Polymarket HFT: How Traders Use AI to Identify Arbitrage and Mispricing
Polymarket, a decentralized prediction market, offers traders opportunities to profit from pricing inefficiencies caused by independent order books and retail-driven volatility. Between April 2024 and April 2025, traders earned an estimated $40 million using strategies like market rebalancing and combinatorial arbitrage. These strategies exploit mismatched probabilities or inconsistencies between related markets.
High-frequency trading (HFT) tools powered by AI have become essential for success. AI systems analyze thousands of markets in real-time, detect pricing gaps, and execute trades faster than manual methods. Traders also use low-latency VPS for algorithmic trading to minimize delays, ensuring trades execute within milliseconds. Key strategies include:
- Market Rebalancing Arbitrage: Profiting from markets where probabilities deviate from $1.00.
- Combinatorial Arbitrage: Identifying mispricings across logically related markets.
- Tail-End Trading: Exploiting near-certain outcomes in markets close to resolution.
Speed and automation are crucial. AI tools like Mistral-7B and trading bots enable traders to execute multi-leg trades efficiently while managing risks. With spreads needing to exceed 2.5–3% to remain profitable after fees, precision and infrastructure are critical for consistent gains.
How Polymarket's Market Structure Creates Pricing Inefficiencies
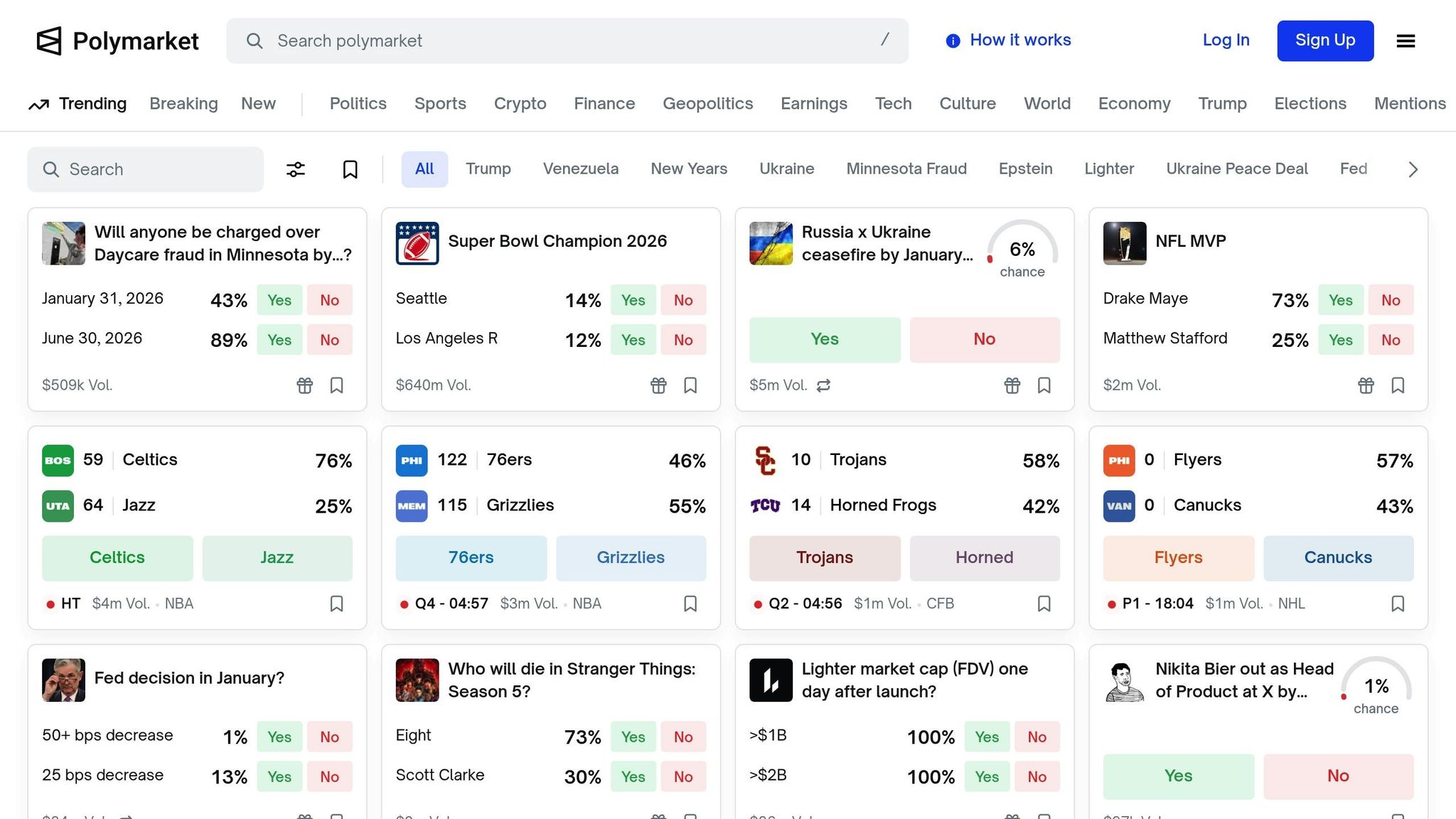
Binary Outcomes and Independent Order Books
Polymarket uses a Central Limit Order Book (CLOB) system on the Polygon blockchain, where each outcome - YES or NO - has its own separate order book. In this setup, the prices of YES and NO should always add up to exactly $1.00. For instance, if YES is priced at $0.48 and NO at $0.50, the total is $0.98. Buying both outcomes guarantees a $1.00 payout, resulting in a $0.02 profit per share. This pricing mismatch highlights the arbitrage opportunities unique to Polymarket's structure.
Retail Trading and Misaligned Probabilities
Polymarket's decentralized nature draws a large number of retail traders, many of whom base their decisions on breaking news or social media trends. These traders often act emotionally or with a delay, causing price swings that can violate the "unity constraint" - where the combined probabilities of outcomes stray from $1.00. Since Polymarket charges a 2% fee on profitable outcomes, arbitrage opportunities generally need spreads exceeding 2.5% to 3% to remain worthwhile after factoring in fees and gas costs.
Why Market Inefficiencies Disappear Quickly
Although these mispricings arise from independent order books and retail-driven volatility, they are short-lived. High-frequency trading bots closely monitor markets and execute trades in milliseconds. During major news events, emotional trading may create a brief 30–60 second window where prices deviate before automated systems restore balance.
"Arbitrage on Polymarket is not gambling, but engineering. Here, you earn not on predictions, but on the inefficiency of the system itself."
– Jeremy Whittaker, Analyst
"Arbitrage on Polymarket is not gambling, but engineering. Here, you earn not on predictions, but on the inefficiency of the system itself."
– Jeremy Whittaker, Analyst
Speed is everything. Traders equipped with advanced natural language processing (NLP) tools scan platforms like Twitter and Telegram to detect sentiment changes and act before retail traders can respond. This split-second advantage explains why only 0.5% of Polymarket users have managed to earn over $1,000 in profit.
Prediction Market Trading Bot in Python (Polymarket API step by step)
Building a custom bot requires a stack of algorithmic trading tools to handle data ingestion and execution. Before deploying to Polymarket, it is essential to validate your logic using Python backtesting libraries to simulate historical performance.
3 Types of Arbitrage Opportunities on Polymarket
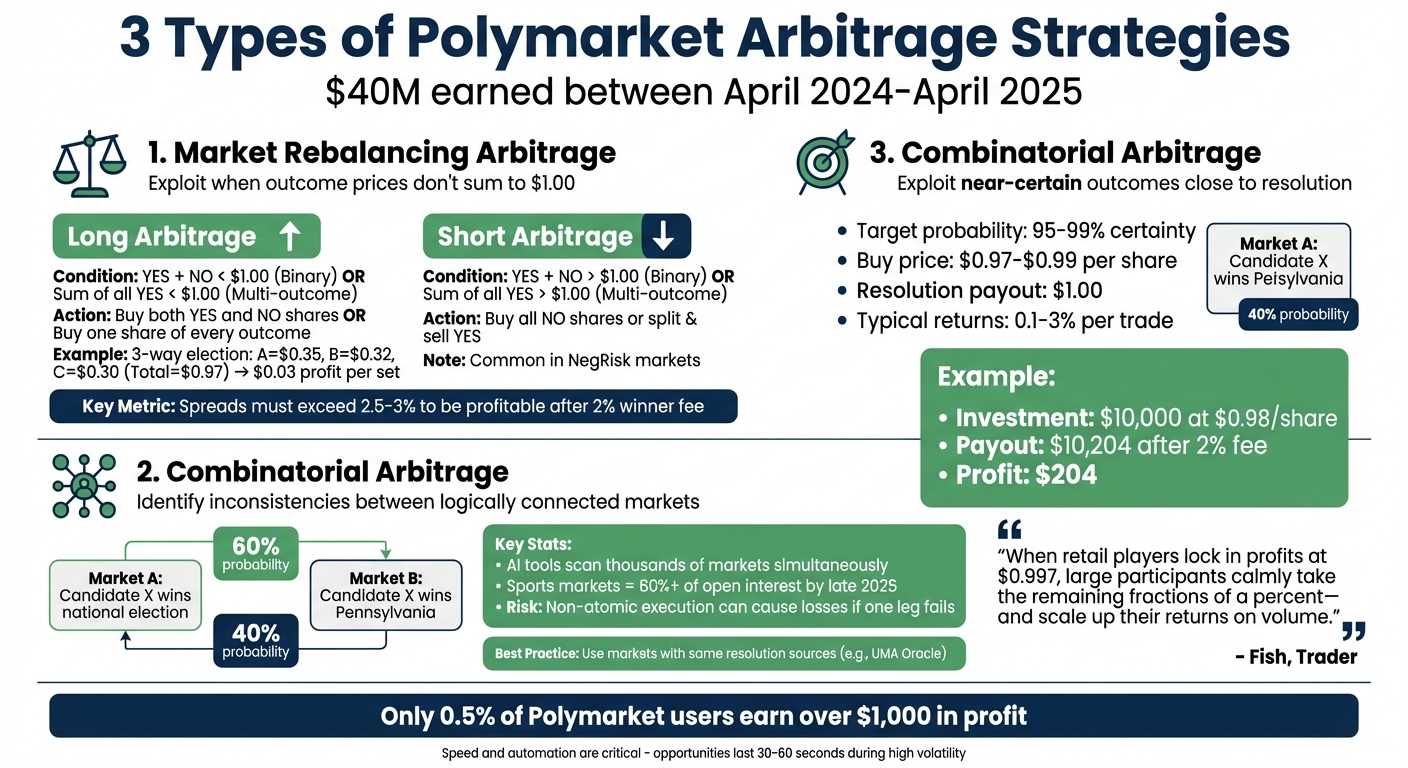
Polymarket Arbitrage Types: Market Conditions and Trading Actions
Polymarket Arbitrage Types: Market Conditions and Trading Actions
Polymarket's setup presents three key strategies for arbitrage, each designed to take advantage of pricing inefficiencies.
Market Rebalancing Arbitrage
This strategy focuses on situations where the total price of all outcomes in a market doesn't add up to exactly $1.00. Here's how it works:
- Long Arbitrage: If the combined price of all "YES" shares is less than $1.00, a trader can buy one share of every outcome to guarantee a $1.00 payout. For example, in a three-way election market (Candidate A: $0.35, B: $0.32, C: $0.30), the total is $0.97. This creates a $0.03 profit per set.
- Short Arbitrage: When the total price exceeds $1.00, traders can buy all "NO" shares or use a "position split" to mint a full set for $1.00 and sell the overpriced "YES" shares. These opportunities are particularly common in NegRisk markets, where only one outcome can win.
Between April 2024 and April 2025, traders earned an estimated $40 million from rebalancing arbitrage. However, Polymarket's 2% winner fee means that spreads must exceed 2% to be profitable. Typically, spreads of 2.5% to 3% are needed to account for fees.
| Arbitrage Type | Market Condition | Trader Action |
|---|---|---|
| Long (Binary) | YES + NO < $1.00 | Buy both YES and NO shares |
| Long (Multi-Outcome) | Sum of all YES < $1.00 | Buy one share of every outcome |
| Short (Binary) | YES + NO > $1.00 | Buy all NO shares or split & sell YES |
| Short (Multi-Outcome) | Sum of all YES > $1.00 | Buy all NO positions |
Traders also capitalize on price differences across related markets, as discussed below.
Combinatorial Arbitrage Across Markets
This approach identifies inconsistencies between logically connected markets. For instance, if one market predicts Candidate X has a 60% chance of winning a national election but another gives only a 40% chance of winning a key state like Pennsylvania, the mismatch signals an opportunity. Traders use AI tools to scan thousands of markets for these discrepancies, as manually comparing them is inefficient. By late 2025, sports markets made up over 60% of Polymarket's open interest, creating new arbitrage opportunities between game winner and point spread markets.
One challenge here is non-atomic execution. If one leg of the trade executes while the other doesn't due to price changes or liquidity issues, it can lead to losses. To reduce this risk, traders should ensure the markets they compare use the same resolution sources, like the UMA Oracle, to avoid discrepancies.
Tail-End Trading Strategies
Tail-end trading focuses on markets nearing resolution, where outcomes are almost certain (usually between 95% and 99% probability). Traders buy shares priced between $0.97 and $0.99 and hold them until the market resolves at $1.00. This strategy takes advantage of retail traders who often sell early to lock in profits.
"When retail players lock in profits at $0.997, large participants calmly take the remaining fractions of a percent - and scale up their returns on volume."
– Fish, Trader
NEVER MISS A TRADE
Your algos run 24/7
even while you sleep.
99.999% uptime • Chicago, New York, London & Amsterdam data centers • From $59.99/mo
"When retail players lock in profits at $0.997, large participants calmly take the remaining fractions of a percent - and scale up their returns on volume."
– Fish, Trader
The returns on each trade are small, typically 0.1% to 3%, but scaling this across multiple markets can lead to meaningful profits. For example, investing $10,000 at $0.98 per share could yield about $204 upon resolution, even after accounting for Polymarket's 2% fee. These opportunities are short-lived, occurring in the brief window between an event's conclusion and on-chain resolution by the oracle. To avoid disputes erasing gains, traders should stick to markets with clear, verifiable resolution sources, such as official government data or sports results.
Using AI to Detect Arbitrage Opportunities in Real-Time
Tracking thousands of markets simultaneously is a task far beyond human capability. That’s where AI steps in, processing real-time data streams across platforms to uncover pricing discrepancies. In August 2025, researchers Oriol Saguillo, Vahid Ghafouri, Lucianna Kiffer, and Guillermo Suarez-Tangil introduced a groundbreaking methodology using the Linq-Embed-Mistral model. This system categorizes Polymarket topics and identifies logical connections between markets, significantly narrowing the search for arbitrage opportunities by leveraging semantic analysis and temporal patterns. This automated approach sets the stage for a deeper dive into how AI models, data inputs, and speed are reshaping arbitrage trading.
Machine Learning Models for Price and Liquidity Analysis
AI models keep a close eye on Polymarket’s Central Limit Order Book (CLOB), identifying when YES and NO token prices stray from their $1.00 benchmark. Tools like Mistral-7B, Llama-3.2, and DeepSeek are employed to analyze human-generated market descriptions and uncover relationships between seemingly unrelated markets. For instance, the AI can link a "winning margin" market to a "winner" market, uncovering combinatorial arbitrage opportunities that would likely go unnoticed by manual traders.
However, the complexity of comparing every possible market combination creates a significant computational challenge. To tackle this, AI systems use heuristic strategies, focusing on factors like temporal proximity, topical similarity, and combinatorial relationships. This approach has proven effective, with an estimated $40 million in arbitrage profits extracted from Polymarket between April 2024 and April 2025.
Data Inputs for AI Trading Systems
For AI-driven arbitrage systems to perform effectively, they rely on a wide array of data inputs. Real-time order book data via WebSockets helps track YES/NO token prices, liquidity levels, and live trading volumes. Cross-platform analysis compares Polymarket odds with those on external platforms like Kalshi, identifying price gaps for identical events. On-chain metrics, such as Polygon gas prices and MATIC/USD exchange rates, are also factored in to calculate net returns after transaction fees. Additionally, external sentiment feeds - covering polling updates, debate schedules, and economic data releases - offer insights into real-world events that often lag behind price movements on-chain.
In October 2025, Polysights introduced an AI-powered analytics suite that consolidates these diverse data streams. By integrating real-time information with machine-learning models, the platform generates trend indicators and predictive signals across thousands of markets, enabling traders to act with precision and speed.
Speed and Accuracy in AI-Driven Arbitrage
Speed is everything in arbitrage trading. AI systems execute trades in milliseconds, with some operations scaling down to microseconds or even nanoseconds to maintain a competitive edge. The evolution of high-frequency trading has shifted toward "preemptive trading", where AI predicts price movements before they happen, rather than merely reacting to them.
One developer shared their experience using an independent arbitrage bot, reporting average earnings of $25 per hour ($500–$700 per day) from a $200 deposit by leveraging a BTC-15m-updown market strategy. This example highlights how small, consistent profits can add up when scaled across multiple trades. However, even the slightest delays in data processing or trade execution can wipe out these gains, underscoring the importance of precision and speed in high-frequency environments.
Why Low-Latency VPS Infrastructure Matters for Polymarket Trading
Running trading bots from your home computer can lead to unpredictable delays caused by ISP routing, network congestion, or even your hardware entering sleep mode. Choosing a VPS or dedicated server places your trading setup closer to Polymarket's API endpoints. This ensures stable, always-on connectivity - an absolute must in fast-paced markets. This setup isn't just convenient; it's critical when even the smallest delays can erase your trading edge.
How Millisecond Delays Impact Arbitrage Profitability
Polymarket's WebSocket connection provides updates with latency under 50ms, but that advantage is useless if your system can't respond just as quickly. Arbitrage opportunities on prediction markets typically offer returns between 0.5% and 3%, with many closing within seconds. A manual trader recalculating probabilities simply can't keep up, losing any potential edge.
Polymarket arbitrage isn't atomic, meaning even a small delay could leave you with an unhedged position. For perspective, the top Polymarket trader earned $2.01 million across 4,049 transactions, averaging about $496 per trade. These slim margins can vanish with execution delays of just a few hundred milliseconds.
Consider the example of an independent developer, 0xalberto, who earned $764 in a single day (December 21, 2025) using an automated bot on the BTC-15m-updown market with just a $200 deposit. This success relied on stable, always-on infrastructure and the ability to continuously update strategies.
Technical Requirements for VPS Performance
To compete in Polymarket's fast-moving environment, your setup must handle real-time data streams across 100+ markets simultaneously. Every part of your system needs to prioritize speed and efficiency. You can configure a trading VPS to meet these specific hardware demands.
Here’s what you’ll need:
- A multi-core processor and plenty of RAM to handle high-throughput WebSocket data.
- High-speed network connectivity to reduce jitter.
- High-performance WebSocket clients, often built with languages like Rust, to process data efficiently.
- Pre-set wallet allowances for Polymarket's smart contracts (USDC and CTF) to avoid errors during automated trading.
| Feature | Local Connection | Trading VPS |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Prone to ISP routing delays | Millisecond-level response times |
| Uptime | Vulnerable to ISP issues | 24/7 reliability |
| Execution | Manual or basic automation | High-frequency, multi-threaded |
| Market Access | Limited by bandwidth | Monitors 100+ markets simultaneously |
These specifications ensure your system operates without interruptions and responds quickly to market changes.
Benefits of Always-On VPS Execution
A VPS operates around the clock, capturing opportunities even during off-hours when a home system might be offline. This is crucial because 75% of matched orders on Polymarket are executed within roughly one hour, and initial matching in the Central Limit Order Book (CLOB) often demands sub-second reaction times. If your bot isn't active when a mispricing arises, you’ve already missed the chance.
With a VPS, you get consistent low-latency routing and 24/7 uptime. Store API credentials securely using environment variables, and when executing arbitrage, apply strict timeouts (under five seconds) to cancel unfilled legs and reduce exposure from partial fills. Keep in mind, Polymarket charges a 2% winner fee, so your arbitrage spread needs to exceed 2.5–3% to stay profitable after fees and potential gas costs.
Execution Strategies and Risk Management for Polymarket HFT
Order Placement Timing and Position Sizing
High-volatility events - like breaking news, economic data releases, or scheduled announcements - open 30–60 second windows where prices deviate significantly from equilibrium. These brief moments are prime opportunities for entry, but they don’t last long.
When deciding your position size, focus on the order book depth, not your profit targets. Always assess the visible depth on both sides of the trade before committing funds. If you’re working on combinatorial arbitrage across multiple outcomes, your maximum position size is capped by the leg with the least liquidity. Exceeding that depth risks slippage, which can wipe out your advantage.
Make sure the spreads are above 2.5–3%, factoring in Polymarket’s 2% winner fee and any potential gas costs during network congestion. To avoid partial fills or unfavorable trades, use Fill or Kill (FOK) or Immediate or Cancel (IOC) orders. These ensure trades only go through when your desired spread is available.
These strategies create a foundation for high-frequency trading, where automation becomes a necessity.
STOP LOSING TO LATENCY
Execute faster than
your competition.
Sub-millisecond execution • Direct exchange connectivity • From $59.99/mo
Automated Bots for High-Frequency Execution
In high-frequency trading, speed is everything. Signing orders via standard Python clients takes about one second per signature, which is far too slow when arbitrage opportunities can vanish in seconds. Automated bots are essential for executing all parts of a trade simultaneously, ensuring you don’t lose the opportunity mid-process.
Between April 1, 2024, and April 1, 2025, research from IMDEA Networks revealed that sophisticated traders earned an estimated $40 million through market rebalancing and combinatorial arbitrage strategies. These profits were made possible by bots capable of monitoring and acting across hundreds of markets at once - something manual trading simply can’t match.
"Manual trading on Polymarket is a knife-fight with latency and fragmentation." - Alea Research Daily Newsletter
"Manual trading on Polymarket is a knife-fight with latency and fragmentation." - Alea Research Daily Newsletter
Advanced traders often rely on tools like Polymarket Agents for autonomous execution and NautilusTrader for seamless integration with the Central Limit Order Book (CLOB) API. These tools provide secure and efficient EIP712 signature handling, making them ideal for high-performance trading setups.
While automation boosts speed, effective inventory management and risk controls are critical to keeping those gains secure.
Inventory Management and Risk Mitigation
Even with precise execution and automated systems, managing inventory and mitigating risks are essential in non-atomic arbitrage. While arbitrage is often labeled "risk-free", it still carries execution risk. Polymarket arbitrage is non-atomic, meaning one leg of your trade could succeed while the other fails, leaving you with unhedged positions and unwanted market exposure.
Smart capital allocation can help mitigate these risks. A recommended approach splits funds as follows:
- 60–70% for active arbitrage positions
- 20–30% for liquid reserves to seize immediate opportunities
- 10% for directional hedges using crypto derivatives
This structure ensures you can react to sudden market shifts without tying up all your capital in slower trades.
For cross-platform arbitrage, balance your investments on both sides to guarantee a $1.00 payout regardless of the outcome. Use this formula: investment_A / investment_B = price_A / price_B. Always double-check that both platforms rely on the same resolution sources to avoid "leg risk", where mismatched criteria can lock up your capital unnecessarily.
Finally, monitor your order statuses carefully. Key states like MATCHED, MINED, and CONFIRMED indicate varying levels of trade finality. If a transaction enters RETRYING status, your bot should quickly decide whether to resubmit or cancel the trade to avoid further risks.
Conclusion
Polymarket's decentralized structure often creates pricing inefficiencies, which AI systems are exceptionally skilled at exploiting. By analyzing thousands of markets, these systems identify arbitrage and mispricing opportunities with remarkable precision. From April 2024 to April 2025, advanced traders leveraged these strategies to extract an estimated $40 million, proving that automated systems can outpace manual analysis. In this high-stakes environment, speed is everything, making a robust trading setup absolutely critical.
Milliseconds can mean the difference between profit and loss. Prices on Polymarket shift faster than human reaction times, and a Virtual Private Server (VPS) eliminates potential bottlenecks like local internet instability, system downtime, or routing delays. With standard Python-based order signing taking roughly one second, every millisecond saved can significantly impact outcomes.
Successful traders pair AI-powered detection with disciplined, automated execution strategies. They aim to maintain spreads above 2.5–3% to cover fees while carefully managing capital across active trades and reserves. Automated bots further enhance efficiency by executing multi-leg trades simultaneously, reducing risks from unhedged positions.
For traders looking to stay ahead in Polymarket high-frequency trading (HFT), QuantVPS offers the low-latency, always-on infrastructure needed to seize fleeting opportunities. Starting at $59.99/month, QuantVPS provides NVMe storage and high-performance CPUs, ensuring that AI models and automated bots operate at peak efficiency. In the world of Polymarket HFT, the advantage goes to those who act first - and QuantVPS helps you do just that.
FAQs
How does AI help traders find arbitrage opportunities on Polymarket?
AI plays a key role in refining arbitrage strategies on Polymarket by monitoring real-time price shifts, order flow, and liquidity fluctuations across various platforms. With the help of machine learning models, traders can pinpoint pricing discrepancies and act on them swiftly, often before the market corrects itself.
To ensure both speed and precision, these systems rely on low-latency VPS infrastructure. This setup provides stable connectivity and lightning-fast execution, reducing delays and enabling traders to seize brief opportunities in rapidly changing markets.
How does a Virtual Private Server (VPS) enhance high-frequency trading (HFT) strategies?
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) plays a crucial role in high-frequency trading (HFT) by offering a fast, stable, and always-on environment for running complex trading algorithms. With faster execution speeds, a VPS allows traders to react instantly to market fluctuations, cutting down on delays that could affect their profits.
Using a VPS ensures stable connectivity and dependable performance, which helps avoid issues like local internet outages, system failures, or routing delays. This reliability is particularly important for AI-driven trading strategies, where even the slightest delay can mean missing out on arbitrage opportunities or failing to act on rapid market shifts.
Why do traders need spreads of 2.5% to 3% for profitable arbitrage on Polymarket?
For arbitrage on Polymarket to be profitable, traders usually need spreads of 2.5% to 3%. This range accounts for transaction costs, market fees, and the risk of price swings during execution. It ensures there's enough margin to cover expenses while still allowing for a potential profit.
Prediction markets like Polymarket can also see prices shift quickly, especially during breaking news or periods of high volatility. Maintaining spreads in this range helps traders manage risks from sudden price changes or execution delays, keeping their strategies effective over time.
AI plays a key role in refining arbitrage strategies on Polymarket by monitoring real-time price shifts, order flow, and liquidity fluctuations across various platforms. With the help of machine learning models, traders can pinpoint pricing discrepancies and act on them swiftly, often before the market corrects itself.
To ensure both speed and precision, these systems rely on low-latency VPS infrastructure. This setup provides stable connectivity and lightning-fast execution, reducing delays and enabling traders to seize brief opportunities in rapidly changing markets.
A Virtual Private Server (VPS) plays a crucial role in high-frequency trading (HFT) by offering a fast, stable, and always-on environment for running complex trading algorithms. With faster execution speeds, a VPS allows traders to react instantly to market fluctuations, cutting down on delays that could affect their profits.
Using a VPS ensures stable connectivity and dependable performance, which helps avoid issues like local internet outages, system failures, or routing delays. This reliability is particularly important for AI-driven trading strategies, where even the slightest delay can mean missing out on arbitrage opportunities or failing to act on rapid market shifts.
For arbitrage on Polymarket to be profitable, traders usually need spreads of 2.5% to 3%. This range accounts for transaction costs, market fees, and the risk of price swings during execution. It ensures there's enough margin to cover expenses while still allowing for a potential profit.
Prediction markets like Polymarket can also see prices shift quickly, especially during breaking news or periods of high volatility. Maintaining spreads in this range helps traders manage risks from sudden price changes or execution delays, keeping their strategies effective over time.
"}}]}





