FPGA Accelerated Network Interface Card
FPGA-accelerated Network Interface Cards (NICs), often called SmartNICs, are transforming high-frequency trading by minimizing latency to nanoseconds. Unlike standard NICs, which rely on CPUs for data processing, FPGA NICs execute tasks like market data decoding and order execution directly in hardware. This approach eliminates delays caused by software layers, ensuring faster and more predictable performance.
Key Takeaways:
- What are FPGA NICs? They combine a network adapter with an FPGA chip for ultra-fast, parallel data processing.
- Why are they important? Speed is critical in trading; FPGA NICs reduce latency by bypassing traditional software processing paths.
- Performance: Some models achieve trigger-to-response times as low as 568 nanoseconds.
- Use Case: Ideal for colocated trading setups near exchange engines, where low latency provides a competitive edge.
FPGA NICs streamline trading operations, handling tasks like market data parsing and risk checks directly in hardware. This reduces the load on CPUs and ensures consistent, low-latency performance. For traders, these cards are a game-changer in the race for speed and efficiency.
Accelerated Algorithmic Trading on Alveo X3522PV: The Ultimate HFT Solution
How FPGA NICs Improve Trading Performance
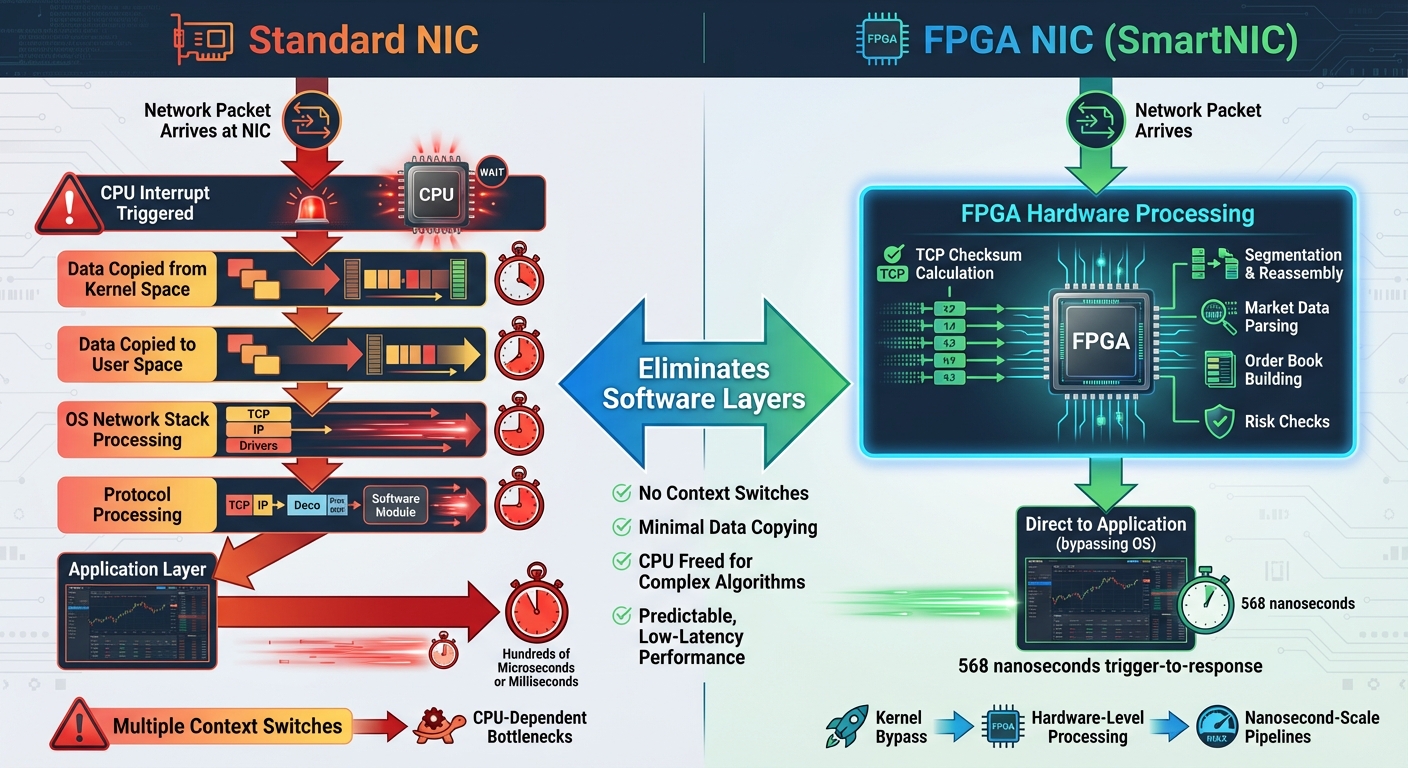
Standard NIC vs FPGA NIC Data Processing Path Comparison
Standard NIC vs FPGA NIC Data Processing Path Comparison
The difference in performance between traditional NICs and FPGA-accelerated cards comes down to how they handle data. Standard NICs rely heavily on the CPU and operating system to process every network packet, which can create bottlenecks. FPGA NICs, on the other hand, offload much of this work to hardware, skipping over software layers entirely. This fundamental distinction shapes how data flows through each type of network path.
Standard vs FPGA-Accelerated Network Paths
In a traditional setup, data takes a more complex journey. When a packet arrives at the NIC, it triggers an interrupt to the CPU. From there, the data is copied from kernel space to user space, passing through the operating system's network stack for protocol processing. Each of these steps involves context switches, which slow down the process.
FPGA NICs streamline this flow. Instead of relying on the CPU, the FPGA handles tasks like TCP checksum calculations, segmentation, and reassembly directly in hardware. It also takes over critical trading operations, such as parsing market data, building order books, and performing risk checks. By cutting out unnecessary context switches and minimizing data copying, FPGA NICs free up the CPU to focus on more complex trading algorithms. This approach ensures low-latency, predictable performance - key factors in high-frequency trading.
Latency Reduction Techniques
FPGA NICs owe their speed to several hardware optimizations. By bypassing the operating system kernel, they avoid the delays caused by jitter and interrupts that are common in software-based processing. Instead, the FPGA processes data inline, filtering out irrelevant market information and decoding protocols at network speeds with almost no delay. Tasks that would normally require significant CPU resources are executed in nanosecond-scale pipelines.
The result? Consistent, predictable latency. In high-frequency trading, where every microsecond counts, this kind of reliability is just as critical as raw speed.
FPGA NIC Architecture
Building on the earlier discussion of performance benefits, this section dives into the internal design and programming models that make FPGA NICs so effective. At the heart of their efficiency lies a design that prioritizes ultra-low latency.
Core Components of FPGA NICs
The core components of an FPGA NIC form the hardware backbone for achieving low latency. At the center is the configurable logic, which includes configurable logic blocks (CLBs), lookup tables (LUTs), and an interconnect fabric - all programmable to handle specific tasks. These cards also feature network MAC/PHY interfaces to manage physical network connections, DDR4 memory for buffering and state management, and DSP cells for executing mathematical operations.
A PCIe interface connects the card to the host system, while high-resolution timestamping and bridging capabilities help reduce latency even further. Integrated flow steering ensures packets are routed instantly.
For trading applications, FPGA NICs often include specialized engines for tasks like market data parsing, protocol decoding, risk management, and order execution. Unlike CPUs, which process data sequentially, FPGAs operate in parallel. This allows a single chip to handle 10 or more control loops simultaneously, each running at different rates. This parallelism avoids the resource bottlenecks common in CPU-based systems, ensuring deterministic and predictable latency even during periods of high market volatility.
Programming and Customization
Programming an FPGA can be done using hardware description languages (HDLs) like Verilog for maximum performance or high-level synthesis (HLS) tools such as C/C++ for faster development. HDLs provide total control over the hardware, enabling fine-grained optimization and the lowest latency possible, but they demand specialized skills and longer development timelines. HLS tools, while quicker and more accessible, often result in lower performance compared to hand-optimized designs.
NEVER MISS A TRADE
Your algos run 24/7
even while you sleep.
99.999% uptime • Chicago, New York, London & Amsterdam data centers • From $59.99/mo
To streamline development, many vendors provide pre-optimized IP cores and frameworks that allow developers to focus on trading-specific logic. A popular approach is the hybrid architecture, where latency-critical functions run directly on the FPGA, while less time-sensitive tasks are handled by the CPU.
The next section explores how SmartNICs and discrete FPGA cards compare, highlighting their unique advantages for trading.
SmartNIC vs Discrete FPGA Cards
Understanding the programmable architecture helps in deciding between SmartNICs and discrete FPGA cards, a choice that can shape deployment strategies in trading environments. A SmartNIC combines network interface components - like MAC/PHY - with programmable FPGA logic on a single card. This integration allows the FPGA to process network data as soon as it arrives, eliminating the need for intermediate data transfers.
In contrast, discrete FPGA cards are general-purpose accelerators that lack built-in network interfaces. They rely on separate NICs to handle network traffic, adding an extra step in the data transfer process. For latency-sensitive trading, where every nanosecond counts, SmartNICs hold a clear edge by avoiding these additional delays.
The choice between the two often depends on the application. SmartNICs are ideal for network-centric tasks like market data processing and order execution. On the other hand, discrete FPGA cards might be better suited for compute-heavy algorithms that don’t require direct network access, though such use cases are rare in latency-critical trading scenarios.
FPGA NICs in Trading Applications
FPGA NICs are transforming the way trading workflows operate, thanks to their ability to perform tasks at lightning-fast speeds. They can complete operations in nanoseconds, cutting out software-induced delays and delivering deterministic speeds that stay under 200 nanoseconds.
Market Data Path Offloading
When it comes to processing market data, FPGA NICs take immediate action. They timestamp, decode protocols, and normalize data as soon as packets arrive. This hardware-based processing eliminates the need to transfer data to system memory or wait for software to handle it. The result? Market data updates are always current, with no lag slowing things down.
Order Path Optimization
On the order execution side, FPGA NICs are equally impressive. They conduct risk checks - like validating volume, price, and collateral - directly on the card before an order even reaches the exchange. This real-time, hardware-driven validation ensures compliance while keeping latency to an absolute minimum. For high-frequency trading, where every microsecond counts, this approach significantly boosts tick-to-trade performance. By reducing the time between a trading signal and its execution, FPGA NICs play a critical role in maintaining the low-latency requirements that drive profitability in these markets.
Hybrid FPGA-CPU Architectures
In dynamic trading environments, hybrid setups that combine FPGA logic with CPU cores take things a step further. FPGAs handle time-critical, repetitive, and parallel tasks, while the CPU focuses on more complex analytics and service-oriented functions. This division of labor not only reduces CPU workload and overall system stress but also enhances performance and scalability. FPGAs ensure ultra-low, predictable latency for critical operations, while CPUs tackle more flexible, computationally demanding algorithms. This setup prevents latency-sensitive tasks from competing with background processes, keeping trading speeds consistently high. By combining the strengths of both components, hybrid designs maximize efficiency and maintain the rapid pace required in trading.
Deploying FPGA NICs with QuantVPS
Using FPGA NICs with QuantVPS can significantly improve trading performance by reducing latency. This is achieved through a combination of specialized hardware and software that works seamlessly together.
Infrastructure and Compatibility Requirements
To deploy FPGA NICs, your server must have PCIe x8 Gen 3 slots (offering 8.0 GT/s per lane). For setups requiring even more bandwidth, PCIe x16 slots might be used, though 100G Ethernet can also be an effective alternative in some configurations. Proper cooling and power delivery are essential to ensure stable operation.
On the software side, driver compatibility is key. Your operating system must support vendor-specific drivers tailored to your FPGA NIC model. Additionally, network topology plays a critical role - direct connections to exchange gateways help reduce hop counts and ensure consistent, low-latency communication. QuantVPS Dedicated Server plans are designed to meet these needs, offering 16+ dedicated cores, 128GB of RAM, and 10Gbps+ network connectivity to handle the demands of FPGA NICs.
This combination of hardware and software creates a solid foundation for seamless integration.
Integration Steps with QuantVPS
Start by selecting a QuantVPS Dedicated Server plan, which provides the direct hardware access necessary for FPGA NIC deployment. Pricing begins at $299.99 per month, or $209.99 per month with an annual commitment. Once your server is provisioned, optimize the operating system for low-latency performance by disabling unnecessary services, fine-tuning network settings, and installing the appropriate FPGA drivers.
The complexity of integration depends on whether you're using vendor-provided frameworks or developing custom FPGA solutions. Pre-built frameworks can simplify the process, allowing you to focus on configuring trading strategies rather than delving into hardware programming. To maximize performance, assign time-sensitive tasks to the FPGA while offloading analytics to the CPU. This division ensures both speed and flexibility.
After integration, maintaining peak performance requires diligent operational practices.
Operating FPGA NICs
STOP LOSING TO LATENCY
Execute faster than
your competition.
Sub-millisecond execution • Direct exchange connectivity • From $59.99/mo
To keep your setup running smoothly, monitor key metrics like latency, throughput, and error rates. Regular firmware updates are essential for unlocking new features and enhancing performance.
The decision to invest in FPGA NICs should align with your trading volume and latency needs. For high-frequency trading (HFT), where every microsecond matters, the return on investment can be substantial. FPGA chips can execute specific trading algorithms up to 1,000 times faster than traditional software-based methods, offering the consistent performance HFT strategies demand. It's also important to monitor environmental conditions to ensure the cards stay within safe operating temperatures. Overheating can lead to thermal throttling, which introduces unwanted latency spikes.
Conclusion
FPGA NICs are reshaping how trading data is processed. By moving compute-heavy tasks directly to hardware, these cards deliver nanosecond-level processing with consistent, repeatable latency - even during the most unpredictable market swings. Their ability to execute multiple functions in parallel, without resource contention, provides a significant performance boost that’s invaluable in high-frequency trading.
These cards handle tasks like kernel bypass, hardware flow steering, and market data pre-processing with incredible efficiency, enabling trading algorithms to execute up to 1,000 times faster. In a world where microseconds can mean the difference between profit and loss, this speed advantage becomes a powerful competitive tool.
For traders looking to integrate FPGA NICs, QuantVPS Dedicated Server plans offer the infrastructure needed to unlock their full potential. With direct hardware access and high bandwidth, these servers ensure FPGA NICs operate at peak performance.
However, adopting FPGA NICs isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. The decision should align with your trading strategy and transaction volume. For algorithmic traders in high-frequency environments, the benefits are clear: faster order execution and more efficient market data handling. But beyond speed, the real value lies in the consistent and deterministic performance these cards provide, regardless of market conditions.
As the demand for lower latency and higher throughput grows, FPGA-accelerated NICs have become essential in modern trading systems. By transforming network interfaces from passive data channels into active, high-speed processors, these devices are driving the evolution of ultra-low latency trading infrastructure. This shift highlights their critical role in the future of high-frequency trading.
FAQs
Why are FPGA-accelerated NICs faster than standard NICs?
FPGA-accelerated NICs stand out for their speed because they process data directly in hardware, bypassing the delays associated with software and CPU involvement. By leveraging the specialized logic of FPGAs, these NICs can handle tasks such as real-time data filtering, protocol decoding, and order execution with incredible efficiency.
This hardware-driven design achieves latency measured in nanoseconds, making FPGA NICs a perfect fit for high-frequency trading and other environments where even a microsecond can make a difference.
What key components make an FPGA NIC perform so efficiently?
An FPGA-accelerated Network Interface Card (NIC) delivers impressive performance thanks to several key components. At its core, it features a high-speed datapath and multiple Ethernet ports that support blazing-fast speeds like 10, 25, 50, or even 100 Gbps. It also includes a PCIe interface, ensuring rapid communication with the host system.
Additional highlights include a DMA engine for smooth and efficient memory access, advanced queue management to handle transmit and receive operations seamlessly, and hardware timestamping for precise time synchronization. The card’s flow steering capability allows it to direct network traffic intelligently, optimizing performance.
What truly sets this type of NIC apart is its programmable FPGA fabric. This feature enables the creation of custom logic and tailored acceleration for specific tasks, making it an excellent choice for demanding workloads like low-latency trading.
What are the advantages of using FPGA-accelerated NICs in high-frequency trading?
FPGA-accelerated Network Interface Cards (NICs) bring key advantages to high-frequency trading (HFT) environments. They cut down latency dramatically and enable real-time inline data processing, allowing traders to react to market shifts faster and with more accuracy.
Another standout feature is their ability to deliver deterministic response times. This means performance stays consistent, even during intense market activity. When paired with faster order execution, these NICs become essential for building low-latency trading systems that thrive under pressure.
FPGA-accelerated NICs stand out for their speed because they process data directly in hardware, bypassing the delays associated with software and CPU involvement. By leveraging the specialized logic of FPGAs, these NICs can handle tasks such as real-time data filtering, protocol decoding, and order execution with incredible efficiency.
This hardware-driven design achieves latency measured in nanoseconds, making FPGA NICs a perfect fit for high-frequency trading and other environments where even a microsecond can make a difference.
An FPGA-accelerated Network Interface Card (NIC) delivers impressive performance thanks to several key components. At its core, it features a high-speed datapath and multiple Ethernet ports that support blazing-fast speeds like 10, 25, 50, or even 100 Gbps. It also includes a PCIe interface, ensuring rapid communication with the host system.
Additional highlights include a DMA engine for smooth and efficient memory access, advanced queue management to handle transmit and receive operations seamlessly, and hardware timestamping for precise time synchronization. The card’s flow steering capability allows it to direct network traffic intelligently, optimizing performance.
What truly sets this type of NIC apart is its programmable FPGA fabric. This feature enables the creation of custom logic and tailored acceleration for specific tasks, making it an excellent choice for demanding workloads like low-latency trading.
FPGA-accelerated Network Interface Cards (NICs) bring key advantages to high-frequency trading (HFT) environments. They cut down latency dramatically and enable real-time inline data processing, allowing traders to react to market shifts faster and with more accuracy.
Another standout feature is their ability to deliver deterministic response times. This means performance stays consistent, even during intense market activity. When paired with faster order execution, these NICs become essential for building low-latency trading systems that thrive under pressure.
"}}]}





