How to Deploy Low-Latency NICs for High-Frequency Trading Networks
In high-frequency trading (HFT), where microseconds can mean the difference between profit and loss, deploying low-latency NICs is critical. These specialized network interface cards bypass traditional bottlenecks like operating system overhead and standard network stacks, enabling lightning-fast data transfers. Here's a quick breakdown of what you need to know:
- Key Features to Look For: Focus on NICs with kernel bypass, RDMA support, and at least 10GbE capabilities. Time synchronization features like PTP and hardware timestamping are essential for precise trade execution.
- Top NIC Options: Mellanox ConnectX NICs deliver sub-microsecond latency, while Arista 7130 Series NICs combine switch and FPGA functionalities for nanosecond-level performance.
- Hosting Plans: Match your NIC to a hosting plan based on workload. For ultra-low latency, consider high-performance VPS or dedicated servers with 10Gbps+ network speeds.
- Configuration Tips: Update drivers, enable RDMA, and tweak settings like interrupt coalescence and flow control. Disabling unnecessary features like LRO or GRO can further reduce latency.
- Testing and Monitoring: Use tools to measure latency, packet loss, and throughput. Regular monitoring ensures your system maintains optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Low-Latency NIC for HFT
What to Look for in a Low-Latency NIC
When selecting a low-latency NIC for high-frequency trading (HFT), focus on latency measured in microseconds (µs) or nanoseconds (ns) and ensure it can handle high packets-per-second (PPS) rates. This is essential for processing the massive volumes of market data and trade orders efficiently.
Features like kernel bypass and RDMA support are critical. These capabilities help minimize delays caused by the operating system and reduce CPU usage, which can make a big difference in trading environments.
A NIC with at least 10GbE support, and the ability to scale up to 25GbE or more, is vital to handle microbursts and heavy message loads without bottlenecks. Additionally, look for high-precision hardware time-stamping and time synchronization features, such as PTP (Precision Time Protocol) and PPS (Pulse Per Second), to ensure accurate order execution and meet regulatory standards.
If you’re considering SmartNICs, FPGA programmability is worth exploring. It allows you to offload specific tasks, reducing latency even further and offering flexibility for application-specific needs.
The table below compares leading NIC models based on these criteria.
Mellanox ConnectX vs. Arista NICs
Two standout options in the HFT world are Mellanox ConnectX NICs and Arista's 7130 Series. Mellanox ConnectX NICs use NVIDIA Rivermax and FastSockets technology to deliver sub-microsecond latency through features like kernel bypass and zero-copy architecture. On the other hand, Arista's 7130 Series combines switch and FPGA functionalities, achieving nanosecond-level latency for specific tasks such as L1 data distribution and order execution.
| Model | Latency Performance | Network Speed & Features | Recommended QuantVPS Plan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mellanox ConnectX NIC | Sub-microsecond latency | High-speed options with enhanced throughput | VPS Ultra+ |
| Arista 7130 Series NIC | Nanosecond-range latency | Integrated switch and FPGA capabilities | VPS Pro+ |
The Mellanox ConnectX NIC is an excellent choice for the most demanding HFT strategies, offering exceptional latency and throughput. Meanwhile, the Arista 7130 Series excels in specific network functions, making it a strong contender for targeted trading operations. Your choice should depend on your latency requirements, budget, and the QuantVPS plan that aligns with your infrastructure needs.
Ultra-Low Latency 25G Ethernet for Electronic Trading
Hardware and Hosting Requirements for NIC Deployment
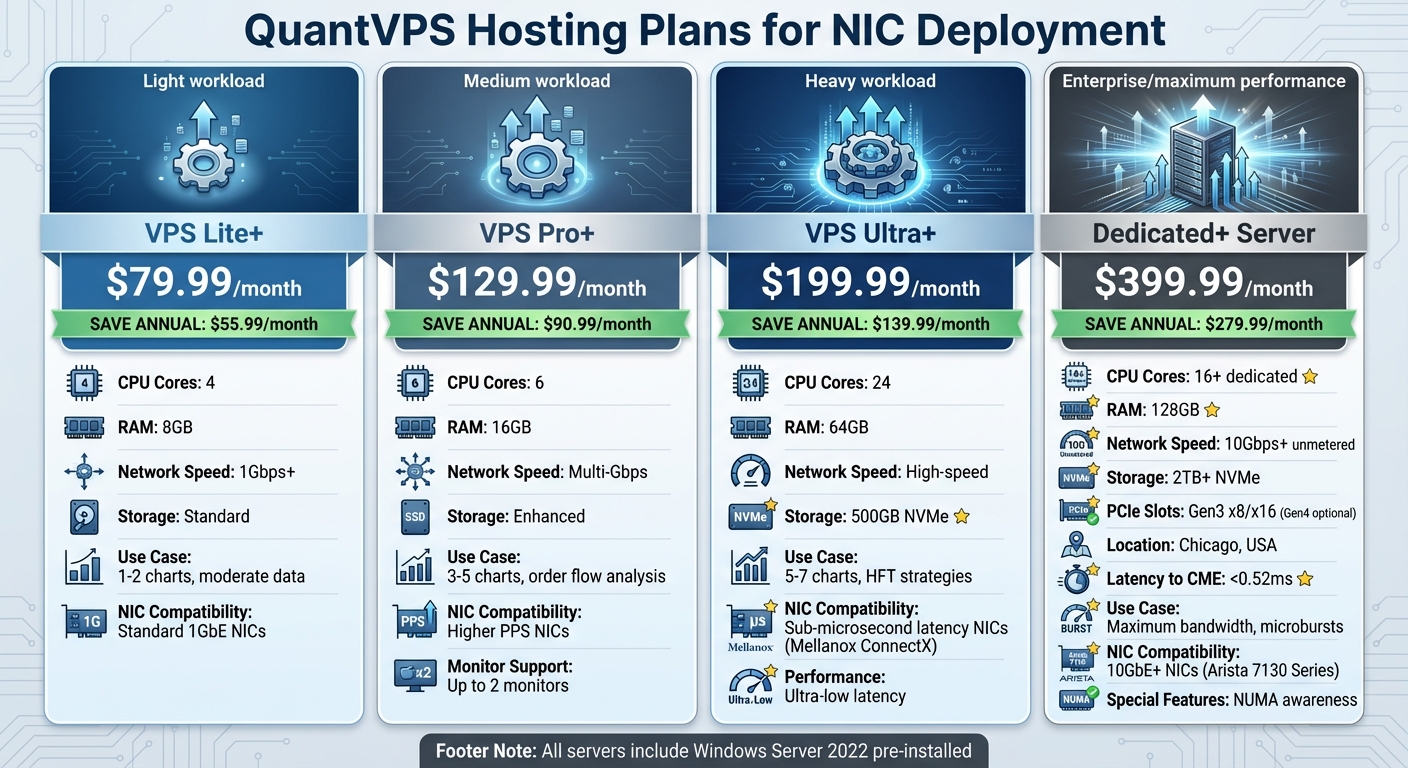
QuantVPS Hosting Plans Comparison for Low-Latency NIC Deployment in HFT
QuantVPS Hosting Plans Comparison for Low-Latency NIC Deployment in HFT
Matching NICs to QuantVPS Plans
Choosing the right hosting plan is crucial to ensure your NIC has the resources it needs for smooth and efficient operation.
If you're working with lighter workloads - say, 1–2 charts with moderate data - the VPS Lite+ plan is a solid choice. Priced at $79.99 per month (or $55.99 per month when billed annually), it offers 4 cores, 8GB RAM, and a network speed of over 1Gbps. This setup works well with standard 1GbE NICs.
For more complex setups, like 3–5 charts involving detailed order flow analysis, the VPS Pro+ plan steps up with 6 cores, 16GB RAM, and support for up to two monitors. At $129.99 per month (or $90.99 per month annually), this plan is designed to handle NICs with higher packet-per-second demands.
If you're diving into high-frequency trading (HFT) strategies that involve 5–7 charts and require ultra-low latency, the VPS Ultra+ plan is the way to go. It offers 24 cores, 64GB RAM, and 500GB of NVMe storage, costing $199.99 per month (or $139.99 per month annually). This plan provides the CPU power needed for advanced NIC performance and sub-microsecond latency. All QuantVPS servers come pre-installed with Windows Server 2022, fully configured for trading environments.
For trading strategies that demand even higher bandwidth and performance, dedicated servers are the next step.
Using Dedicated Servers for 10Gbps+ Networks
NEVER MISS A TRADE
Your algos run 24/7
even while you sleep.
99.999% uptime • Chicago, New York, London & Amsterdam data centers • From $59.99/mo
When your trading setup requires bandwidth of 10Gbps or more, VPS plans simply won't cut it. The QuantVPS Dedicated+ Servers offer the power and capacity to meet these demands. Priced at $399.99 per month (or $279.99 per month annually), these servers come with 16+ dedicated cores, 128GB RAM, 2TB+ NVMe storage, and an unmetered 10Gbps+ network connection. This configuration is built to handle the large data volumes and microbursts typical of high-frequency trading without performance bottlenecks.
These servers also feature PCIe Gen3 x8/x16 slots, with the option for PCIe Gen4 for users seeking even greater performance.
Located in Chicago, USA, this infrastructure achieves ultra-low latency of <0.52ms to the CME Group's matching engines. Such proximity dramatically reduces transmission delays, bringing them down to mere microseconds.
Additionally, the dedicated server setup is optimized for NUMA (Non-Uniform Memory Access) awareness. By aligning NICs with CPU cores on the same socket, this configuration maximizes efficiency, making it a perfect fit for latency-sensitive trading strategies.
Configuring NICs for Minimum Latency
Driver and Firmware Setup
To get the best performance and address critical issues, make sure you install the latest NIC drivers from your manufacturer. Once updated, adjust these key settings to fine-tune your NIC:
-
Set ring buffer sizes: Use the command
/usr/sbin/ethtool -G ethN rx 8192 tx 8192(for Linux kernels earlier than 6.8). -
Enable interrupt coalescence: Run
/usr/sbin/ethtool -C ethN adaptive-rx on adaptive-tx onto manage interrupts more efficiently. -
Enable flow control: Activate it with
/usr/sbin/ethtool -A ethN rx on tx onto manage traffic better.
In addition to these NIC-specific tweaks, disable SMT (Simultaneous Multithreading) in the BIOS and enable IOMMU to potentially boost performance by up to 40%. Also, set the CPU governor to "performance" mode to ensure consistent CPU speeds. For further latency reductions, consider using kernel bypass and hardware offload features.
Enabling RDMA and Offload Features
Once your driver and firmware are optimized, you can further minimize latency by enabling RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) and offload capabilities. Kernel bypass tools like OpenOnload or DPDK can significantly reduce CPU load and improve latency. For advanced setups like FPGA-based NICs or SmartNICs, processing data directly on the hardware can further enhance performance.
For latency-sensitive TCP streams, disable throughput-focused features such as Large Receive Offload (LRO) and Generic Receive Offload (GRO). Instead, enable hardware features like Accelerated Receive Flow Steering (ARFS), which routes packets more efficiently to the CPU.
If ultra-low latency is your goal, consider these additional optimizations:
-
Enable
SO_BUSY_POLL: This can reduce latency by about 7 microseconds. - Use userspace busy polling: Cuts latency further by roughly 4 microseconds.
- Pin trading processes to specific CPU cores: Saves approximately 1 microsecond.
- Optimize NUMA locality: Improves latency by around 2 microseconds.
These adjustments work hand-in-hand with your NIC's hardware capabilities, setting the stage for rigorous performance testing in demanding, low-latency environments.
Testing and Monitoring NIC Performance
Measuring NIC Latency and PPS Throughput
Once your NIC is configured, it's crucial to ensure these adjustments deliver the expected performance gains. This involves running detailed latency and throughput tests. Start by measuring latency using application-level metrics or the kernel packet time-stamping API. For high-frequency trading (HFT), hardware packet timestamping is invaluable - it attaches a 64-bit, nanosecond-precision timestamp directly to incoming packets, avoiding delays caused by software processing.
To identify potential bottlenecks, compare timestamps from hardware, kernel, and application levels. If you notice significant delays between hardware and kernel timestamps, the issue likely lies in the network stack. On the other hand, delays between kernel and application timestamps often point to CPU or software processing inefficiencies. This layered analysis helps pinpoint exactly where latency issues originate.
Throughput testing is equally important. Tools like iperf2 and iperf3 can measure throughput effectively. Typically, you should see values around 30 Gbps for a single stream and exceed 95 Gbps when using eight streams.
To ensure optimal performance, check for packet loss using counters such as rx_errors, tx_errors, rx_missed, and tx_dropped via ethtool -S ethN. Ideally, these values should be zero or very low. Any packet loss, no matter how minimal, can severely impact the efficiency of your trading system, regardless of your NIC’s theoretical speed. These tests feed directly into QuantVPS’s monitoring framework, ensuring your system maintains ultra-low latency.
Monitoring Latency on QuantVPS
After measuring performance, continuous monitoring becomes essential. QuantVPS servers provide the foundation for deploying robust monitoring tools to track your NIC performance. Use a monitoring and analysis system that combines technical metrics with business indicators to detect early signs of performance degradation. Configure alert systems to notify you immediately of any issues, enabling you to resolve them before they disrupt your trading operations.
It's also wise to implement ongoing failover tests to evaluate how your system performs during network disruptions. This ensures your ultra-low latency setup remains stable even under challenging conditions. For HFT environments requiring nanosecond-level precision, custom monitoring tools may be necessary.
"An FX trading platform must contend with various latency types, such as network, propagation, processing, and software-related delays. Achieving ultra-low latency requires a holistic approach that meticulously optimises each step from data transmission to execution." - Alexander Culiniac, CTO/Managing Director of the commercial banking & payment product business group, SmartTrade Technologies
"An FX trading platform must contend with various latency types, such as network, propagation, processing, and software-related delays. Achieving ultra-low latency requires a holistic approach that meticulously optimises each step from data transmission to execution." - Alexander Culiniac, CTO/Managing Director of the commercial banking & payment product business group, SmartTrade Technologies
STOP LOSING TO LATENCY
Execute faster than
your competition.
Sub-millisecond execution • Direct exchange connectivity • From $59.99/mo
When monitoring reveals latency issues, conduct a root cause analysis to determine whether the problem stems from software inefficiencies, code bottlenecks, network congestion, or hardware limitations. This diagnostic process helps you decide whether to focus on software improvements or hardware upgrades to maintain your competitive edge in the demanding world of high-frequency trading.
Conclusion
To achieve peak performance in high-frequency trading (HFT), deploying low-latency NICs requires careful selection, precise configuration, and ongoing optimization. FPGA-based SmartNICs are a top choice, offering features like nanosecond-level latency, hardware time-stamping, and PTP/PPS support (IEEE 1588). These capabilities are critical in an environment where programmed trading drives 70% of daily volume on the New York Stock Exchange, and milliseconds can separate profit from loss.
Once you've chosen the right hardware, proper configuration becomes essential. Keep drivers and firmware updated, activate kernel bypass and offload features, and use Firmware Development Kits (FDKs) to program custom logic directly onto the NIC's FPGA. This reduces dependency on the host CPU and can boost latency performance by up to 10x.
Sustaining ultra-low latency demands constant monitoring and prompt adjustments. As Eugene Markman, ION FX Chief Operating Officer, aptly puts it:
"Enabling ultra-low latency trading is an ongoing process".
"Enabling ultra-low latency trading is an ongoing process".
Leverage tools like hardware timestamping, packet loss counters, and throughput testing to ensure your NIC performs at its best throughout the trading day. Quickly address any issues caused by hardware wear, network congestion, or software inefficiencies.
FAQs
What should I look for in a low-latency NIC for high-frequency trading?
When choosing a low-latency NIC for high-frequency trading (HFT), focus on features that directly reduce latency and improve overall performance. Start by selecting NICs that support ultra-fast data transfer speeds, such as 10GbE or higher, and consider options with hardware acceleration like FPGAs, which enable parallel processing to handle complex tasks more efficiently. Compatibility with RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) is another key factor, as it helps minimize delays during data transmission.
It's also important to look for NICs designed with low packet processing latency, often measured in microseconds or even nanoseconds. To get the best results, ensure the NIC integrates smoothly with high-speed, low-latency switches, maintaining steady performance across your network. With these features in place - and paired with proper configuration and tuning - you can significantly enhance the speed and responsiveness of your trading system.
What are the best practices for configuring NICs to minimize latency in high-frequency trading systems?
To minimize latency in high-frequency trading (HFT) systems, it's crucial to fine-tune both hardware and software settings for your network interface cards (NICs). Start by choosing high-performance, low-latency NICs, like FPGA-based models, specifically built for HFT scenarios.
On the software side, make key adjustments to your NIC configurations. Enable interrupt coalescence, maximize ring buffer sizes (e.g., 8,192), and disable hyperthreading (SMT) in your system's BIOS. Set your CPU governor to 'performance' mode, activate IOMMU, and ensure your NIC drivers are current. Turn off unnecessary features like flow control, and tweak kernel parameters - such as setting net.core.default_qdisc to fq_codel - to enhance performance.
By combining these optimizations with seamless integration into your trading system, you can greatly reduce latency and boost network efficiency, giving you a competitive edge in HFT environments.
What is the best hosting plan for deploying low-latency NICs in high-frequency trading networks?
When deploying low-latency NICs in high-frequency trading (HFT) networks, a dedicated high-performance colocation plan is your best bet. These hosting solutions are designed to place your infrastructure close to major trading exchanges, helping to keep latency to an absolute minimum.
Such plans often come with key features tailored to HFT needs, including direct connections to financial markets, ultra-fast data transmission, and hardware specifically built for low-latency performance. Opting for a colocation plan optimized for these requirements ensures the speed and reliability essential for staying competitive in the fast-paced world of trading.
When choosing a low-latency NIC for high-frequency trading (HFT), focus on features that directly reduce latency and improve overall performance. Start by selecting NICs that support ultra-fast data transfer speeds, such as 10GbE or higher, and consider options with hardware acceleration like FPGAs, which enable parallel processing to handle complex tasks more efficiently. Compatibility with RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) is another key factor, as it helps minimize delays during data transmission.
It's also important to look for NICs designed with low packet processing latency, often measured in microseconds or even nanoseconds. To get the best results, ensure the NIC integrates smoothly with high-speed, low-latency switches, maintaining steady performance across your network. With these features in place - and paired with proper configuration and tuning - you can significantly enhance the speed and responsiveness of your trading system.
To minimize latency in high-frequency trading (HFT) systems, it's crucial to fine-tune both hardware and software settings for your network interface cards (NICs). Start by choosing high-performance, low-latency NICs, like FPGA-based models, specifically built for HFT scenarios.
On the software side, make key adjustments to your NIC configurations. Enable interrupt coalescence, maximize ring buffer sizes (e.g., 8,192), and disable hyperthreading (SMT) in your system's BIOS. Set your CPU governor to 'performance' mode, activate IOMMU, and ensure your NIC drivers are current. Turn off unnecessary features like flow control, and tweak kernel parameters - such as setting net.core.default_qdisc to fq_codel - to enhance performance.
By combining these optimizations with seamless integration into your trading system, you can greatly reduce latency and boost network efficiency, giving you a competitive edge in HFT environments.
When deploying low-latency NICs in high-frequency trading (HFT) networks, a dedicated high-performance colocation plan is your best bet. These hosting solutions are designed to place your infrastructure close to major trading exchanges, helping to keep latency to an absolute minimum.
Such plans often come with key features tailored to HFT needs, including direct connections to financial markets, ultra-fast data transmission, and hardware specifically built for low-latency performance. Opting for a colocation plan optimized for these requirements ensures the speed and reliability essential for staying competitive in the fast-paced world of trading.
"}}]}





