Market Making in Prediction Markets: How Liquidity Providers Trade
Prediction markets let traders bet on future events, with contract prices reflecting the probability of an outcome. For example, a $0.65 contract means a 65% chance of the event occurring. Market makers are critical in these markets, ensuring liquidity by posting bid-ask prices, absorbing imbalances, and enabling smoother trading. However, they face challenges like event risk, adverse selection, and inventory risk.
Key takeaways from the article:
- Market Growth: By November 2025, platforms like Kalshi and Polymarket handled nearly $10 billion in monthly volumes.
- Market Maker Role: They stabilize markets by narrowing spreads, managing inventory, and facilitating trades.
- Strategies: Effective order placement, spread adjustments, and inventory balancing are crucial.
- Risk Management: Tools like kill switches, Good Till Date (GTD) orders, and circuit breakers help mitigate risks.
- Automation: Algorithms like LMSR and BMM determine pricing and liquidity, while real-time data integration ensures quick reactions to market shifts.
- Infrastructure: Low-latency systems and proximity to exchange servers are essential for success.
Prediction market-making requires a mix of precise strategies, risk controls, and technical efficiency to thrive in a fast-moving, high-stakes environment.
Core Market Making Strategies
How to Place Orders for Liquidity
Market making relies on placing simultaneous bid and ask orders to profit from the spread - the difference between the buy and sell prices - when both orders are filled. The goal is simple: buy low and sell high, but the execution requires careful planning.
Choosing the right order type is essential. For consistent, passive quoting, Good Till Cancelled (GTC) orders stay active until they’re either filled or manually canceled. On the other hand, Good Till Date (GTD) orders are ideal when you want your quotes to automatically expire after a set period.
Batching orders can help reduce network load, but always verify your balances before quoting to ensure you stay within your inventory limits. To protect against unexpected risks, implement a "cancel all" kill switch. This allows you to instantly withdraw all open orders if you exceed position limits or encounter technical issues.
If your inventory becomes lopsided - for example, holding too much of one asset - use inventory skewing to bring it back into balance. For instance, if you’re holding too much YES, you can lower both your bid and ask prices. This encourages sellers while discouraging additional buys, helping to restore equilibrium.
Once your order placement strategy is solid, the next step is managing your bid-ask spreads to secure liquidity while staying competitive.
Setting and Adjusting Bid-Ask Spreads
The bid-ask spread is at the heart of market making. It directly impacts your profitability and ability to compete effectively. One popular approach is the Stoikov model, which calculates optimal bid and ask prices by weighing potential profits against inventory risks. However, this model may require adjustments in markets with binary outcomes, such as those that settle at $0 or $1.
Several factors influence how wide or narrow your spreads should be:
- Market Volatility: Spreads are typically widened during periods of uncertainty.
- Competition: Higher competition may force you to tighten spreads to stay attractive.
- Event Timing: As key events approach, spreads should be widened to manage the increased risk.
To ensure your quotes are accurate and competitive, use price guards to cross-check quotes against the midpoint of the order book. This helps you avoid setting prices that deviate too far from the market. Additionally, real-time monitoring through reliable WebSocket feeds - capable of delivering updates with latencies as low as 50ms - allows you to react quickly to market shifts.
With current fee structures set at 0 basis points for both makers and takers, managing your spreads effectively is critical. Your profits depend on capturing even the smallest margins, making precision and timing key to success in this space.
Using Models and Market Data Together
Creating Probability Models
Market makers rely on statistical models like the adapted Stoikov model, especially for binary outcomes (either $0 or $1), to calculate fair prices and adjust their quotes based on inventory levels. These models determine a "fair value" midpoint, then dynamically shift bid and ask prices to encourage trades that balance their inventory and reduce risk.
"Market makers... need to propose bid and offer/ask prices in an optimal way... they also need to mitigate the risk associated with price changes, and subsequently skew their quotes dynamically."
"Market makers... need to propose bid and offer/ask prices in an optimal way... they also need to mitigate the risk associated with price changes, and subsequently skew their quotes dynamically."
"The Yes + No = 1 formula in prediction markets means that ultimately only one contract becomes worth $1 while the other becomes worthless... forcing market makers to manage inventory more aggressively than in traditional markets."
"The Yes + No = 1 formula in prediction markets means that ultimately only one contract becomes worth $1 while the other becomes worthless... forcing market makers to manage inventory more aggressively than in traditional markets."
Because prediction market contracts have limited lifespans, market makers automate the adjustment of mid-price quotes as the contract resolution date approaches, helping to manage risk effectively. Professional systems also incorporate Time-Weighted Average Prices (TWAP) and external oracles to ensure pricing remains aligned with broader market trends.
To refine these models further, real-time news and sentiment data are integrated for sharper pricing adjustments.
Adding News and Sentiment Data
News events can cause rapid shifts in prediction market prices, making real-time data integration essential. Market makers use live data streams, such as order book updates, cryptocurrency prices, and social sentiment, to quickly adapt their strategies. These updates are often delivered via WebSocket feeds, ensuring minimal delay.
NEVER MISS A TRADE
Your algos run 24/7
even while you sleep.
99.999% uptime • Chicago, New York & London data centers • From $59.99/mo
Automated strategies also use news feeds to trigger circuit breakers, pausing quoting or widening spreads during significant events. This quick reaction is critical in markets where some traders may access news faster or use advanced models to gain an edge.
More advanced systems employ Agentic AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) to process news summaries and uncover semantic relationships across markets. For example, AI can identify when two differently phrased markets actually refer to the same outcome or when events are causally linked - such as U.S. tariffs prompting retaliatory actions from the EU. Trading strategies based on these AI-detected connections have shown average returns of about 20% over week-long periods, with accuracy in identifying these relationships ranging from 60% to 70%.
Managing Risk and Position Size
After exploring order placement and spread management, let’s turn to an equally important aspect of prediction markets: managing risk and controlling position size. These strategies are crucial for maintaining both liquidity and profitability.
Adjusting Positions as Probabilities Change
In prediction markets, contracts settle at either $0 or $1, meaning any unbalanced inventory carries the risk of total loss. For instance, holding too many "YES" positions can push market makers to adjust mid-prices downward (known as quote skewing) to rebalance their inventory.
"Inventory risk is the biggest threat to prediction market makers. Unlike stocks where you can hold positions indefinitely, prediction contracts settle at 0 or 1." – NYCServers
"Inventory risk is the biggest threat to prediction market makers. Unlike stocks where you can hold positions indefinitely, prediction contracts settle at 0 or 1." – NYCServers
To avoid overexposure, market makers need to set clear position limits for each market. If passive quoting isn’t enough to balance the portfolio, they may use aggressive strategies like Fill or Kill (FOK) or Fill and Kill (FAK) orders to shed excess inventory. As the settlement date approaches, it becomes increasingly important to actively scale back positions since markets tend to favor one outcome more strongly over time.
Sophisticated trading systems often include kill switches (such as cancelAll()) to instantly pull all active orders if risk thresholds are breached. Additionally, GTD (Good Till Date) orders can help limit exposure by automatically expiring quotes before high-impact events.
These proactive measures are just one part of a broader approach that includes real-time monitoring and interpreting order flow patterns.
Reading Order Flow Patterns
Real-time updates via WebSocket connections allow for instant adjustments to positions. For example, if a series of large buy orders consistently hits the ask side, it could indicate informed traders are active. This might prompt market makers to widen spreads or temporarily pause quoting to manage risk. Many trading platforms provide order book updates with latencies as low as 50 milliseconds, enabling swift responses to shifting market conditions.
Automated circuit breakers also play a key role in risk management. These systems cancel all outstanding orders if price movements exceed predefined thresholds, often within seconds. Such tools are especially useful during breaking news events, helping to prevent adverse selection by pausing or adjusting quotes. Integrating real-time news feeds into trading engines ensures that reactions happen faster than any human could manage.
| Order Type | Behavior | Risk Management Use |
|---|---|---|
| GTC (Good Till Cancelled) | Stays active until filled or canceled | Ideal for passive quoting |
| GTD (Good Till Date) | Expires at a specific time | Useful for managing exposure before major events |
| FOK (Fill or Kill) | Completes the entire order immediately or cancels it | Effective for precise inventory rebalancing |
| FAK (Fill and Kill) | Fills available quantities and cancels the rest | Allows for partial, flexible rebalancing |
For professional market makers, speed is everything. Many aim for sub-10 millisecond total round-trip latency during critical market events, combining rapid execution with constant position monitoring to stay ahead of the curve.
Automated Market Making Algorithms
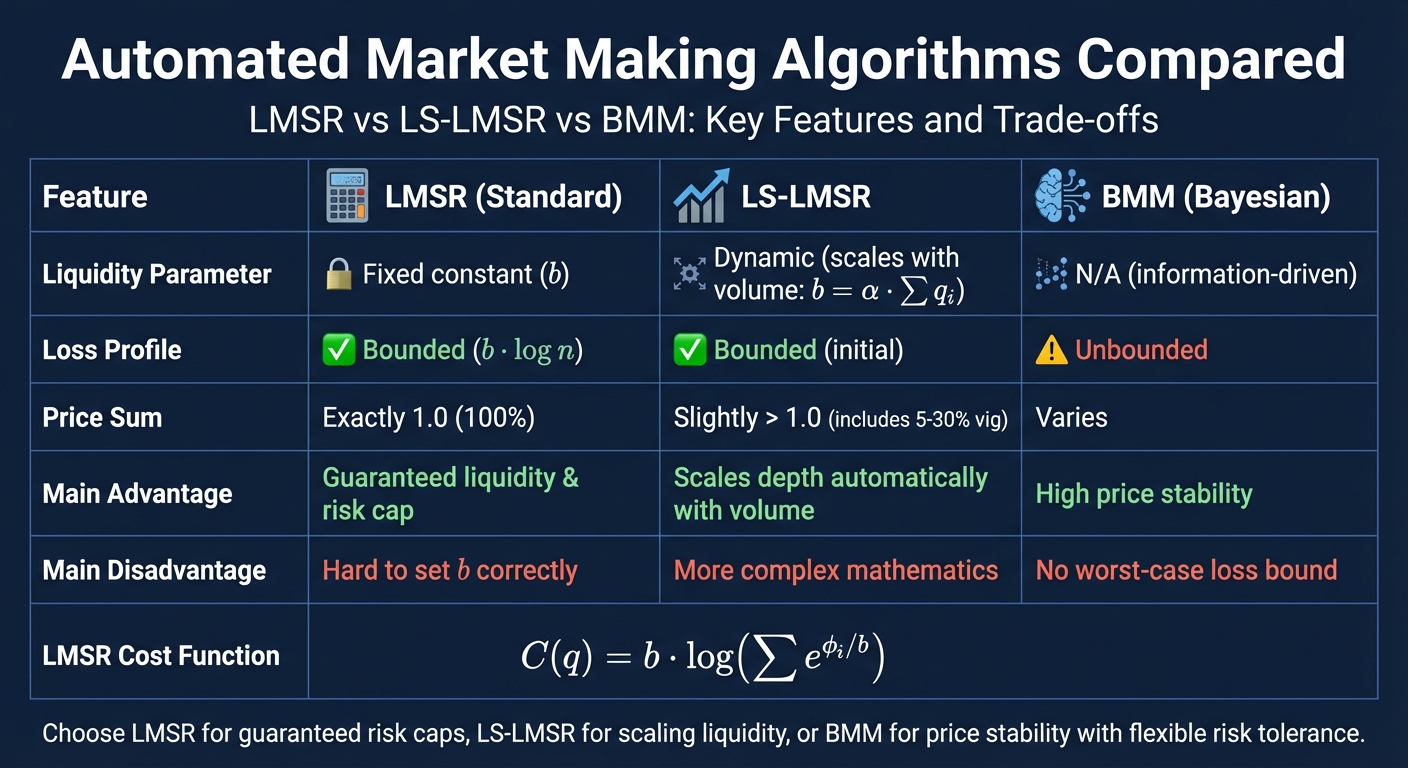
Comparison of Automated Market Making Algorithms: LMSR vs LS-LMSR vs BMM
Comparison of Automated Market Making Algorithms: LMSR vs LS-LMSR vs BMM
Automated algorithms ensure continuous liquidity, functioning round-the-clock. Two primary approaches dominate prediction market making: the Logarithmic Market Scoring Rule (LMSR) and the Bayesian Market Maker (BMM). Each relies on distinct mathematical methods to determine prices and manage risk.
Logarithmic Market Scoring Rule (LMSR)
LMSR operates using a cost function: C(q) = b · log(∑ e^(q_i/b)). This formula calculates prices based on outstanding shares, where the parameter b determines market depth. Prices are derived as partial derivatives of the cost function and always sum to 1.0, representing probabilities within the market.
One of LMSR’s standout features is its bounded risk. The maximum potential loss is capped at b · log(n), where n is the number of possible outcomes. This makes financial planning straightforward. For instance, Delphi leverages an on-chain LMSR market maker for machine learning competitions. Traders invest in claims like "Model $i$ wins the competition", with winning shares paying 1 token and losing shares paying 0. To manage potential losses, Delphi charges a trading fee of 0.5%–2% and uses a community vault where stakers contribute capital in exchange for a portion of the fee revenue.
However, choosing the right value for b is critical. For example, the Gates Hillman Prediction Market at Carnegie Mellon University used b = 32, which led to excessive price volatility. Sophisticated traders exploited this by taking advantage of rapid price shifts. Dr. Abe Othman from Augur explains:
"The biggest difficulty in using the LMSR in practice comes from choosing the value of b. Setting b too low means that prices will shift around too quickly... Setting b too high means that every interested trader could place a bet... and not significantly shift market prices."
"The biggest difficulty in using the LMSR in practice comes from choosing the value of b. Setting b too low means that prices will shift around too quickly... Setting b too high means that every interested trader could place a bet... and not significantly shift market prices."
To address this issue, LS-LMSR introduces a dynamic b that adjusts based on total wagers (b = α · ∑ q_i). This allows market depth to grow as trading volume increases, mimicking the behavior of traditional equity markets. For example, the University of Texas at Austin deployed LS-LMSR for a prediction market about the Gates Building opening, successfully scaling liquidity as participation increased. However, this approach introduces a slight "vig" (typically 5%–30%), as prices in LS-LMSR sum to slightly more than 1.0.
In comparison, the Bayesian Market Maker (BMM) offers a different approach, focusing on probability updates to manage prices.
Bayesian Market Maker (BMM)
BMM relies on Bayesian probability theory to adjust prices based on uncertainty and incoming data. Unlike LMSR, which uses a cost-function model, BMM updates its beliefs dynamically as new information emerges. This approach leads to greater price stability and reduced expected losses when liquidity is carefully managed.
STOP LOSING TO LATENCY
Execute faster than
your competition.
Sub-millisecond execution • Direct exchange connectivity • From $59.99/mo
However, BMM lacks the guaranteed loss cap that LMSR offers. This makes it challenging for market makers to predict and budget for potential risks. The choice between LMSR and BMM ultimately depends on priorities. If controlling losses is essential, LMSR is the better option. But for those who value price stability and are willing to accept unbounded risk, BMM provides better adaptability during market fluctuations.
| Feature | LMSR (Standard) | LS-LMSR | BMM (Bayesian) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquidity Parameter | Fixed constant | Dynamic (scales with volume) | N/A (information-driven) |
| Loss Profile | Bounded (b · log n) | Bounded (initial) | Unbounded |
| Price Sum | Exactly 1.0 (100%) | Slightly > 1.0 (includes vig) | Varies |
| Main Advantage | Guaranteed liquidity & risk cap | Scales depth automatically | High price stability |
| Main Disadvantage | Hard to set b correctly | More complex math | No worst-case loss bound |
Operational Requirements for Market Makers
Market-making in prediction markets demands precision and quick decision-making. The tools and infrastructure you use directly affect your ability to profit from spreads while avoiding unfavorable trades during volatile moments.
Technical Infrastructure for Fast Execution
Professional market makers aim for sub-10ms total round-trip latency, which includes receiving market data, processing strategy updates, and sending orders. Achieving this speed requires more than just a fast internet connection - your servers need to be located in data centers close to the exchange infrastructure. For platforms like Polymarket and Kalshi, this typically means hosting servers near the New York area on the US East Coast.
To stay on top of fast-moving markets, leverage low-latency WebSocket feeds for real-time order book updates and batch order functions to send multiple quotes in a single request. For instance, Polymarket’s WebSocket feed often delivers updates with a latency of less than 50ms. On blockchain-based platforms, using a Safe Wallet enables gasless, batched transactions while supporting pre-trade risk checks, real-time exposure tracking, and an instant cancel-all kill switch for emergencies.
In November 2025, Kalshi handled approximately $5.8 billion in trading volume, while Polymarket reached $3.74 billion. In such high-activity environments, even a small delay in execution can lead to missed opportunities or unfavorable trades.
For hosting, services like QuantVPS offer plans tailored for low-latency trading. The VPS Lite plan starts at $59.99/month (or $41.99/month with annual billing) and includes 4 cores, 8GB RAM, 70GB NVMe storage, and 1Gbps+ network connectivity. For higher trading volumes or multiple strategies, the VPS Pro plan at $99.99/month (or $69.99/month billed annually) offers 6 cores, 16GB RAM, 150GB NVMe storage, and support for up to 2 monitors. Both plans come with DDoS protection, automatic backups, and Windows Server 2022.
This type of setup not only speeds up order execution but also ensures you’re ready to step in manually when automated systems encounter issues.
When to Override Your Models
Even with advanced automation, there are times when human judgment is essential to manage pricing errors or limit risk. For instance, if your model generates quotes that deviate significantly from the order book midpoint, manual intervention can help prevent costly mistakes. Tools like Price Guards can automatically reject outlier prices before they hit the exchange, safeguarding against errors like "fat-finger" trades or algorithm glitches.
To avoid exposure during high-impact events, use GTD (Good Till Date) orders to ensure your quotes expire automatically before major announcements like election results or economic reports. Real-time monitoring of fills via WebSocket user channels is equally important - if you notice adverse selection in your fill rates, you may need to manually widen your spread.
In extreme situations, such as worsening market conditions, the kill switch becomes a critical tool to halt trading immediately. Unlike traditional markets where inventory can be held indefinitely, prediction market contracts settle at $0 or $1, making it crucial to aggressively manage positions as resolution dates approach. If your automated inventory adjustments fail to balance positions effectively, stepping in manually can prevent overexposure to a single outcome.
| Override Trigger | Recommended Action | Tool/Method |
|---|---|---|
| Position Limit Breach | Immediate halt | Kill Switch / cancelAll() |
| High Latency/Stale Data | Cancel stale quotes | WebSocket Monitoring |
| Outlier Pricing | Reject order | Price Guards vs. Midpoint |
| Major News Event | Auto-expire quotes | GTD (Good Till Date) Orders |
Conclusion
Successful market making in prediction markets relies on a careful mix of quantitative strategies, real-time data integration, and solid technical infrastructure. Combining elements like probability models tailored to binary outcomes, live news updates, and automated risk management is critical for navigating these fast-moving markets. With platforms like Kalshi and Polymarket handling close to $10 billion in combined monthly volume as of November 2025, the potential is immense - but so are the risks for those without the right systems in place.
A strong technical foundation is key. Features like low-latency data feeds, batch order processing, and infrastructure located near exchange servers help maintain steady performance and quick execution. Automated risk controls are equally important - such as GTD orders that expire quotes before major announcements and kill switches that cancel orders during severe market disruptions or system failures. As contracts approach resolution, snapping to $0 or $1, manual intervention becomes essential to avoid holding unfavorable positions.
"The trader who can cancel stale orders fastest when news breaks suffers fewer adverse fills." – Matthew Hinkle, Lead Writer, NYCServers
"The trader who can cancel stale orders fastest when news breaks suffers fewer adverse fills." – Matthew Hinkle, Lead Writer, NYCServers
Blending these strategies ensures smooth operations and the ability to adapt to rapid market changes. The core principles remain clear: balance automation with strategic decision-making, keep a constant eye on inventory, and stay prepared for how quickly prediction markets shift in response to real-world events.
FAQs
How do market makers reduce risk in prediction markets?
Market makers in prediction markets rely on sophisticated algorithms and pricing strategies to balance risk and maintain liquidity. By dynamically adjusting prices in response to market activity and liquidity levels, they work to prevent large price fluctuations that could result in losses. This approach ensures trades flow smoothly while limiting the market maker's exposure to unnecessary risk.
A widely used method is Hanson's automated market maker formula, which guarantees liquidity at all times. This system also tackles issues like rounding errors and guards against potential manipulation. By setting strict limits on potential losses, market makers can remain profitable, even in quieter markets or during unexpected events. In the end, effective risk management comes down to striking the right balance between liquidity, profitability, and exposure, using carefully designed automated tools.
How do market makers adjust bid-ask spreads in prediction markets?
Market makers in prediction markets use strategies that adjust bid-ask spreads to strike a balance between offering liquidity and managing risk. A key tool in their arsenal is dynamic pricing algorithms, which adapt to changing market conditions. For example, when markets are less liquid, these algorithms increase spreads to mitigate higher risks. Conversely, in more active markets, spreads are tightened to encourage greater trading activity.
Another approach involves risk-based models, which determine spreads by factoring in the market maker's risk tolerance and the market's overall liquidity. These models are designed to limit potential losses while ensuring steady liquidity. Additionally, some systems incorporate scoring rules that automatically tweak spreads to maintain fair pricing and guard against exploitation. Together, these methods help market makers optimize liquidity, control risk, and sustain profitability.
How does integrating real-time data improve market making?
Integrating real-time data transforms market making by enabling liquidity providers to react immediately to shifting market conditions. With precise, up-to-the-second information, they can adjust prices on the fly, maintain a better equilibrium between supply and demand, and reduce exposure to risks.
This level of agility doesn’t just boost profitability - it also creates a more seamless trading experience for users, building trust and improving efficiency in prediction markets.





