show a corresponding move, the reversal may lack the institutional support needed to sustain it.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader and TradingView)
Platforms like TradingView simplify the process of manual trendline drawing with tools like the "Trend-Line Angle", which objectively measures trend strength. NinjaTrader enhances this further with custom indicators designed to filter out noise in fast-moving futures markets. Hosting these platforms on QuantVPS ensures that manual drawings and alerts execute with minimal latency, even during highly volatile trading periods.
14. Heikin Ashi Candles
Heikin Ashi candles take standard price data and turn it into a smoother visual format, making it easier to identify trends while cutting down on market noise. Unlike traditional candlesticks that show exact open, high, low, and close values, Heikin Ashi recalculates these components using averaged data. The result? A cleaner, more uniform chart where trends are easier to spot. Consecutive candles of the same color often indicate a steady trend, making this tool a practical choice for both quick day trades and longer swing strategies.
Day Trading Performance (Speed and Momentum)
On shorter timeframes, like 5- to 15-minute charts for ES and NQ, Heikin Ashi helps filter out the noise that can lead to false signals. Solid green or red candles often confirm sustained momentum, though the averaging process can slightly delay entry points. This makes it less ideal for scalpers but highly effective for traders who rely on other trend indicators in fast-moving markets.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength and Structure)
For swing traders using 1- to 4-hour charts on instruments like GC and CL, Heikin Ashi offers valuable insights into trend exhaustion. When candles start forming small bodies with long wicks, it often signals a potential reversal. Pairing this with an ADX reading above 25 adds another layer of confirmation, helping traders distinguish between genuine reversals and short-term consolidations.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
Heikin Ashi excels in volatile futures markets by smoothing out erratic price swings that can trigger false breakouts. For CL, this feature is particularly useful in taming sharp, unpredictable movements. NQ traders, dealing with rapid tech-sector fluctuations, can rely on the smoothed visuals to stay focused on the overarching trend instead of reacting to every small tick. ES traders often combine Heikin Ashi with moving averages - if the price stays above a 50-period EMA and the candles remain green, it validates a bullish bias. For GC, where trends can last for weeks, Heikin Ashi on daily charts provides a clear framework for managing positions effectively.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader and TradingView)
Both TradingView and NinjaTrader come with built-in Heikin Ashi charting options. Simply select "Heikin Ashi" from the chart type menu. For a broader perspective, traders often use a traditional candlestick chart alongside it. Hosting your trading platform on QuantVPS ensures smooth, lag-free performance during high-volatility periods, keeping your charts responsive when you need them most.
15. ATR-Based Trend Indicators
ATR-based indicators are a step forward in refining trend analysis by incorporating market volatility into their calculations. These tools use the Average True Range (ATR) to adapt dynamically to changing conditions, expanding and contracting based on volatility rather than sticking to fixed price levels. This flexibility makes them especially useful in futures markets, where volatility can shift rapidly. The concept is simple: when the price closes above the indicator line, it signals an uptrend; when it closes below, it indicates a downtrend.
Day Trading Performance (Speed and Momentum)
For day traders working with 5- to 15-minute charts in futures markets like the ES and NQ, ATR-based indicators are invaluable. They quickly adjust to fluctuating market conditions, helping traders avoid false signals while tracking trends effectively. These tools are particularly useful for pinpointing entry and exit points, as well as setting precise stop-loss and take-profit levels. In fast-moving markets like NQ, where volatility can surge during major events, the ATR component automatically widens its thresholds to reduce the chances of premature exits. Many traders pair ATR-based signals with other confirmation tools to filter out periods of choppy, non-trending activity.
Swing Trading Performance (Strength and Structure)
Swing traders operating on 1- to 4-hour charts for contracts like CL and GC benefit greatly from ATR-based indicators. These tools align with longer-term trends while accounting for natural pullbacks. For instance, crude oil traders often face overnight gaps and news-driven volatility, which can cause abrupt market shifts. ATR-based trailing stops adapt by tightening during calmer periods and loosening when volatility spikes. Gold traders, on the other hand, often combine ATR-based indicators with an ADX reading above 25 to confirm the strength of a breakout, signaling a move strong enough to hold. When paired with solid automated futures trading systems and risk management practices, these indicators can significantly enhance a trader's strategy.
Futures Market Applications (ES, NQ, CL, GC)
ATR-based tools shine when implementing the best automated trading strategies for futures, helping traders manage risk and stay aligned with market trends. For ES traders, these indicators are particularly useful during sessions with thinning liquidity and rising volatility. NQ traders rely on them to balance quick responsiveness with stability in fast-paced environments. In the CL market, ATR-based stop-loss settings are tailored to handle sharp, sudden price moves, with wider thresholds signaling increased volatility and potential trend continuation. GC traders, meanwhile, use ATR-based trailing stops on daily charts to capture multi-week trends without being shaken out by routine corrections. This adaptability ensures both day and swing traders can navigate their markets effectively.
Platform Settings (NinjaTrader and TradingView)
Both NinjaTrader and TradingView offer built-in Supertrend indicators that use customizable ATR multipliers and periods. A common starting point is a 10-period ATR with a multiplier of 3.0. Day traders often tighten these settings to generate quicker signals, while swing traders might prefer a wider multiplier to minimize the risk of getting caught in whipsaws. Hosting on QuantVPS ensures that ATR calculations remain accurate and up-to-date in real-time.
Indicator Comparison Table
Selecting the right trend indicator boils down to your trading style, the timeframe you work within, and the specific futures market you're targeting. For example, day traders require tools that respond quickly to price fluctuations, while swing traders prioritize indicators that filter out short-term noise and focus on sustained trends. The table below evaluates 15 indicators based on key performance metrics, helping you pinpoint which ones align best with your strategy.
The day trading score measures how effectively an indicator works on short-term charts (5- to 30-minute), where speed and responsiveness are crucial. Meanwhile, the swing trading score assesses performance on longer timeframes (1- to 4-hour charts), where understanding trend structure and strength is more important. Additionally, each indicator is paired with the futures markets it suits best - whether it's the fast-paced NQ, the broad movements of ES, the volatility of CL, or the structured patterns of GC.
| Indicator | Day Trading Score (1-10) | Swing Trading Score (1-10) | Best Futures Markets | Key Strength | Key Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moving Averages (SMA/EMA) | 7 | 10 | ES, NQ, CL, GC | Smooths out noise; great for trend analysis | Lags behind price changes |
| MACD | 8 | 8 | ES, NQ | Tracks both momentum and trend direction | Struggles in highly volatile markets |
| ADX | 6 | 9 | CL, GC | Measures trend strength objectively | Doesn't indicate trend direction |
| Supertrend | 8 | 7 | NQ, CL | Great for trailing stops in trending markets | Prone to false signals in sideways markets |
| VWAP | 10 | 2 | ES, NQ | Tracks institutional order flow intraday | Resets daily; ineffective for multi-day trends |
| Parabolic SAR | 6 | 8 | GC, CL | Clear exit and reversal points | Generates false signals in choppy conditions |
| Ichimoku Cloud | 5 | 9 | ES, GC | Offers a complete view of trend and support | Complex visuals can overwhelm beginners |
| Donchian Channels | 7 | 9 | CL | Ideal for spotting commodity breakouts | Needs filters to avoid false breakouts |
| Keltner Channels | 7 | 8 | ES, NQ | Adapts to volatility; confirms trends | Less effective in calm markets |
| Bollinger Bands | 8 | 7 | ES, GC | Highlights volatility-driven breakouts | Touching bands doesn't guarantee reversals |
| Hull Moving Average (HMA) | 9 | 7 | NQ, ES | Reduces lag while staying smooth | Overreacts to minor price changes |
| Linear Regression Channel | 6 | 8 | GC, ES | Displays statistical trend deviations | Requires manual adjustments |
| Trendlines & Channels | 7 | 9 | GC, CL | Respects historical price structures | Subjective and relies on manual drawing |
| Heikin Ashi Candles | 8 | 8 | NQ, CL | Filters noise; emphasizes sustained trends | Masks precise entry and exit points |
| ATR-Based Indicators | 8 | 9 | ES, NQ, CL, GC | Adjusts to market volatility dynamically | Needs careful multiplier tuning |
For day trading, VWAP stands out with a perfect 10/10 score. Its ability to reset daily and track institutional order flow makes it indispensable for ES and NQ scalpers. On the other hand, Moving Averages and Ichimoku Cloud excel at swing trading, scoring 10/10 and 9/10 respectively, thanks to their strength in identifying long-term trends and support/resistance areas.
ADX is another powerful tool for swing traders, especially when its readings exceed 25, signaling strong trends - perfect for those committing to multi-day positions.
The Hull Moving Average earns a 9/10 for day trading, as it minimizes lag while retaining smoothness, making it ideal for fast-paced NQ trading. Meanwhile, Donchian Channels and Trendlines shine in swing trading with 9/10 scores, particularly in CL and GC, where breakout levels and price structures are more pronounced. However, tools like Parabolic SAR perform better in established trends, scoring lower for day trading (6/10) but higher for swing trading (8/10) due to its reliability in less volatile conditions.
Conclusion
No trend indicator can guarantee profits, but combining multiple tools can help filter out false signals and confirm market momentum. As Jack Schwager, a respected author and trader, aptly notes:
"A mistake made by many traders is they become so involved in trying to catch the minor market swings that they miss the major price moves".
"A mistake made by many traders is they become so involved in trying to catch the minor market swings that they miss the major price moves".
This highlights the importance of an integrated approach, especially for managing both day and swing trades. For instance, pairing a trend-following tool like Moving Averages with a confirmation tool such as MACD can reduce the risk of being misled by whipsaws.
It’s important to remember that most trend indicators are lagging - they reflect price movements rather than predict them. To address this, many traders incorporate leading indicators like On-Balance Volume (OBV) or use the ADX to gauge trend strength. An ADX reading above 25 often signals a strong trend worth trading, while readings below 20 suggest choppy, directionless markets that are better avoided. Additionally, when indicators align - such as a bullish moving average crossover combined with a positive MACD histogram - the likelihood of a successful trade increases.
Risk management and understanding market context are just as important as choosing the right indicators. Define your trading timeframe - whether it's day trading ES on a 5-minute chart or swing trading GC on a daily chart. Use your indicators to set objective stop-loss and take-profit levels. For example, a trailing stop based on ATR can help protect your gains during volatile market conditions.
Before committing real capital, thoroughly backtest your indicator combinations across different market environments to ensure reliability. For seamless execution, especially during high-volatility sessions, having a high-performance VPS like QuantVPS can be a game-changer. Offering ultra-low latency (0–1ms) and guaranteed uptime, QuantVPS ensures your strategies execute without a hitch. Plans start at $59.99/month, catering to setups ranging from 1–2 charts to professional configurations handling 7 or more charts.
The takeaway? Indicators are most effective when used together. Master a few complementary tools, respect the broader market context, and always trade with disciplined risk management.
FAQs
How can I select the best trend indicator for my trading strategy?
Choosing the right trend indicator boils down to your trading style, the time frame you operate in, and the market you're trading. For day traders - those focusing on quick intraday moves in futures like the E-mini S&P 500 (ES) or Nasdaq (NQ) - it’s often best to use tools that react quickly. Indicators like short-period Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs), the Supertrend, or VWAP are popular choices. These provide timely signals to help identify market bias and pinpoint entry and exit opportunities with minimal lag.
On the other hand, swing traders, who hold positions for days or even weeks in markets like crude oil (CL) or gold (GC), typically favor indicators that focus on broader trends and momentum. Tools such as the 200-period SMA, ADX, Donchian Channels, or the Ichimoku Cloud can offer a better perspective on long-term trends and strength.
To make things easier, start with just one or two indicators that suit your trading goals and time frame. Test them thoroughly on demo accounts or with back-tested data to evaluate their performance. For instance, a day trader might pair a 9-period EMA with the Parabolic SAR to track short-term trends and reversals. Meanwhile, a swing trader could use a 50-day SMA alongside an ADX reading above 25 to confirm the strength of a trend. Keep your charts clean - too many indicators can clutter your analysis and make it harder to act on clear signals.
Finally, ensure the indicators you choose are a good match for the specific futures market you trade. High-liquidity contracts like ES and NQ often respond well to volume-based tools such as VWAP. In contrast, more volatile markets like CL and GC may yield better results with tools like Donchian or Keltner Channels. Always test your indicators under various market conditions and combine them with sound risk management strategies to ensure they align with your overall trading approach.
Can using multiple trend indicators improve trading accuracy?
Combining multiple trend indicators can improve trading accuracy by offering a more detailed view of market conditions. When used together, complementary tools help traders confirm signals and filter out false breakouts, minimizing the impact of market noise. For example, a moving average crossover can indicate the trend direction, the ADX can measure the trend's strength, and a volume-based tool like VWAP can confirm institutional activity.
That said, it’s crucial to select indicators that work well together rather than duplicate each other. Overloading your chart with too many tools can create confusion and make decision-making harder. A well-rounded setup could include a trend-direction indicator (like SMA, EMA, or Supertrend), a strength or volatility measure (such as ADX or ATR-based bands), and a volume or price-action confirmation tool (like VWAP or Heikin Ashi). This approach helps traders stay focused and make informed decisions, whether they’re day trading or swing trading.
What’s the difference between indicators for day trading and swing trading?
Day trading indicators are all about capturing short-term price moves and thriving on intraday volatility. These tools typically operate on shorter timeframes, such as 1- to 15-minute charts, and churn out frequent signals to help traders seize quick opportunities. Among the favorites are VWAP, Supertrend, and short-term moving averages, which deliver rapid buy or sell cues. To stay ahead of the game, day traders often lean on leading indicators like MACD histograms or stochastic oscillators, which are designed to predict immediate price shifts.
Swing trading indicators, in contrast, cater to those who take a longer view, holding positions for several days or even weeks. These indicators rely on longer look-back periods, such as 20- to 200-day moving averages, ADX, or Ichimoku clouds, to sift through short-term noise and focus on the bigger trend picture. Swing traders usually prefer lagging indicators, which confirm the direction and strength of a trend. To manage the larger price swings that come with this approach, they often combine these tools with volatility-based stop-loss strategies, like those using ATR, for added precision.
Choosing the right trend indicator boils down to your trading style, the time frame you operate in, and the market you're trading. For day traders - those focusing on quick intraday moves in futures like the E-mini S&P 500 (ES) or Nasdaq (NQ) - it’s often best to use tools that react quickly. Indicators like short-period Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs), the Supertrend, or VWAP are popular choices. These provide timely signals to help identify market bias and pinpoint entry and exit opportunities with minimal lag.
On the other hand, swing traders, who hold positions for days or even weeks in markets like crude oil (CL) or gold (GC), typically favor indicators that focus on broader trends and momentum. Tools such as the 200-period SMA, ADX, Donchian Channels, or the Ichimoku Cloud can offer a better perspective on long-term trends and strength.
To make things easier, start with just one or two indicators that suit your trading goals and time frame. Test them thoroughly on demo accounts or with back-tested data to evaluate their performance. For instance, a day trader might pair a 9-period EMA with the Parabolic SAR to track short-term trends and reversals. Meanwhile, a swing trader could use a 50-day SMA alongside an ADX reading above 25 to confirm the strength of a trend. Keep your charts clean - too many indicators can clutter your analysis and make it harder to act on clear signals.
Finally, ensure the indicators you choose are a good match for the specific futures market you trade. High-liquidity contracts like ES and NQ often respond well to volume-based tools such as VWAP. In contrast, more volatile markets like CL and GC may yield better results with tools like Donchian or Keltner Channels. Always test your indicators under various market conditions and combine them with sound risk management strategies to ensure they align with your overall trading approach.
Combining multiple trend indicators can improve trading accuracy by offering a more detailed view of market conditions. When used together, complementary tools help traders confirm signals and filter out false breakouts, minimizing the impact of market noise. For example, a moving average crossover can indicate the trend direction, the ADX can measure the trend's strength, and a volume-based tool like VWAP can confirm institutional activity.
That said, it’s crucial to select indicators that work well together rather than duplicate each other. Overloading your chart with too many tools can create confusion and make decision-making harder. A well-rounded setup could include a trend-direction indicator (like SMA, EMA, or Supertrend), a strength or volatility measure (such as ADX or ATR-based bands), and a volume or price-action confirmation tool (like VWAP or Heikin Ashi). This approach helps traders stay focused and make informed decisions, whether they’re day trading or swing trading.
Day trading indicators are all about capturing short-term price moves and thriving on intraday volatility. These tools typically operate on shorter timeframes, such as 1- to 15-minute charts, and churn out frequent signals to help traders seize quick opportunities. Among the favorites are VWAP, Supertrend, and short-term moving averages, which deliver rapid buy or sell cues. To stay ahead of the game, day traders often lean on leading indicators like MACD histograms or stochastic oscillators, which are designed to predict immediate price shifts.
Swing trading indicators, in contrast, cater to those who take a longer view, holding positions for several days or even weeks. These indicators rely on longer look-back periods, such as 20- to 200-day moving averages, ADX, or Ichimoku clouds, to sift through short-term noise and focus on the bigger trend picture. Swing traders usually prefer lagging indicators, which confirm the direction and strength of a trend. To manage the larger price swings that come with this approach, they often combine these tools with volatility-based stop-loss strategies, like those using ATR, for added precision.
"}}]}




