Prediction Market Liquidity: How Traders Earn From Spreads Instead of Direction
Prediction markets let traders profit without predicting outcomes. Instead of betting on events, you can earn steady returns by providing liquidity and capitalizing on bid-ask spreads. Here's how it works:
- What are prediction markets? These platforms trade contracts tied to events (e.g., elections, sports) that settle at $1 (if true) or $0 (if false). Contract prices reflect the market's probability of an outcome.
- How do spreads work? The bid-ask spread is the gap between the highest price buyers offer and the lowest price sellers accept. Traders profit by buying low (bid) and selling high (ask), regardless of the event's result.
- Why focus on spreads? Spread trading reduces risk compared to betting on outcomes. For example, a trader who started with $10,000 in 2024 earned $200–$800 daily by focusing on low-volatility markets.
- Key strategies: Use two-sided quoting to place buy and sell orders simultaneously, adjust spreads based on market conditions, and manage inventory to avoid directional exposure.
- Tools and tech: Real-time data feeds, automated systems, and low-latency infrastructure for algorithmic trading are essential for success.
In 2024, market makers on platforms like Polymarket earned over $20 million, with monthly returns ranging from 5% to 15%. Spread trading offers a systematic way to profit in prediction markets without relying on guesses.
How Spread-Based Trading Works in Prediction Markets
Spread Width Strategy by Market Conditions in Prediction Markets
Spread Width Strategy by Market Conditions in Prediction Markets
Spread-based trading is all about profiting from the difference between the bid and ask prices, rather than predicting which way the market will move. By placing simultaneous buy and sell orders, traders can take advantage of the existing spread dynamics. While the concept might sound complex at first, it becomes much clearer once you understand how to read the order book and position your trades effectively.
Reading Order Flow and Market Depth
Before diving into trades, it’s essential to analyze where other traders are placing their orders. The order book lists all pending buy and sell orders at different price levels, and market depth reveals how many contracts are available at each price. Spotting areas with sparse liquidity - zones with few sell orders above a support level - can highlight opportunities to profit from spreads.
Traders often rely on heatmaps to identify clusters of liquidity, which show where orders are concentrated. Real-time order flow tracking, typically done through WebSocket feeds, allows you to monitor the market midpoint and adjust quotes instantly as prices move. This speed is critical because outdated quotes can be exploited by faster traders. Having this live insight enables you to execute precise, two-sided orders with confidence.
Placing Trades to Capture Spreads
The main strategy here is two-sided quoting - placing both a buy order (bid) and a sell order (ask) on the Central Limit Order Book at the same time. For instance, if you set a bid at $0.49 and an ask at $0.51, and both orders are filled, you’ve earned a $0.02 spread per share, regardless of how the event plays out.
To manage your trades effectively, use GTC (Good-Till-Canceled) orders for ongoing quotes and GTD (Good-Till-Date) orders for contracts tied to specific events. Adjust your quotes based on inventory levels: lower your ask price if you’ve accumulated too much and raise your bid if you’re running low.
"Market makers profit from the spread between their buy price (bid) and sell price (ask). If someone sells to the market maker at $0.49, then another trader buys at $0.51, the market maker earns $0.02 per share regardless of the market outcome." – AL, Founder of PolyTrack
"Market makers profit from the spread between their buy price (bid) and sell price (ask). If someone sells to the market maker at $0.49, then another trader buys at $0.51, the market maker earns $0.02 per share regardless of the market outcome." – AL, Founder of PolyTrack
This strategic placement of orders forms the foundation for various spread-based trading approaches.
Examples of Spread-Based Strategies
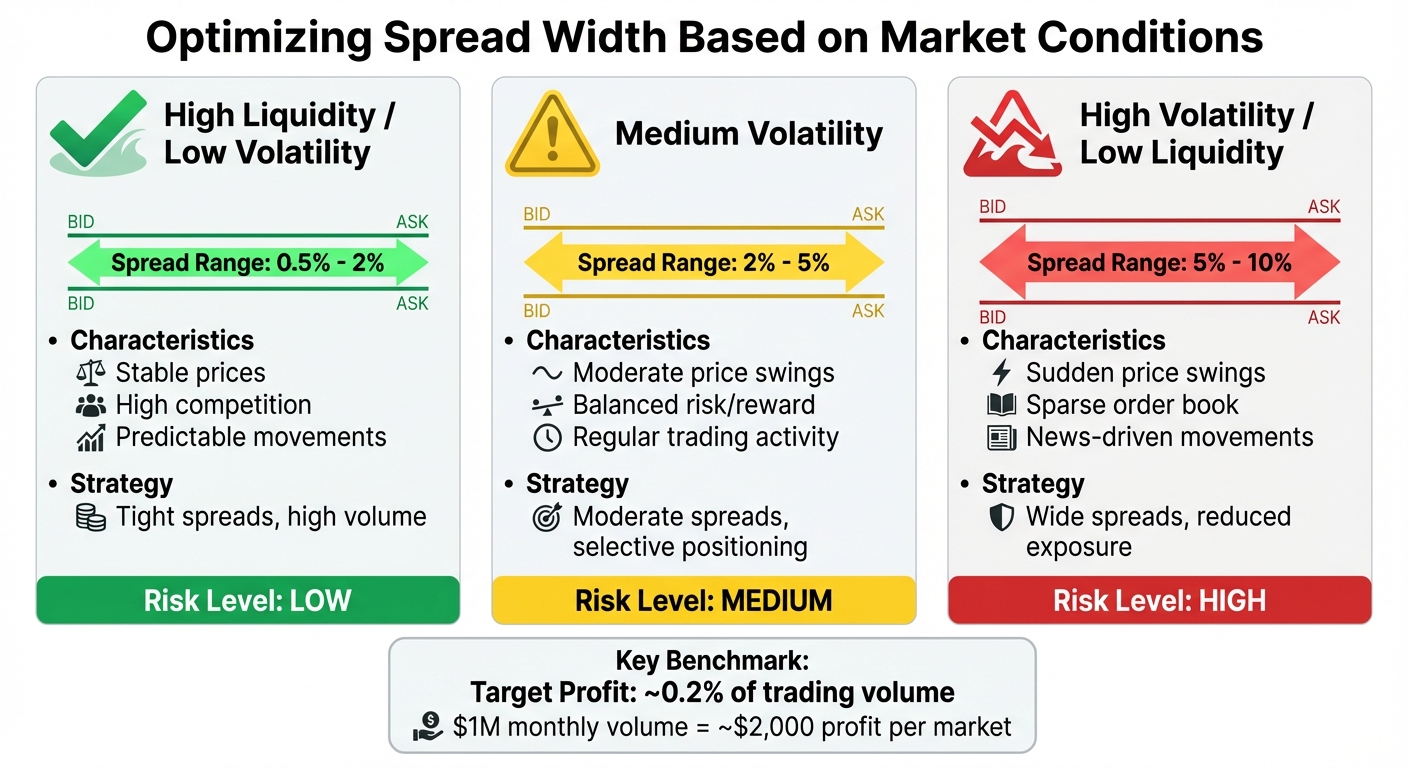
Once you’ve mastered order placement, it’s time to tailor your strategies to market conditions. In stable, high-liquidity markets, traders can work with tight spreads of 0.5% to 2%, as competition is intense and prices tend to be predictable. In markets with medium volatility, spreads usually expand to 2% to 5% to account for greater risk. For high-volatility or low-liquidity markets, spreads may need to widen further, often ranging from 5% to 10%, to offset the risk of sudden price swings.
One effective method is the "bands" strategy, where you set multiple layers of orders at different distances from the mid-price - such as 0.5%, 1%, and 2% offsets. This approach captures varying levels of trading activity without requiring constant adjustments. Additionally, holding equal amounts of YES and NO shares allows you to merge them back into USDC (since YES + NO always equals $1.00), freeing up capital for new trades without incurring extra spread costs.
Focusing on markets with generous liquidity rewards relative to volatility can also pay off. For example, low-volatility markets can yield significant returns if you maintain depth on both sides, potentially tripling your earnings. A useful benchmark for market makers is earning about 0.2% of their total trading volume. So, if you handle $1 million in trades over a month, you could expect around $2,000 in profit per market.
Liquidity Provision Strategies for Prediction Markets
Providing liquidity in prediction markets requires a shift in perspective compared to traditional trading. Instead of focusing on predicting outcomes, the goal is to facilitate trades. This involves adapting to market conditions, carefully managing your inventory, and knowing when to tweak your approach. These strategies help refine your market-making efforts.
Adjusting Spreads Based on Market Conditions
To succeed as a liquidity provider, it's critical to adjust your spread width depending on market conditions. In stable, high-liquidity scenarios, keeping your spreads competitive helps capture more trading volume. However, when volatility spikes, widening your spreads can shield you from sudden price swings and the risk of trading against better-informed participants.
Timing plays a huge role here. As a market approaches resolution, prices tend to converge quickly toward $0 or $1. Even small price shifts in this phase can have a big impact, prompting many traders to widen their spreads or scale back their activity. Similarly, when breaking news hits, pausing your quotes or immediately widening spreads can prevent you from being "picked off" by traders with faster access to information.
Managing Inventory and Reducing Risk
NEVER MISS A TRADE
Your algos run 24/7
even while you sleep.
99.999% uptime • Chicago, New York & London data centers • From $59.99/mo
Managing your inventory effectively is key to minimizing risk. Avoid building up excessive directional exposure by frequently adjusting your quotes and merging balanced YES and NO positions to free up capital. If your inventory becomes unbalanced - say you've accumulated too many YES shares - you can use quote skewing to bring it back to neutral. Lowering your YES ask price encourages buyers, while raising your YES bid discourages further accumulation, naturally rebalancing your positions.
Automating position merging at regular intervals can also prevent your capital from being unnecessarily tied up. On top of that, setting hard limits - like capping your exposure in a single market to 10% of your total portfolio - can protect you from major losses due to unexpected market swings.
Combining Passive and Active Trading
Effective liquidity provision often involves blending passive and active strategies. Instead of just waiting for orders to fill, successful traders use a mix of tactics to stay ahead. One popular method is the "bands" strategy. This involves placing multiple layers of orders at different distances from the mid-price - for instance, at offsets of 0.5%, 1%, and 2% - to capture various levels of trading activity without constant manual adjustments.
Automation can take this strategy to the next level. By using bots that rebalance every 30 to 60 seconds, you can keep your quotes aligned with the current midpoint. During calm periods, you can tighten your spreads to maximize fill rates. But if you notice aggressive institutional flows or increased order book activity, widening your spreads temporarily can help reduce the risk of adverse selection.
"Polymarket's reward system isn't perfectly calibrated to risk. Some markets barely move but offer huge rewards relative to their volatility. Finding these gems is where the profit lies." – @defiance_cr, Polymarket Trader
"Polymarket's reward system isn't perfectly calibrated to risk. Some markets barely move but offer huge rewards relative to their volatility. Finding these gems is where the profit lies." – @defiance_cr, Polymarket Trader
Managing Risks in Spread-Based Trading
Prediction contracts are unique - they either settle at $0 or $1. This binary outcome introduces risks that aren’t present in traditional stock markets. Prices can shift dramatically, sometimes jumping 40 to 50 points in an instant when major news breaks. To navigate this, successful liquidity providers need solid strategies that protect them from being wiped out by a single unexpected event.
How Volatility and Liquidity Changes Affect Spreads
Volatility and liquidity are two key factors that can make or break your profitability as a spread trader. In stable, liquid markets, tight spreads of 0.5% to 2% can generate solid trading volume. However, during periods of high volatility, those same tight spreads can become a liability.
Liquidity in prediction markets can dry up quickly. Warning signs include wide bid-ask spreads, large gaps in the order book, low historical trading volumes, and fewer active participants. For example, Polymarket saw an 84% drop in volume after the 2024 election, which significantly altered the trading dynamics for 2025. When you observe these red flags, it’s time to adjust. Tight spreads of 2% might work in calm conditions, but in medium volatility, they should widen to 5%, and in highly volatile or illiquid markets, spreads may need to stretch to 10%.
Automation tools can help manage these shifts. Configure your system to automatically widen spreads, reduce quote sizes, or pause market-making activities when volatility exceeds a certain threshold. This can shield you from losses caused by traders with faster access to market-moving information. In volatile conditions, these adjustments are critical for minimizing execution risks.
Reducing Execution Risks
Execution risks in prediction markets often stem from trading against better-informed participants who exploit outdated quotes. Breaking news is a common trigger. Traders with real-time data feeds can act on new information before you have a chance to update your prices. One effective countermeasure is integrating news feeds into your system. This allows you to pause quoting or adjust spreads as announcements occur.
"The trader who can cancel stale orders fastest when news breaks suffers fewer adverse fills." – Matthew Hinkle, Lead Writer, NYCServers
"The trader who can cancel stale orders fastest when news breaks suffers fewer adverse fills." – Matthew Hinkle, Lead Writer, NYCServers
To minimize these risks, you need a robust infrastructure. A system with sub-10ms round-trip latency is crucial for canceling stale orders in time. Using a dedicated VPS ensures high uptime and low latency, reducing the likelihood of unfavorable trades during volatile periods.
Advanced order types like Good-Till-Date (GTD) and Fill-Or-Kill (FOK) can further protect against execution risks by adapting to rapid market changes. But fast execution alone isn’t enough - ongoing monitoring of your risk exposure is equally important.
Monitoring and Adjusting Risk Exposure
Effective risk management is essential for protecting your earnings in volatile markets. Real-time position tracking and strict position limits are key tools. Most professional traders cap their exposure to 2% to 5% of their total capital in any single prediction market to avoid catastrophic losses from sudden reversals. Setting absolute limits on the number of shares held per market and across your portfolio adds another layer of protection.
Automated tools like circuit breakers and kill switches can instantly cancel all active orders if technical issues arise or risk thresholds are breached. These systems act faster than manual responses, helping you avoid significant losses.
As contracts near settlement, risk management becomes even more critical. Prices tend to converge toward $0 or $1 in the final hours, making it harder to offload inventory. During this phase, it’s wise to aggressively reduce your exposure or widen your spreads. Additionally, keeping an eye on "smart money" movements - such as whale activity or institutional trades - can provide valuable insights. These players often signal an impending liquidity drain, and when you notice such patterns, it’s better to pull back rather than try to compete with better-informed participants.
Technology for Spread-Based Trading
Spread trading thrives on a solid technology setup capable of handling real-time data and executing orders in the blink of an eye. We're talking milliseconds here. To make the strategies from earlier sections work, you'll need an infrastructure that processes live data feeds, executes trades instantly, and keeps a constant eye on risk. Without this tech backbone, the entire operation could falter.
Tools for Spread-Based Trading
When it comes to spread trading, three tools are indispensable: real-time data feeds, order management systems, and risk management systems.
- Real-time data feeds: These are your eyes and ears in the market. Polymarket's WebSocket feed, for example, delivers order book updates with about 100ms latency, making it a solid choice for market-making activities. If you're after broader market metrics like volume and liquidity, the Gamma API provides updates at roughly 1-second intervals. Your choice depends on how fast you need to move - high-frequency strategies demand WebSocket feeds, while slower methods can get by with REST API polling.
-
Order management systems (OMS): These systems handle the nitty-gritty of posting, canceling, and modifying orders. Polymarket’s Central Limit Order Book (CLOB) API, with its support for TypeScript and Python SDKs, streamlines these tasks. Pro tip: Use batch functions like
postOrders()instead of making individual API calls. This reduces network overhead and speeds up adjustments when managing multiple quotes. And don’t forget to set up automatic reconnection logic with exponential backoff - this ensures your WebSocket streams stay active during temporary hiccups. - Risk management systems: Protecting your capital is non-negotiable. Automated kill switches can cancel all active orders in an instant if rapid price movements or technical issues are detected. Pair that with real-time profit and loss tracking and strict position limits to avoid overexposure. For lightning-fast execution, keep a local copy of the order book and apply incremental updates from the WebSocket feed rather than repeatedly requesting the full book.
STOP LOSING TO LATENCY
Execute faster than
your competition.
Sub-millisecond execution • Direct exchange connectivity • From $59.99/mo
The Importance of High-Performance Infrastructure
When you're trading spreads, you can't afford downtime. Home computers? Not going to cut it. They’re prone to ISP outages, power failures, and network delays - any of which could leave you with outdated quotes at the worst possible moment. With prediction markets like Kalshi and Polymarket hitting a combined $10 billion in monthly volume as of November 2025, even a few seconds of lag can cost you big. Prices can swing wildly, jumping from $0.50 to $0.90 in an instant when major news breaks.
This is where a dedicated VPS (Virtual Private Server) comes in. A VPS offers high hardware redundancy, 99.9%+ uptime, and low-latency routing, keeping your system sharp and responsive. If you're serious about spread trading, aim for these minimum specs: 4+ CPU cores (preferably AMD EPYC or Ryzen), 8–16GB RAM, 100GB+ NVMe storage, and a 1Gbps+ network connection with low-latency routing.
Using Analytics to Find Spread Opportunities
Analytics tools are your secret weapon for spotting the best spreads and maximizing returns. Take PolyTrack, for instance - it monitors large trades (over $10,000) and sends instant alerts when big players make moves. These signals often precede volatility spikes, creating short-term windows for skilled traders to capitalize on wider spreads.
For ongoing monitoring, tools like Grafana and Kibana can track system performance, latency, and market prices in real time. Keeping an eye on sequence numbers in your data feeds is also crucial to catch any missed messages and maintain an accurate local order book.
Another powerful technique is inventory-adjusted quoting. Let’s say your system shows an overexposure to "YES" shares in a market. Analytics can automatically adjust your quotes to encourage trades that balance your inventory. This way, you can capture spreads while minimizing directional risk.
Spread-based trading is as much about precision as it is about strategy. With the right tools, infrastructure, and analytics, you can navigate the fast-paced world of prediction markets with confidence.
Key Takeaways for Spread-Based Trading Success
Spread-based trading in prediction markets isn’t about guessing outcomes - it’s about leveraging the bid-ask spread and earning liquidity rewards through consistent trading volume. For example, market makers on Polymarket pulled in over $20 million in 2024, with typical profits hovering around 0.2% of their trading volume. The secret? Treat trading as a volume-driven strategy, not a gamble on market direction.
Inventory management is the backbone of this approach. If you find yourself holding too many YES or NO shares, use quote skewing to adjust prices and bring your position back to neutral. Automated rebalancing helps you stay aligned with the market midpoint, while regularly merging positions - turning 1 YES and 1 NO share back into $1 USDC - ensures you free up capital and keep your system flexible. These tactics are essential for managing risk effectively.
To maximize returns, focus on markets that balance volatility and risk. Low-volatility markets with strong liquidity rewards offer a sweet spot, allowing you to capture opportunities while keeping exposure under control.
Risk management is critical. Widen your spreads during periods of high volatility and step back entirely before major news events to avoid unfavorable trades. Automated kill switches that instantly cancel all orders during rapid price swings are a must-have. With monthly returns now settling in the 5–15% range, managing risk has never been more important.
Finally, your infrastructure plays a decisive role. A reliable VPS with sub-10ms latency, 99.9%+ uptime, and at least 4 CPU cores ensures your quotes stay competitive during fast-moving markets. Start small with low-volatility markets to learn the ropes, then scale up as you refine your systems and expand into multiple markets. Continuously comparing high-performance VPS providers and strategies is the key to long-term success in spread-based trading.
FAQs
How can I start earning from bid-ask spreads in prediction markets?
To start generating income from bid-ask spreads in prediction markets, focus on market-making strategies. This means placing buy orders slightly below the current market price and sell orders just above it. By doing so, you can earn the difference (the spread) while also contributing liquidity to the market.
Using automated tools or APIs can help you manage your orders efficiently and adapt to changing market conditions. It's wise to start with a small amount of capital to limit your risk and gradually increase your investment as you become more confident. Take the time to understand the specific features of each platform, like liquidity rewards or tools for managing inventory risk, to fine-tune your strategy and aim for steady returns.
What tools do traders need to profit from bid-ask spreads in prediction markets?
To thrive in spread trading within prediction markets, traders depend on a few key tools that streamline the process and manage risks effectively.
First up are automated trading algorithms. These are indispensable for continuously setting buy and sell prices, allowing traders to efficiently capture bid-ask spreads. These algorithms also help manage inventory risks by quickly adjusting to shifts in the market, ensuring spreads remain optimized for steady returns.
Equally important are risk management systems, which keep a close watch on positions and inventory. These systems are designed to minimize losses from sudden, unfavorable price swings, giving traders a safety net in volatile conditions.
Many platforms also sweeten the deal with incentive programs. These rewards often encourage traders to maintain tight spreads, enabling them to combine liquidity rewards with their trading strategies for better earnings.
By blending automation, reliable risk management, and platform incentives, traders can create a solid foundation for providing liquidity and generating consistent profits in prediction markets.
How can I effectively manage risks when trading spreads in prediction markets?
To navigate the risks in spread-based trading, it's crucial to grasp the difficulties tied to providing liquidity. These include unpredictable price swings and the chance of a complete loss if an outcome becomes worthless when the market resolves.
Here are two key approaches to help manage these risks:
- Adjusting spreads and monitoring inventory: Place buy orders slightly below the midpoint price and sell orders just above it to earn from the spread. Keep a close eye on your inventory to ensure you’re not overly exposed to adverse market shifts.
- Leveraging automation and robust infrastructure: Automated market-making tools, paired with a reliable VPS, can help you maintain steady pricing and react to market changes in real time.
By actively managing your positions and staying ahead of potential challenges, you can reduce risks and aim for better returns in prediction markets.





