Cross-Market Arbitrage on Polymarket: Bots vs Sportsbooks & Exchanges
Cross-market arbitrage on Polymarket involves exploiting price differences for the same event across platforms like sportsbooks, exchanges, and prediction markets. Automated bots dominate this space due to their speed, precision, and ability to monitor hundreds of markets simultaneously. Between April 2024 and April 2025, traders earned an estimated $40 million in profits from arbitrage, with bots driving the majority of these gains.
Here’s why bots outperform manual traders:
- Speed: Bots execute trades in milliseconds, while humans take seconds to react.
- Consistency: Bots operate 24/7 without fatigue or emotional biases.
- Efficiency: They handle complex calculations and multi-leg trades instantly.
- Profitability: Bots target spreads of 2.5–3% to offset fees and ensure gains.
Manual trading struggles to compete due to slower execution, emotional delays, and limited scalability. Platforms like Polymarket and Kalshi offer lucrative opportunities, but success requires automation and infrastructure like QuantVPS, which ensures low latency and reliable performance.
Key Takeaways:
- Bots execute trades faster and more accurately than humans.
- Arbitrage profits hinge on tight spreads, minimal fees, and swift execution.
- Infrastructure like QuantVPS enhances bot performance with sub-1ms latency.
- Manual trading is inefficient for arbitrage in today’s fast-paced markets.
Automation and advanced tools are essential to thrive in this competitive space.
Prediction Market Trading Bot in Python (Polymarket API step by step)
How Bots Automate Polymarket Arbitrage
Bots have transformed arbitrage into an automated and efficient process, removing the guesswork and emotional pitfalls that often hinder manual trading. By leveraging Polymarket's Central Limit Order Book (CLOB) API, bots constantly pull real-time data, scanning for price discrepancies every second. When the combined cost of YES and NO shares drops below $1.00, the bot springs into action, executing both sides of the trade using Fill-or-Kill (FOK) orders. These orders ensure the trade either completes at the quoted price or is canceled entirely, avoiding issues like partial fills or slippage.
"Polymarket arbitrage is mechanical. If you execute it correctly and repeatedly, the edge already exists."
– DevSphere, Coding Nexus
"Polymarket arbitrage is mechanical. If you execute it correctly and repeatedly, the edge already exists."
– DevSphere, Coding Nexus
Bots don’t just operate quickly - they also analyze hundreds of markets at once. For example, in sports arbitrage, bots pull odds from "sharp" sportsbooks via APIs, strip out the house edge to calculate true probabilities, and flag opportunities that offer positive Expected Value (+EV). Some advanced systems even use Large Language Models (LLMs) to uncover Combinatorial Arbitrage, identifying logical connections between related markets, like linking a national election's outcome to a specific state's result.
Benefits of Bot-Driven Arbitrage
Automated arbitrage offers a range of advantages, with scale and consistency being the most notable. Unlike human traders, bots can monitor markets around the clock without fatigue, reacting to price changes in milliseconds. For instance, a bot targeting Polymarket's BTC-15m market once turned a $200 deposit into $764 profit in a single day. Another trader, @defiance_cr, developed an automated system that peaked at $700–$800 daily, by calculating volatility and placing orders based on risk-adjusted returns.
Bots also sidestep the emotional delays that often trip up manual traders. They use the Kelly Criterion to dynamically adjust stake sizes, optimizing capital allocation while avoiding over-betting. During high-volatility events, bots can exploit price differences of 5–10% between platforms, though these opportunities typically vanish within 15–30 minutes.
Technical Process Behind Polymarket Bots
The efficiency of these bots lies in their precise execution process. It starts with real-time data ingestion. By analyzing API data, bots calculate the "pair cost" (avg_YES + avg_NO). If the combined cost is less than $1.00, the bot identifies a risk-free profit opportunity. For cross-platform arbitrage, bots normalize prices from different sources into a standard 0.00–1.00 probability format to uncover discrepancies.
Once an opportunity is flagged, the bot executes trades using FOK orders to ensure both sides of the trade are completed simultaneously at the quoted prices. In one example from December 2025, a bot named "gabagool" purchased 1,266.72 YES shares at an average price of $0.517 and 1,294.98 NO shares at $0.449 in a 15-minute Bitcoin market. The combined cost of $0.966 for a guaranteed $1.00 payout led to a profit of $58.52 in that single instance.
"He never needs to guess direction. He simply waits, identifies cheapness, and adds to his position while keeping his averages in check."
– Michal Stefanow, CoinsBench
"He never needs to guess direction. He simply waits, identifies cheapness, and adds to his position while keeping his averages in check."
– Michal Stefanow, CoinsBench
Advanced bots also manage execution risks effectively. Using Python-based threading, they handle multiple markets simultaneously, track active trades, and maintain price history. They also employ thread-safe state management to minimize errors and protect against slippage. Since Polymarket imposes a 2% fee on profitable outcomes, bots must target arbitrage spreads of at least 2.5–3% to ensure profitability after fees and Polygon network gas costs.
Sportsbooks: Why Manual Trading Falls Short
Relying on manual trading in sportsbooks today feels like using a flip phone in the age of smartphones - simply outdated. Bots now dominate the arbitrage scene, executing trades in under 200 milliseconds (and as fast as 20 milliseconds on high-speed networks). Meanwhile, manual traders take precious seconds - or even minutes - to identify, verify, and execute a trade. By the time a human spots a price gap and attempts to act, the opportunity is often long gone. Automated systems thrive on these fleeting moments, while manual methods struggle to keep up.
"Manual trading on Polymarket is a knife-fight with latency."
– Alea Research
"Manual trading on Polymarket is a knife-fight with latency."
– Alea Research
The numbers back this up. Bots drive around 86% of cryptocurrency trading volume, with arbitrage bots alone accounting for roughly 12% of total market activity. On Polymarket, only 0.51% of users have managed to earn over $1,000 in profits. These figures highlight a harsh reality: manual traders can’t compete with bots that work tirelessly, make split-second decisions, and process data at speeds far beyond human capability. This lag doesn’t just slow down trade execution - it amplifies the risks inherent in manual trading.
Common Problems with Manual Trading
One major flaw of manual trading is the delay in response time. Bots can monitor over 75 exchanges or sportsbooks at once, analyzing hundreds of trading pairs in real-time. A human, on the other hand, might track a handful of markets while juggling calculations for probabilities, fees, and resolution criteria. When market conditions shift - say, due to breaking news - bots instantly adjust their strategies, leaving manual traders scrambling to catch up.
On top of that, emotional biases often cloud judgment. For example, manual traders might sell contracts too early - say at $0.997 instead of holding out for the full $1.00 settlement - due to impatience or nervousness. This hesitation leaves profits on the table for bots and large-scale traders ("whales") to scoop up. In arbitrage, where profit margins are razor-thin (typically 0.1% to 2% before fees), even a small misstep or overlooked fee can turn a potential gain into a loss.
Modern arbitrage strategies also demand a level of complexity that manual trading simply can’t handle. Strategies involving multiple asset conversions require precise calculations and near-instant execution, which are far beyond human capability. As Volodymyr Huz, founder of 5hz.io, aptly described it:
"Manual trading [is] comparable to bringing a calculator to a Formula 1 race."
– Volodymyr Huz
"Manual trading [is] comparable to bringing a calculator to a Formula 1 race."
– Volodymyr Huz
Cryptocurrency Exchanges: Liquidity and Price Volatility Issues
Cryptocurrency exchanges operate in a vastly different environment compared to platforms like Polymarket. While Polymarket’s liquidity is mostly driven by retail traders, crypto exchanges depend heavily on institutional participants. This creates unique challenges for each. Polymarket struggles with fragmented liquidity, whereas crypto exchanges face issues like uneven liquidity depth and sharp price swings. On these exchanges, even slight price changes can quickly turn a potentially profitable trade into a losing one.
Unlike major crypto exchanges that rely on institutional-grade market makers deploying millions of dollars, Polymarket’s liquidity comes from individual traders and small-scale bots. As @defiance_cr, a developer of liquidity bots, explains:
"The space is less mature compared to traditional crypto markets. In DeFi, you have sophisticated market makers with millions in capital. On Polymarket, it's mostly individual traders clicking buttons."
"The space is less mature compared to traditional crypto markets. In DeFi, you have sophisticated market makers with millions in capital. On Polymarket, it's mostly individual traders clicking buttons."
This difference creates notable execution challenges. For instance, in highly liquid markets like the NBA Championship on Polymarket, trades worth tens of thousands of dollars can be executed without much price impact. But in smaller, niche markets, spreads can be as wide as 34 cents, leading to losses of up to 50% when exiting a position. On the other hand, while crypto exchanges generally offer deeper liquidity, they’re not without risks. Price volatility and execution delays can significantly affect trade outcomes.
How Liquidity Affects Arbitrage Trades
Liquidity plays a key role in determining the success of arbitrage trades. A trade promising a 5% profit can quickly become unprofitable if the order book lacks the depth to support the trade size. In thin markets, executing large trades can cause slippage, wiping out the arbitrage margin before the trade is even completed. On Polymarket, traders need minimum spreads of 3.0% for $100 trades, 2.5% for $500 trades, and 2.2% for trades over $1,000 just to cover the 2% winner fee, gas costs, and slippage. Professional traders often size their positions based on the smaller side of the order book to avoid driving prices into unprofitable territory.
NEVER MISS A TRADE
Your algos run 24/7
even while you sleep.
99.999% uptime • Chicago, New York & London data centers • From $59.99/mo
In low-liquidity markets, partial fills can create additional risks. If one leg of the trade is left unhedged, a supposedly risk-free arbitrage can transform into a directional bet.
Managing Volatility Risks
Price volatility adds another layer of complexity to arbitrage trading. Markets can shift in the time it takes to detect and execute a trade, and this risk grows exponentially with multi-leg arbitrage. During high-volatility news events, arbitrage opportunities might only last 30 to 60 seconds, and even a one-second delay can be the difference between profit and loss.
"Slippage Kills Small Edges: Markets move between when you identify the opportunity and when your trades execute. With multiple legs to an arbitrage trade, this risk compounds." – PolyMaster
"Slippage Kills Small Edges: Markets move between when you identify the opportunity and when your trades execute. With multiple legs to an arbitrage trade, this risk compounds." – PolyMaster
To mitigate these risks, experienced traders use advanced tools and strategies. High-performance bots, often written in Rust, enable simultaneous execution of all trade legs with sub-millisecond latency. Techniques like delta-neutral hedging - pairing a prediction market position with an offsetting futures contract on a crypto exchange - help minimize directional risk. Additionally, circuit breakers can automatically halt trading if losses exceed preset limits or if multiple execution errors occur in a row.
Infrastructure matters too. While gas fees on Polymarket’s Polygon network are usually just fractions of a cent, they can spike to $0.50–$1.00 during periods of network congestion on crypto exchanges. These spikes can render small-margin trades unprofitable.
Ultimately, success in arbitrage trading isn’t just about spotting price gaps. It requires robust automation and infrastructure to execute trades faster than the market can react. Without these tools, even the most promising opportunities can slip away.
Bots vs Sportsbooks: Speed and Execution Performance
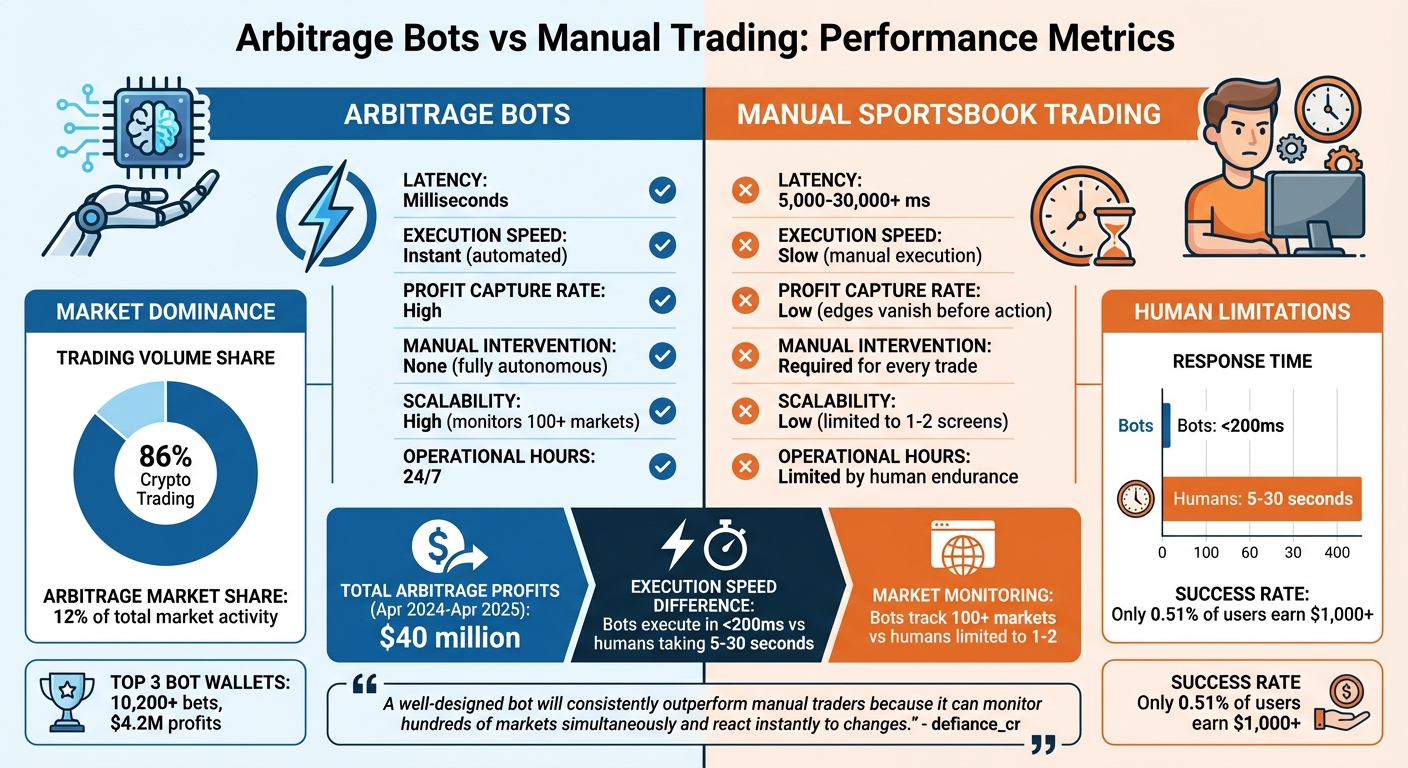
Bots vs Manual Trading Performance Comparison in Polymarket Arbitrage
Bots vs Manual Trading Performance Comparison in Polymarket Arbitrage
On Polymarket, arbitrage opportunities disappear in a flash - literally within seconds. For manual traders, the process of spotting, calculating, and acting on these opportunities takes several seconds. That delay often means missing out entirely. Bots, on the other hand, operate at lightning speed, detecting and executing trades in just milliseconds. This speed isn’t just an advantage - it’s the key to profiting from fleeting market inefficiencies, as VPS latency impacts algorithmic trading profitability directly.
From April 2024 to April 2025, arbitrageurs pulled in around $40 million from Polymarket, analyzing 86 million bets along the way. Among these, the top three wallets - distinguished by their bot-like efficiency - placed over 10,200 bets and raked in $4.2 million in profits. As defiance_cr, an automated market maker, put it:
"A well-designed bot will consistently outperform manual traders because it can monitor hundreds of markets simultaneously and react instantly to changes."
"A well-designed bot will consistently outperform manual traders because it can monitor hundreds of markets simultaneously and react instantly to changes."
This stark contrast highlights why bots dominate sportsbook arbitrage. Manual trading simply can’t keep up. Bots can scan hundreds of markets and execute trades in under 100 milliseconds, while humans take anywhere from 5 to 30 seconds to process and act. In arbitrage, where prices shift constantly, that kind of delay is a dealbreaker.
Performance Comparison: Bots vs Sportsbooks
| Metric | Arbitrage Bots | Manual Sportsbook Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Milliseconds | 5,000–30,000+ ms |
| Execution Speed | Instant (automated) | Slow (manual execution) |
| Profit Capture Rate | High | Low (edges vanish before action) |
| Manual Intervention | None (fully autonomous) | Required for every trade |
| Scalability | High (monitors 100+ markets) | Low (limited to 1–2 screens) |
| Operational Hours | 24/7 | Limited by human endurance |
These numbers make it clear: bots have a distinct edge over manual methods. One standout advantage is scalability. To put it in perspective, executing just 50 trades on Polymarket places a user ahead of 77% of the platform’s user base. Bots, however, can handle thousands of trades, locking in small but steady profits that humans simply can’t match.
Arbitrage isn’t about predicting outcomes - it’s all about math. And in this numbers game, bots excel. They don’t get tired, hesitate, or miss opportunities. For manual traders, the odds of competing with these tireless systems are slim.
Bots vs Exchanges: Opportunity Detection and Risk Management
When it comes to identifying arbitrage opportunities, bots and manual traders have very different approaches. Bots use APIs to pull real-time data, scanning the Central Limit Order Book (CLOB) in milliseconds to spot pricing mismatches. Manual traders, however, rely on visually comparing data across a few screens, a process that takes several seconds - often too slow to capitalize on fleeting opportunities. This speed advantage, often achieved through a VPS for Polymarket, allows bots to detect opportunities and set the stage for automated risk management.
The mechanics of bot-driven arbitrage are straightforward. Bots calculate the "Pair Cost" (the sum of the average YES price and average NO price) and execute trades only when this total is below $1.00. This ensures a guaranteed profit, no matter the outcome. On the other hand, manual traders must perform separate calculations and place sequential orders, which exposes them to potential price changes and execution errors. This precision in calculation gives bots a clear advantage in fast-moving exchange environments.
Where bots truly excel is in risk management. They use Fill-or-Kill (FOK) orders to execute both legs of a trade simultaneously, factoring in the 2% winner fee and gas costs to ensure profitability after all expenses. This eliminates the risk of partial fills on exchanges. Manual traders, however, often overlook these additional costs until after the trade, which can erode profitability.
Another key difference is scalability. While manual traders can only monitor a handful of markets at a time, bots can track hundreds simultaneously, reacting to pricing discrepancies across platforms like Polymarket and Kalshi in real time. Analyst Jeremy Whittaker aptly described this dynamic:
"Arbitrage on Polymarket is not gambling, but engineering. Here, you earn not on predictions, but on the inefficiency of the system itself."
"Arbitrage on Polymarket is not gambling, but engineering. Here, you earn not on predictions, but on the inefficiency of the system itself."
Performance Comparison: Bots vs Exchanges
| Metric | Arbitrage Bots | Cryptocurrency Exchanges (Manual) |
|---|---|---|
| Price Discrepancy Detection | Real-time (API-driven) | Manual (visual/delayed) |
| Multi-Market Monitoring | Yes (hundreds of markets) | No (limited to 1–2 markets) |
| Risk-Free Profit Potential | 1–3% per cycle | Highly variable (directional betting) |
| Capital Efficiency | High (automated recycling) | Low (manual execution lag) |
| Regulatory Exposure | Low (private scripts) | High (KYC/AML compliance) |
| Execution Method | Programmatic (simultaneous legs) | Manual (one leg at a time) |
These differences highlight why automated systems have a distinct edge in exchange arbitrage, offering faster detection, better risk management, and greater scalability.
Arbitrage Opportunities: Polymarket vs. Kalshi and Limitless
Arbitrage opportunities pop up when the same event is priced differently across platforms. These differences often stem from variations in user bases and regulatory environments. For example, Polymarket caters to a global audience of crypto-savvy traders using USDC, while Kalshi focuses exclusively on U.S.-based, regulated users transacting in USD. These contrasting ecosystems can lead to pricing gaps, especially in fast-moving, short-term markets.
Short-duration crypto markets are particularly ripe for arbitrage. Take the case of a developer known as 0xalberto, who deployed a bot between December 21 and 22, 2025, to trade Bitcoin 15-minute "Up/Down" contracts on Polymarket. In just one day, this bot generated $764 in profit by executing automated trades across multiple windows. These rapid markets are constantly shifting due to changing sentiment, creating frequent opportunities for traders who can act quickly.
Political and economic events also create pricing discrepancies. For instance, in September 2025, ArbBets spotted a +3.09% arbitrage opportunity involving James Talarico's potential nomination as the Democratic Senate candidate in Texas. Kalshi priced the likelihood at 38%, while Polymarket had it at 59%. Polymarket’s high liquidity enables fast price discovery, but during sudden market changes, its pricing can temporarily lag behind Kalshi. These event-driven mismatches highlight the need for precise execution strategies and careful management of fees.
Speaking of fees, they play a huge role in determining whether an arbitrage trade is profitable. Polymarket charges no fees, while Kalshi calculates fees using the formula: ceil(0.07 × contracts × price × (1 – price)). Limitless, leveraging blockchain infrastructure, offers some of the lowest fees in the game. Managing these costs is critical for ensuring a positive net outcome.
Execution methods are equally important. In volatile or thin markets, executing both legs of a trade almost simultaneously is key to minimizing slippage. However, this type of arbitrage isn't atomic - one leg of the trade could succeed while the other fails. To reduce this risk, savvy traders often use limit orders to set maximum acceptable prices for each leg, helping to avoid excessive slippage.
Running Arbitrage Bots on QuantVPS Infrastructure
QuantVPS takes bot-driven arbitrage to the next level by combining unmatched speed and reliable performance, giving traders a distinct advantage in fast-paced markets.
Why QuantVPS Works for Arbitrage Trading
When it comes to cross-market arbitrage, speed is everything. QuantVPS offers 0.52ms latency to CME matching engines in Chicago and sub-1ms execution to major crypto exchanges. This ultra-low latency is essential since arbitrage opportunities often vanish in milliseconds, as competitors' bots scramble to exploit fleeting price differences.
The platform operates on enterprise-grade hardware, ensuring it can handle the heavy data processing required to monitor multiple order books across platforms like Polymarket, Kalshi, and major crypto exchanges. Servers are strategically positioned near key financial hubs, minimizing data travel time and giving your bot a crucial edge in executing complex, multi-leg trades. With an impressive 99.999% uptime, your bot stays active and responsive, even during volatile market conditions.
"QuantVPS revolutionized my trading experience. The low-latency servers are lightning-fast, allowing me to execute trades with precision and speed." – Smutchings
STOP LOSING TO LATENCY
Execute faster than
your competition.
Sub-millisecond execution • Direct exchange connectivity • From $59.99/mo
"QuantVPS revolutionized my trading experience. The low-latency servers are lightning-fast, allowing me to execute trades with precision and speed." – Smutchings
QuantVPS supports popular exchanges such as Binance, Kraken, and Coinbase Pro, making it easier to implement cross-market strategies involving these platforms and Polymarket. The platform's reliability is evidenced by its ability to handle massive trading volumes - over $100 billion was traded on QuantVPS servers in just one week in late 2025. This infrastructure ensures that your bot operates efficiently, even under intense market activity.
Step-by-Step Bot Setup on QuantVPS
To get started, install Python 3.9+ and Node.js 18+ on your QuantVPS instance, as these are essential for running most Polymarket arbitrage bots. Clone your bot's repository and install the required dependencies using pip install -r requirements.txt for Python and npm install for the dashboard setup.
Next, create a .env file to securely store sensitive information like your wallet's private key, Polymarket proxy wallet address, and USDC contract details. In the bot’s configuration file, define key trading parameters such as:
-
trade_unit: The size of your USDC position -
slippage_tolerance: Typically set to 0.02 -
spike_threshold: A value to identify price spikes
Ensure your arbitrage spread is at least 2.5–3% to account for fees and gas costs.
Deploy the bot using a process manager like PM2 or run it in a persistent screen session (e.g., python main.py) to keep it operational. Configure API keys for Polymarket's CLOB and your counter-party exchange, then launch the backend API and frontend dashboard to monitor price discrepancies in real time. To stay agile during market fluctuations, reserve 20–30% of your capital in liquid assets, allowing you to quickly act on sudden volatility.
Risks and Challenges in Cross-Market Arbitrage
Cross-market arbitrage might sound straightforward - buy low in one market, sell high in another - but the process is far from simple in practice. While automation and bots can enhance speed and efficiency, they don’t eliminate risks. Traders still face hurdles like regulatory oversight, technical glitches, and market unpredictability, any of which can turn a seemingly risk-free trade into a costly mistake. These operational challenges are further complicated by intricate legal and regulatory frameworks.
Regulatory and Legal Factors
The regulatory environment surrounding cross-market arbitrage is anything but straightforward. For example, sports betting in the United States is governed by a patchwork of state-specific laws. Meanwhile, platforms like Polymarket and Kalshi fall under the jurisdiction of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). A notable case occurred in December 2025, when Polymarket resumed operations in the U.S. after resolving earlier regulatory issues. This quick turnaround underscores how rapidly the legal landscape can shift.
Regulators are particularly vigilant about distinguishing lawful arbitrage from manipulative practices. In December 2021, a global bank faced $35 million in fines and restitution for manipulating U.S. Treasury securities and futures markets. Similarly, in 2018, the CFTC fined a firm and an individual $2.3 million for spoof trading in copper futures on COMEX, which was designed to influence prices on the London Metal Exchange (LME). These examples make it clear: while arbitrage itself is legal, using trades on one platform to manipulate prices on another crosses ethical and legal boundaries.
Tax compliance is another significant challenge. Frequent trades often lead to numerous taxable events, which can quickly eat into the already slim profit margins of 1% to 5%. Add transaction costs like trading fees, withdrawal charges, and gas fees into the mix, and the narrow edge that makes arbitrage attractive can vanish. Traders should also be cautious about platform policies, as many sportsbooks penalize or restrict accounts suspected of engaging in arbitrage.
Technical and Execution Risks
Even if regulatory hurdles are managed, technical execution presents its own set of risks. Timing is everything in multi-leg arbitrage, and even a millisecond delay can turn a profitable trade into a loss. A case in point: in December 2025, a developer named 0xalberto created a Polymarket arbitrage bot that earned $764 in a single day from a $200 deposit on the BTC 15-minute market. However, when the bot was expanded to trade across multiple markets (BTC, ETH, SOL, and XRP), instability led to losses, forcing a retreat to single-market strategies.
"Execution timing errors plague multi-leg arbitrage. You identify an opportunity, buy the first leg, then discover the other side has moved against you while you were executing." – AL, Founder of PolyTrack
"Execution timing errors plague multi-leg arbitrage. You identify an opportunity, buy the first leg, then discover the other side has moved against you while you were executing." – AL, Founder of PolyTrack
Prediction markets are fiercely competitive, with high-speed trading systems dominating the space. Being even a second slower than competitors can cost traders valuable opportunities. Slippage is another concern; attempting larger trades than the order book can handle may erode profits. Additionally, network congestion can spike gas fees, further eating into already thin margins.
To mitigate these risks, traders should carefully check order book depth before placing larger trades and configure their bots with strict slippage limits to cancel orders if prices move beyond acceptable levels. Even flawless execution doesn’t guarantee smooth sailing - disputes over market resolutions, often handled through arbitration processes like UMA oracles, can tie up capital for days or weeks, creating opportunity costs that may outweigh the initial profit.
Conclusion
Cross-market arbitrage on Polymarket isn’t about instinct or guesswork - it’s all about precision and leveraging technology. The numbers tell the story: only 0.51% of Polymarket users manage to achieve profits exceeding $1,000, and those who do depend heavily on automation to make it happen. Research highlights that around $40 million has been earned through arbitrage across 86 million bets, with automated systems responsible for the bulk of these gains.
Here’s why automation matters: bots can execute trades in under 200 milliseconds, while manual traders often miss fleeting opportunities. Even a delay of just 50–100 milliseconds can mean the difference between profit and loss when dealing with spreads of 1–3%.
To overcome these hurdles, using the best VPS for algorithmic trading infrastructure provides a clear path forward. Starting at $59.99/month (or $41.99/month when billed annually), the VPS Lite plan offers low latency, 24/7 reliability, and the processing power needed to track hundreds of markets at once. For more demanding operations, the VPS Pro plan at $99.99/month (or $69.99/month billed annually) delivers 6 cores and 16GB of RAM - more than enough for most arbitrage setups.
The importance of automation becomes even clearer when you consider that bots now account for 86% of crypto trading volume, with arbitrage bots capturing roughly 12% of that. Advanced bots, especially those running on optimized infrastructure, can generate monthly returns of 7–12%, compared to the 3–5% returns from basic setups. This combination of speed, reliability, and robust infrastructure underscores the critical role automation plays in modern arbitrage trading.
For serious traders, the message is clear: automate your trades, minimize delays, and invest in professional-grade infrastructure. The results speak for themselves - automation has driven multimillion-dollar profits. The question isn’t whether automation works; it’s whether you’re ready to harness its potential and stay ahead of the competition.
FAQs
Why are bots more effective than manual trading for Polymarket arbitrage?
Bots have a clear edge in Polymarket arbitrage because they can track multiple markets - like Polymarket contracts and external sportsbooks or exchanges - in real-time. They’re designed to spot price differences instantly and execute trades within milliseconds, taking advantage of opportunities that human traders simply can’t react to quickly enough. Plus, bots don’t need breaks - they run 24/7 without tiring, maintaining consistent performance around the clock.
Their speed and automation give bots the upper hand in capturing short-lived arbitrage opportunities far faster than any manual trader could. By eliminating delays and reducing human error, bots dominate this space, leaving manual traders at a significant disadvantage. For anyone aiming to profit from cross-market price gaps, automation isn’t just helpful - it’s practically essential.
How does using QuantVPS improve arbitrage trading on Polymarket?
A solid infrastructure, like QuantVPS, plays a crucial role in arbitrage trading. It keeps your trading bots running around the clock, ensures they respond within milliseconds, and handles the non-stop data crunching needed to spot price differences across platforms like Polymarket, sportsbooks, and exchanges. With its low latency and high uptime, QuantVPS helps reduce missed opportunities and slippage, giving your bots the speed and reliability to capitalize on market inefficiencies instantly.
On top of that, QuantVPS offers a secure space to store your API keys while allowing you to scale operations as you expand into more markets. By providing the speed, security, and reliability essential for fast-paced prediction markets, QuantVPS transforms your arbitrage strategy into a streamlined and consistent trading powerhouse.
What are the key risks of using cross-market arbitrage on Polymarket?
Cross-market arbitrage on Polymarket can offer profit potential, but it’s not without its challenges. One of the biggest obstacles is the presence of high-frequency trading bots. These bots operate at lightning speed, executing trades in milliseconds. For manual traders or those using slower automated systems, it’s tough to compete, often resulting in missed opportunities or even losses.
Another hurdle is the fleeting nature of arbitrage opportunities. Price differences between markets can vanish almost as quickly as they appear. Any delay - whether from data processing, order execution, or network latency - can turn what looks like a sure win into a costly mistake. On top of that, liquidity issues or sudden market volatility can cause slippage, eating into your profits or wiping them out entirely.
Lastly, there’s the technical complexity of executing these trades. From miscalculations to unexpected transaction fees or software glitches, even small errors can undermine your efforts. Before jumping into cross-market arbitrage, traders need to carefully assess these risks and ensure their strategies and tools are up to the task.
Bots have a clear edge in Polymarket arbitrage because they can track multiple markets - like Polymarket contracts and external sportsbooks or exchanges - in real-time. They’re designed to spot price differences instantly and execute trades within milliseconds, taking advantage of opportunities that human traders simply can’t react to quickly enough. Plus, bots don’t need breaks - they run 24/7 without tiring, maintaining consistent performance around the clock.
Their speed and automation give bots the upper hand in capturing short-lived arbitrage opportunities far faster than any manual trader could. By eliminating delays and reducing human error, bots dominate this space, leaving manual traders at a significant disadvantage. For anyone aiming to profit from cross-market price gaps, automation isn’t just helpful - it’s practically essential.
A solid infrastructure, like QuantVPS, plays a crucial role in arbitrage trading. It keeps your trading bots running around the clock, ensures they respond within milliseconds, and handles the non-stop data crunching needed to spot price differences across platforms like Polymarket, sportsbooks, and exchanges. With its low latency and high uptime, QuantVPS helps reduce missed opportunities and slippage, giving your bots the speed and reliability to capitalize on market inefficiencies instantly.
On top of that, QuantVPS offers a secure space to store your API keys while allowing you to scale operations as you expand into more markets. By providing the speed, security, and reliability essential for fast-paced prediction markets, QuantVPS transforms your arbitrage strategy into a streamlined and consistent trading powerhouse.
Cross-market arbitrage on Polymarket can offer profit potential, but it’s not without its challenges. One of the biggest obstacles is the presence of high-frequency trading bots. These bots operate at lightning speed, executing trades in milliseconds. For manual traders or those using slower automated systems, it’s tough to compete, often resulting in missed opportunities or even losses.
Another hurdle is the fleeting nature of arbitrage opportunities. Price differences between markets can vanish almost as quickly as they appear. Any delay - whether from data processing, order execution, or network latency - can turn what looks like a sure win into a costly mistake. On top of that, liquidity issues or sudden market volatility can cause slippage, eating into your profits or wiping them out entirely.
Lastly, there’s the technical complexity of executing these trades. From miscalculations to unexpected transaction fees or software glitches, even small errors can undermine your efforts. Before jumping into cross-market arbitrage, traders need to carefully assess these risks and ensure their strategies and tools are up to the task.
"}}]}




