What Is Sklearn? Introduction to Python's Machine Learning Toolkit
Sklearn, or Scikit-learn, is a Python library designed for machine learning tasks like classification, regression, clustering, and dimensionality reduction. Built on NumPy, SciPy, and Matplotlib, it offers a consistent API, making it simple to switch between algorithms. Its tools for data preprocessing, model evaluation, and workflow management are widely used in fields like finance, especially for prototyping trading strategies.
Key highlights include:
- Estimator API: A unified interface for training and predicting with models.
- Modules: Tools for preprocessing, regression, decision trees, and more.
- Pipelines: Combine preprocessing and modeling steps into a single process.
- Integration: Works seamlessly with pandas and NumPy for data handling.
Traders use Sklearn to analyze financial data, backtest strategies, and generate trading signals. However, it has limitations, like handling non-stationary data or multicollinearity in financial datasets. Best practices, such as time-aware validation and regular model updates, help address these challenges. Sklearn's simplicity and flexibility make it a go-to tool for machine learning in trading and beyond.
Core Components and Features of Sklearn
The Estimator API
At the core of Sklearn is the Estimator API, a standardized interface that simplifies working with a wide range of machine learning algorithms. This design ensures you can switch between models - like linear regression or random forests - without needing to learn a different syntax for each one.
The API is built around a few essential methods. The fit(X, y) method is used to train your model by identifying patterns in your input data X and target values y. For example, in trading, this could involve using historical price data and technical indicators to predict future trends. The method returns the estimator itself, allowing for method chaining. Once the model is trained, you can use predict(X) to make predictions on new data or transform(X) to preprocess data without needing target values. For combined preprocessing and fitting, the fit_transform(X) method handles both tasks in one step, making it ideal for operations like scaling or feature extraction.
This uniformity across algorithms reduces the learning curve, making it easier to experiment with different models without changing your workflow.
Key Modules for Trading
Sklearn builds on its consistent Estimator API with modules tailored to specific tasks, making it particularly useful for trading applications.
-
sklearn.preprocessing: This module is crucial for preparing financial data, which often comes in different scales - stock prices in dollars, trading volume in millions, and percentage changes. Tools likeStandardScalerandMinMaxScalerensure your data is appropriately scaled, while imputers handle any missing values. -
sklearn.linear_model: Provides a variety of regression algorithms that are useful for predictive modeling. -
sklearn.treeandsklearn.ensemble: These modules include decision trees and ensemble methods like Random Forests and Gradient Boosting, which are great for capturing non-linear relationships in market data. -
sklearn.svm: Offers support vector machines for both classification and regression tasks, making it valuable for predicting market trends or identifying regimes.
For strategy development, the sklearn.model_selection module is indispensable. It includes tools like train_test_split for dividing datasets and GridSearchCV or RandomizedSearchCV for tuning hyperparameters to avoid overfitting - a common challenge in backtesting trading strategies. Additionally, sklearn.pipeline helps streamline workflows by combining preprocessing steps and model training into a single, repeatable process, ensuring consistency from research to production.
Sklearn's compatibility with familiar tools like pandas and NumPy ensures a smooth transition from raw financial data to actionable models.
Data Structures and Datasets
Efficient data handling is critical for building effective trading models. Sklearn works seamlessly with popular data structures like NumPy arrays, pandas DataFrames, and SciPy sparse matrices. Traders often organize financial data in pandas DataFrames, with rows representing dates and columns containing financial indicators. This structure easily converts into the feature matrices Sklearn requires.
Pandas DataFrames can be converted to NumPy arrays for faster computations. For high-dimensional datasets, such as text features derived from earnings reports or SEC filings, SciPy sparse matrices provide an efficient way to store and process data, and Sklearn fully supports them.
A 2023 guide titled "Building Financial Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn" showcased this workflow using the "200+ Financial Indicators of US stocks (2014–2018)" dataset from Kaggle. The process involved loading data into pandas DataFrames, removing outliers, calculating market-adjusted returns, scaling data with StandardScaler, selecting features with SelectKBest, and training regression models to differentiate between strong and weak-performing stocks.
This flexibility with data structures allows you to move seamlessly from raw market data to trained models without struggling with format conversions or compatibility issues.
Scikit-learn Crash Course - Machine Learning Library for Python
Building Machine Learning Models with Sklearn
Sklearn Machine Learning Workflow for Trading Strategies
NEVER MISS A TRADE
Your algos run 24/7
even while you sleep.
99.999% uptime • Chicago, New York & London data centers • From $59.99/mo
Sklearn Machine Learning Workflow for Trading Strategies
Creating a Trading Model
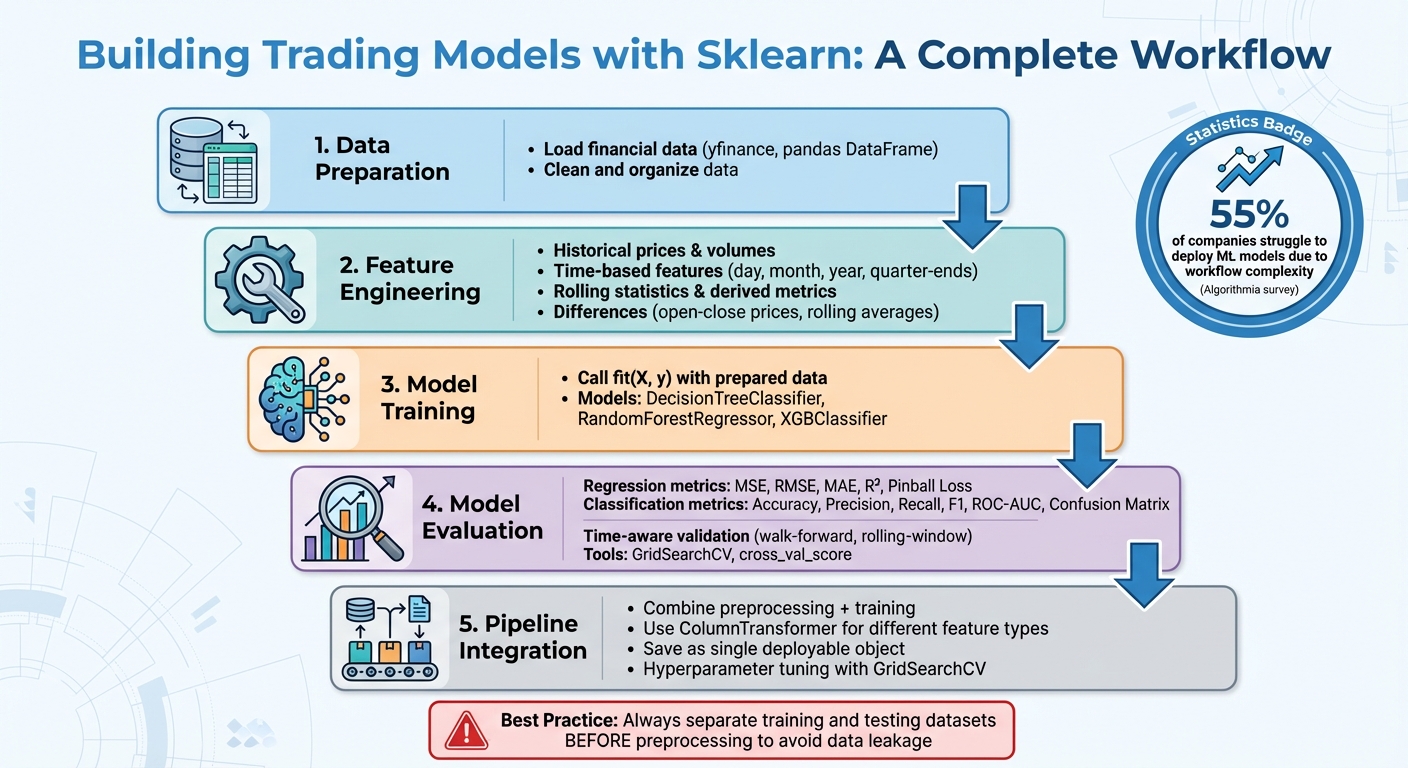
To kick things off, start by loading and organizing financial data - libraries like yfinance can be a great help here. Load this data into a pandas DataFrame, clean it up, and then focus on crafting features that provide meaningful insights. These features might include historical prices, trading volumes, date-based elements, and rolling statistics.
Feature engineering is where your understanding of the market meets machine learning. For instance, you can use historical price and volume data from previous days to create predictors. Time-related features, like breaking down dates into day, month, or year, or tagging specific dates like quarter-ends, can also be useful. Other derived metrics, such as differences between opening and closing prices or rolling averages, help capture broader market trends.
Once the features are ready, train your model by calling fit(X, y) with your prepared data. From there, it's time to evaluate how well the model performs.
Model Evaluation and Validation
Choosing the right evaluation metrics is key and should align with your trading goals. For regression models, metrics like MSE, RMSE, MAE, R², or Pinball Loss are commonly used. For classification tasks, focus on metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, ROC-AUC, or confusion matrices. Be cautious about relying too much on accuracy, especially with imbalanced datasets, as it can paint an overly optimistic picture.
Cross-validation is another critical step - it provides a more reliable performance estimate compared to a single train-test split, especially when dealing with small or skewed datasets. In financial modeling, where data is highly time-sensitive, using time-aware validation methods is crucial to avoid look-ahead bias. Stratified sampling can also help ensure that all classes are well-represented during data splits. One important tip: always separate your training and testing datasets before applying preprocessing steps to avoid data leakage. Tools like Sklearn's GridSearchCV and cross_val_score make it easier to evaluate models across different metrics by leveraging their scoring parameters.
After evaluating your model, you can simplify and improve your process by integrating preprocessing and training into a single, cohesive workflow.
Using Pipelines for Workflow Management
Sklearn pipelines are a game-changer when it comes to organizing your workflow. By chaining together steps like data preprocessing, feature extraction, and model training, pipelines eliminate repetitive code and help prevent data leakage. This makes your code cleaner, easier to maintain, and more efficient.
For example, tools like ColumnTransformer allow you to apply specific preprocessing steps to different types of features - numerical and categorical - within the same pipeline. Once the pipeline is built and trained, you can save it as a single object. This means you can deploy both the preprocessing steps and the trained model together. This approach addresses a common issue in the industry: according to a survey by Algorithmia, 55% of companies struggle to deploy machine learning models due to the complexity of managing workflows and deployment.
Pipelines also make hyperparameter tuning more efficient. Using tools like GridSearchCV, you can optimize both preprocessing and modeling steps in one go by employing nested parameter syntax (e.g., step__parameter). To speed things up, set n_jobs=-1 to utilize all available CPU cores for parallel processing. This not only saves time but also ensures a streamlined and scalable workflow.
Applying Sklearn to Trading Strategies
From Research to Backtesting
To apply machine learning to trading, start by transforming historical market data into structured input (X) and output (y) sets. These might include features like past prices, trading volume, and technical indicators, aimed at predicting future returns. With this setup, you can train models such as DecisionTreeClassifier, RandomForestRegressor, or XGBClassifier to identify patterns in the data.
Backtesting plays a crucial role in evaluating how these models might have performed historically. While it's essential to remember that past performance doesn't guarantee future success, backtesting provides valuable insights. Python has become a favorite tool for this process, thanks to libraries like Pandas and NumPy for data handling, and Sklearn for machine learning. To maintain the integrity of financial time-series data, consider validation techniques like walk-forward or rolling-window testing. These methods help avoid pitfalls like look-ahead bias while aligning with the structured workflows mentioned earlier, ensuring a seamless transition from research to application.
Once backtesting is complete, the next step is transforming model predictions into actionable trading signals.
Generating Trading Signals
After training and validating your models, the focus shifts to generating trading signals. Classification models, such as LogisticRegression or SVC, can output probabilities that reflect the likelihood of specific market movements. For instance, a model predicting a 75% probability of an uptrend might trigger a "buy" signal if it surpasses a predefined threshold. On the other hand, regression models like ElasticNet can estimate future price levels or returns, which can guide position sizing or entry and exit points. Additionally, models can help classify market conditions - such as "uptrend", "downtrend", or "sideways" - allowing you to adapt your strategy based on the current environment.
Infrastructure for Sklearn Strategies
Implementing these strategies in real-time trading requires reliable infrastructure. Sklearn-based trading systems need robust computational setups to handle both research and live execution. High-performance VPS (Virtual Private Server) solutions are often used to manage large datasets, ensure low latency, and support real-time data feeds and order execution. A reliable VPS ensures that your models operate without interruptions, process market data in real time, and execute trades as signals arise. These elements are critical for building a successful quantitative trading system.
Limitations and Best Practices
Sklearn's Limitations
STOP LOSING TO LATENCY
Execute faster than
your competition.
Sub-millisecond execution • Direct exchange connectivity • From $59.99/mo
Sklearn is a versatile library, but it isn't specifically designed for financial markets, which come with their own set of challenges. For example, many of its linear models assume straightforward relationships between variables, while market behavior is often far more intricate and unpredictable. These linear models can also be heavily skewed by outliers, as they aim to minimize squared errors, which amplifies the impact of extreme values.
Another issue is multicollinearity. When features are highly correlated - such as overlapping technical indicators - it can lead to unstable and unreliable coefficient estimates. This is an especially common problem in financial data, where many variables are interconnected. Moreover, financial markets are constantly changing, meaning models trained on historical data can quickly lose their relevance. This non-stationarity makes continuous monitoring and recalibration critical. Lastly, Sklearn's linear models can become computationally expensive for large datasets due to their complexity scaling with O(n_samples * n_features^2), which can slow down processing significantly.
To address these challenges, it's important to adopt strategies that improve model reliability and adaptability.
Best Practices for Trading
Start by implementing time-aware validation techniques. Methods like walk-forward optimization or k-fold cross-validation are crucial for ensuring your model can generalize well to unseen data. Using Sklearn's Pipeline feature can also help maintain consistency by linking data transformations and estimators, minimizing the risk of data leakage.
Another key practice is ensuring reproducibility. Always set a fixed numpy.random.RandomState to ensure consistent results across Sklearn objects. Monitor your models regularly with metrics such as KL divergence and key percentiles (e.g., P1, P10, P90, P99) to quickly identify any signs of model drift. Additionally, regular retraining is essential to incorporate fresh market data and keep your model accurate over time.
Integrating Sklearn with Other Trading Tools
Beyond building and maintaining models, integrating Sklearn with other tools can enhance your trading system. For example, trained models can be saved using joblib and deployed via REST APIs using frameworks like Flask, making them accessible to other systems for real-time predictions. Sklearn also works well with specialized libraries like Macrosynergy, which extends Pandas and Matplotlib to provide finance-focused functionality. These integrations make it easier to deploy Sklearn-based models within a robust, real-time trading infrastructure.
Conclusion
Sklearn has become a key tool for traders looking to incorporate machine learning into their quantitative workflows. With a rich array of algorithms - spanning regression, classification, clustering, and dimensionality reduction - it enables traders to perform predictive data analysis across financial markets effectively. This makes it invaluable for forecasting price movements, spotting trends, and fine-tuning portfolio allocations.
The library simplifies the entire process, from data preprocessing to backtesting. Features like its Pipeline functionality ensure workflows remain organized while minimizing risks like data leakage. By offering a structured approach - from sourcing data to strategy design and backtesting - Sklearn provides traders with a clear roadmap for transitioning from research to deployment. This versatility extends beyond research, empowering traders to apply these tools in real-time scenarios.
One of Sklearn's standout qualities is how well it integrates with the broader Python ecosystem. It works seamlessly with libraries for data acquisition and backtesting. Additionally, interpretable models like decision trees can be translated into simple if/else logic, enabling deployment in trading bots without relying on external libraries.
Its growing use in the finance industry highlights its accessibility and practical value. For instance, hedge funds like Man Group's AHL Dimension program, which oversees over $5.1 billion, have embraced AI and machine learning, while firms like Taaffeite Capital operate entirely on proprietary machine learning systems. As Python solidifies its position as a leading programming language, Sklearn's robust features and integration capabilities make it a cornerstone of modern quantitative trading. This underscores its significant role in shaping the future of trading strategies.
FAQs
How can Sklearn be used with non-stationary financial data?
Sklearn isn't equipped to directly manage non-stationary data, which is often encountered in financial markets. To make this type of data suitable for machine learning models, you can use preprocessing methods like differencing, log transformations, or performing statistical tests to achieve stationarity.
By stabilizing the data, these techniques help models identify patterns and relationships more effectively, leading to improved predictions. Proper preprocessing is a crucial step before leveraging Sklearn's tools for tasks such as regression or classification.
What are some best practices for using Sklearn in trading strategies?
To make the most of Sklearn for trading strategies, start by implementing cross-validation. This technique evaluates your model's performance on unseen data, ensuring it can handle new scenarios effectively. It's a crucial step for building a model that performs consistently.
When it comes to improving your model's accuracy, tools like grid search and randomized search are invaluable. These methods help you efficiently identify the best hyperparameters, saving time while fine-tuning your model.
Be cautious about data leakage, which can skew your results. Using pipelines to combine preprocessing steps with model training is a smart way to prevent this issue. Pipelines ensure that information from the test set doesn't accidentally influence the training process.
Lastly, don't underestimate the importance of feature engineering and data preprocessing. Clean, well-organized data is often the key to generating more accurate predictions and uncovering better trading opportunities.
How can Sklearn be used with trading tools for real-time predictions?
Scikit-learn (Sklearn) can play a pivotal role in trading workflows by enabling real-time predictions. Once you've trained a model, it can be deployed to analyze live data streams and provide insights that guide trading decisions, such as when to buy or sell.
To make this work, traders can preprocess incoming data, extract key features, and feed it into Sklearn models for continuous predictions. These outputs can then be integrated with trading platforms via APIs, allowing for automated decision-making and dynamic trade execution. Additionally, this setup supports ongoing backtesting, helping refine strategies and enhance overall performance.





